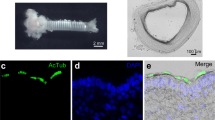
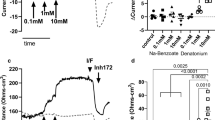
Abstract
Specialized epithelial cells of the respiratory tract have been termed “solitary chemosensory cells” based upon the expression of components of the canonical sweet, umami and bitter taste transduction pathway, or “brush cells” based upon their characteristic morphological feature, i.e. an apical, brush-like tuft of rigid, villin containing microvilli. Cells defined by these criteria might not match one-to-one, and a generally accepted terminology is still lacking. With respect to cellular shape, ultrastructure, expression of elements of the taste transduction cascade, innervation and synapse formation, and effects evoked upon their stimulation, it appears that chemosensory/brush in the upper respiratory tract (nasal respiratory mucosa, vomeronasal duct, auditory tube), in the olfactory mucosa, in the larynx, in the lower airways (trachea, bronchi) and in the alveolar region (rat only) each represent distinct groups. Still, they have in common to monitor the chemical composition of the mucosal lining fluid. They serve as sentinels detecting bacterial colonization or the presence of other harmful components in the mucosal lining fluid, leading to the initiation of avoidance reflexes and/or local defense mechanisms which are adapted to their anatomical localization. Free nerve endings are also responsive to inhaled irritants and further work will be needed to discriminate between the contributions of such nerve endings and chemosensory cells in chemical monitoring and defense initiation. Interestingly, there is first emerging evidence that respiratory chemosensory cells may respond to more than one canonical taste quality so that they, in analogy to polymodal nociceptors, may serve as polymodal chemosensors of potentially dangerous signals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler E, Hoon MA, Mueller KL, Chandrashekar J, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2000) A novel family of mammalian taste receptors. Cell 100(6):693–702
Allan EM (1978) The ultrastructure of the brush cell in bovine lung. Res Vet Sci 25(3):314–317
Asan E, Drenckhahn D (2005) Immunocytochemical characterization of two types of microvillar cells in rodent olfactory epithelium. Histochem Cell Biol 123(2):157–168
Barth AL, Pitt JTL (1996) The high amino-acid content of sputum from cystic fibrosis patients promotes growth of auxotrophic Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Med Microbiol 45:110–119
Bartlett JA, Fischer AJ, McCray PB Jr (2008) Innate immune functions of the airway epithelium. Contrib Microbiol 15:147–163
Basbaum C, Jany B (1990) Plasticity in the airway epithelium. Am J Physiol 259(2 Pt 1):L38–L46
Baskerville A (1970) Ultrastructural studies of the normal pulmonary tissue of the pig. Res Vet Sci 11:150–155
Basset F, Poirier J, Le Crom M, Turiaf J (1971) Etude ultrastructurale de l’epithelium bronchiolaire humain. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 116:425–442
Behrens M, Meyerhof W (2009) Mammalian bitter taste perception. Results Probl Cell Differ 47:203–220
Behrens M, Meyerhof W, Hellfritsch C, Hofmann T (2011) Sweet and umami taste: natural products, their chemosensory targets, and beyond. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50(10):2220–2242
Bessac BF, Jordt SE (2010) Sensory detection and responses to toxic gases: mechanisms, health effects, and countermeasures. Proc Am Thorac Soc 7(4):269–277
Braun T, Mack B, Kramer MF (2011) Solitary chemosensory cells in the respiratory and vomeronasal epithelium of the human nose: a pilot study. Rhinology 49(5):507–512
Breer H, Eberle J, Frick C, Haid D, Widmayer P (2012) Gastrointestinal chemosensation: chemosensory cells in the alimentary tract. Histochem Cell Biol (Epub ahead of print)
Canning BJ (2010) Afferent nerves regulating the cough reflex: mechanisms and mediators of cough in disease. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 43(1):15–25
Canning BJ, Mori N (2011) Encoding of the cough reflex in anesthetized guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300(2):R369–R377
Canning BJ, Spina D (2009) Sensory nerves and airway irritability. Handb Exp Pharmacol 194:139–183
Canning BJ, Mori N, Mazzone SB (2006) Vagal afferent nerves regulating the cough reflex. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 152(3):223–242
Castelo Branco NAA, Monteiro E, Costa e Silva A, Martins Dos Santos J, Reis Ferreira JM, Alves-Pereira M (2004) The lung parenchyma in low frequency noise exposed Wistar rats. Rev Port Pneumol 10(1):77–85
Chandrashekar J, Mueller KL, Hoon MA, Adler E, Feng L, Guo W, Zuker CS, Ryba NJ (2000) T2Rs function as bitter taste receptors. Cell 100:703–711
Chandrashekar J, Yarmolinsky D, von Buchholtz L, Oka Y, Sly W, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2009) The taste of carbonation. Science 326(5951):443–445
Chang LY, Mercer RR, Crapo JD (1986) Differential distribution of brush cells in the rat lung. Anat Rec 216(1):49–54
Chaudhari N, Pereira E, Roper SD (2009) Taste receptors for umami: the case for multiple receptors. Am J Clin Nutr 90(3):738S–742S
Chou YL, Scarupa MD, Mori N, Canning BJ (2008) Differential effects of airway afferent nerve subtypes on cough and respiration in anesthetized guinea pigs. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295(5):R1572–R1584
Clapp TR, Medler KF, Damak S, Margolskee RF, Kinnamon SC (2006) Mouse taste cells with G protein-coupled taste receptors lack voltage-gated calcium channels and SNAP-25. BMC Biol 4:7
Cutz E, Yeger H, Pan J (2007) Pulmonary neuroendocrine cell system in pediatric lung disease-recent advances. Pediatr Dev Pathol 10(6):419–435
Dehkordi O, Rose JE, Balan KV, Millis RM, Bhatti B, Jayam-Trouth A (2010) Co-expression of nAChRs and molecules of the bitter taste transduction pathway by epithelial cells of intrapulmonary airways. Life Sci 86(7–8):281–288
DiMaio MF, Dische R, Gordon RE, Kattan M (1988) Alveolar brush cells in an infant with desquamative interstitial pneumonitis. Pediatr Pulmonol 4(3):185–191
DiMaio MF, Kattan M, Ciurea D, Gil J, Dische R (1990) Brush cells in the human fetal trachea. Pediatr Pulmonol 8(1):40–44
Dvoryanchikov G, Tomchik SM, Chaudhari N (2007) Biogenic amine synthesis and uptake in rodent taste buds. J Comp Neurol 505(3):302–313
Dvoryanchikov G, Huang YA, Barro-Soria R, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2011) GABA, its receptors, and GABAergic inhibition in mouse taste buds. J Neurosci 31(15):5782–5791
Ericson LE, Håkanson R, Larson B, Owman C, Sundler F (1972) Fluorescence and electron microscopy of amine-storing enterochromaffin-like cells in tracheal epithelium of mouse. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 124(4):532–545
Finger TE, Kinnamon SC (2011) Taste isn’t just for taste buds anymore. F1000 Biol Rep 3:20
Finger TE, Böttger B, Hansen A, Anderson KT, Alimohammadi H, Silver WL (2003) Solitary chemoreceptor cells in the nasal cavity serve as sentinels of respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(15):8981–8986
Finger TE, Danilova V, Barrows J, Bartel DL, Vigers AJ, Stone L, Hellekant G, Kinnamon SC (2005) ATP signaling is crucial for communication from taste buds to gustatory nerves. Science 310(5753):1495–1499
Gulbransen BD, Finger TE (2005) Solitary chemoreceptor cell proliferation in adult nasal epithelium. J Neurocytol 34(1–2):117–122
Gulbransen BD, Clapp TR, Finger TE, Kinnamon SC (2008a) Nasal solitary chemoreceptor cell responses to bitter and trigeminal stimulants in vitro. J Neurophysiol 99(6):2929–2937
Gulbransen B, Silver W, Finger TE (2008b) Solitary chemoreceptor cell survival is independent of intact trigeminal innervation. J Comp Neurol 508(1):62–71
Gulisano M, Polli G, Biondi G, Pacini P (1988) Study of the nasopharynx in man by scanning electron microscopy. J Laryngol Otol 102(12):1102–1106
Hansen A, Finger TE (2008) Is TRPM5 a reliable marker for chemosensory cells? Multiple types of microvillous cells in the main olfactory epithelium of mice. BMC Neurosci 9:115
Hijiya K (1978) Electron microscope study of the alveolar brush cell. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 27(3):223–227
Hijiya K, Okada Y, Tankawa H (1977) Ultrastructural study of the alveolar brush cell. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 26(4):321–329
Höfer D, Drenckhahn D (1992) Identification of brush cells in the alimentary and respiratory system by antibodies to villin and fimbrin. Histochemistry 98(4):237–242
Höfer D, Drenckhahn D (1998) Identification of the taste cell G-protein, alpha-gustducin, in brush cells of the rat pancreatic duct system. Histochem Cell Biol 110(3):303–309
Höfer D, Shin DW, Drenckhahn D (2000) Identification of cytoskeletal markers for the different microvilli and cell types of the rat vomeronasal sensory epithelium. J Neurocytol 29(3):147–156
Huang YA, Roper SD (2010) Intracellular Ca(2+) and TRPM5-mediated membrane depolarization produce ATP secretion from taste receptor cells. J Physiol 588(Pt 13):2343–2350
Huang L, Shanker YG, Dubauskaite J, Zheng JZ, Yan W, Rosenzweig S, Spielman AI, Max M, Margolskee RF (1999) Ggamma13 colocalizes with gustducin in taste receptor cells and mediates IP3 responses to bitter denatonium. Nat Neurosci 2(12):1055–1062
Huang YJ, Maruyama Y, Dvoryanchikov G, Pereira E, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2007) The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell–cell communication in mouse taste buds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(15):6436–6441
Jeffery PK, Reid L (1975) New observations of rat airway epithelium: a quantitative and electron microscopic study. J Anat 120(Pt 2):295–320
Kaske S, Krasteva G, König P, Kummer W, Hofmann T, Gudermann T, Chubanov V (2007) TRPM5, a taste-signaling transient receptor potential ion-channel, is a ubiquitous signaling component in chemosensory cells. BMC Neurosci 8:49
Kasper M, Höfer D, Woodcock-Mitchell J, Migheli A, Attanasio A, Rudolf T, Müller M, Drenckhahn D (1994) Colocalization of cytokeratin 18 and villin in type III alveolar cells (brush cells) of the rat lung. Histochemistry 101(1):57–62
Kinnamon SC (2012) Taste receptor signaling—from tongues to lungs. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 204(2):158–168
Krasteva G, Canning BJ, Hartmann P, Veres TZ, Papadakis T, Mühlfeld C, Schliecker K, Tallini YN, Braun A, Hackstein H, Baal N, Weihe E, Schütz B, Kotlikoff M, Ibanez-Tallon I, Kummer W (2011) Cholinergic chemosensory cells in the trachea regulate breathing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(23):9478–9483
Krasteva G, Hartmann P, Papadakis T, Bodenbenner M, Wessels L, Weihe E, Schütz B, Langheinrich AC, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Ibanez-Tallon I, Kummer W (2012a) Cholinergic chemosensory cells in the auditory tube. Histochem Cell Biol 137(4):483–497
Krasteva G, Canning BJ, Papadakis T, Kummer W (2012b) Cholinergic brush cells in the trachea mediate respiratory responses to quorum sensing molecules. Life Sci (accepted)
Kugler P, Höfer D, Mayer B, Drenckhahn D (1994) Nitric oxide synthase and NADP-linked glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase are co-localized in brush cells of rat stomach and pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem 42(10):1317–1321
Kummer W, Lips KS, Pfeil U (2008) The epithelial cholinergic system of the airways. Histochem Cell Biol 130(2):219–234
Kusakabe Y, Yamaguchi E, Tanemura K, Kameyama K, Chiba N, Arai S, Emori Y, Abe K (1998) Identification of two alpha-subunit species of GTP-binding proteins, Galpha15 and Galphaq, expressed in rat taste buds. Biochim Biophys Acta 1403(3):265–272
Lauweryns JM, Van Ranst L (1988) Protein gene product 9.5 expression in the lungs of humans and other mammals. Immunocytochemical detection in neuroepithelial bodies, neuroendocrine cells and nerves. Neurosci Lett 85(3):311–316
Leeson TS (1961) The development of the trachea in the rabbit, with particular reference to its fine structure. Anat Anz 110:214–223
Lembrechts R, Pintelon I, Schnorbusch K, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D, Brouns I (2011) Expression of mechanogated two-pore domain potassium channels in mouse lungs: special reference to mechanosensory airway receptors. Histochem Cell Biol 136(4):371–385
Lembrechts R, Brouns I, Schnorbusch K, Pintelon I, Timmermans JP, Adriaensen D (2012) Neuroepithelial bodies as mechanotransducers in the intrapulmonary airway epithelium: involvement of TRPC5. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol (Epub ahead of print)
Li X, Staszewski L, Xu H, Durick K, Zoller M, Adler E (2002) Human receptors for sweet and umami taste. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4692–4696
Lin W, Ezekwe EA Jr, Zhao Z, Liman ER, Restrepo D (2008a) TRPM5-expressing microvillous cells in the main olfactory epithelium. BMC Neurosci 9:114
Lin W, Ogura T, Margolskee RF, Finger TE, Restrepo D (2008b) TRPM5-expressing solitary chemosensory cells respond to odorous irritants. J Neurophysiol 99(3):1451–1460
Lips KS, Volk C, Schmitt BM, Pfeil U, Arndt P, Miska D, Ermert L, Kummer W, Koepsell H (2005) Polyspecific cation transporters mediate luminal release of acetylcholine from bronchial epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33(1):79–88
Liu P, Shah BP, Croasdell S, Gilbertson TA (2011) Transient receptor potential channel type M5 is essential for fat taste. J Neurosci 31(23):8634–8642
Luciano L, Reale E, Ruska H (1968) Über eine ‘chemorezeptive’ Sinneszelle in der Trachea der Ratte. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 85:350–375 (in German)
Luciano L, Reale E, Ruska H (1969) Bürstenzellen im Alveolarepithel der Rattenlunge. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 95:198–201 (in German)
Margolskee RF (2002) Molecular mechanisms of bitter and sweet taste transduction. J Biol Chem 277(1):1–4
Mattes RD (2008) Oral detection of short-, medium-, and long-chain free fatty acids in humans. Chem Senses 34(2):145–150
McLaughlin SK, McKinnon PJ, Margolskee RF (1992) Gustducin is a taste-cell-specific G protein closely related to the transducins. Nature 357(6379):563–569
Merigo F, Benati D, Tizzano M, Osculati F, Sbarbati A (2005) α-Gustducin immunoreactivity in the airways. Cell Tissue Res 319(2):211–219
Merigo F, Benati D, Di Chio M, Osculati F, Sbarbati A (2007) Secretory cells of the airway express molecules of the chemoreceptive cascade. Cell Tissue Res 327(2):231–247
Meyrick B, Reid L (1968) The alveolar brush cell in rat lung–a third pneumonocyte. J Ultrastruct Res 23(1):71–80
Monteiro-Riviere NA, Popp JA (1984) Ultrastructural characterization of the nasal respiratory epithelium in the rat. Am J Anat 169(1):31–43
Montgomery PQ, Stafford ND, Stolinski C (1990) Ultrastructure of human fetal trachea. A morphological study of the luminal and glandular epithelia at the mid-trimester. J Anat 173:43–59
Morris JB, Wilkie WS, Shusterman DJ (2005) Acute respiratory responses of the mouse to chlorine. Toxicol Sci 83(2):380–387
Nelson G, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Zhang Y, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2001) Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 106(3):381–390
Nielsen GD, Hougaard KS, Larsen ST, Hammer M, Wolkoff P, Clausen PA, Wilkins CK, Alarie Y (1999) Acute airway effects of formaldehyde and ozone in BALB/c mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 18(6):400–409
Ogura T, Margolskee RF, Tallini YN, Shui B, Kotlikoff MI, Lin W (2007) Immuno-localization of vesicular acetylcholine transporter in mouse taste cells and adjacent nerve fibers: indication of acetylcholine release. Cell Tissue Res 330(1):17–28
Ogura T, Krosnowski K, Zhang L, Bekkerman M, Lin W (2010) Chemoreception regulates chemical access to mouse vomeronasal organ: role of solitary chemosensory cells. PLoS One 5(7):e11924
Ogura T, Szebenyi SA, Krosnowski K, Sathyanesan A, Jackson J, Lin W (2011) Cholinergic microvillous cells in the mouse main olfactory epithelium and effect of acetylcholine on olfactory sensory neurons and supporting cells. J Neurophysiol 106(3):1274–1287
Ohkuri T, Horio N, Stratford JM, Finger TE, Ninomiya Y (2012) Residual chemoresponsiveness to acids in the superior laryngeal nerve in “Taste-Blind” (P2X2/P2X3 Double-KO) Mice. Chem Senses (Epub ahead of print)
Ohmoto M, Matsumoto I, Yasuoka A, Yoshihara Y, Abe K (2008) Genetic tracing of the gustatory and trigeminal neural pathways originating from T1R3-expressing taste receptor cells and solitary chemoreceptor cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 38(4):505–517
Okamura H, Sugai N, Ohtani I (1996a) Identification of nasal epithelial cells with carbonic anhydrase activity. Brain Res 728(2):263–266
Okamura H, Sugai N, Kanno T, Shimizu T, Ohtani I (1996b) Histochemical localization of carbonic anhydrase in the trachea of the guinea pig. Histochem Cell Biol 106(2):257–260
Pack RJ, Al-Ugaily LH, Morris G, Widdicombe JG (1980) The distribution and structure of cells in the tracheal epithelium of the mouse. Cell Tissue Res 208(1):65–84
Pérez CA, Huang L, Rong M, Kozak JA, Preuss AK, Zhang H, Max M, Margolskee RF (2002) A transient receptor potential channel expressed in taste receptor cells. Nat Neurosci 5(11):1169–1176
Pezzulo AA, Gutiérrez J, Duschner KS, McConnell KS, Taft PJ, Ernst SE, Yahr TL, Rahmouni K, Klesney-Tait J, Stoltz DA, Zabner J (2011) Glucose depletion in the airway surface liquid is essential for sterility of the airways. PLoS One 6(1):e16166
Reid L, Jones R (1979) Bronchial mucosal cells. Fed Proc 38(2):191–196
Rhodin JA (1966) The ciliated cell. Ultrastructure and function of the human tracheal mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis 93(3 Suppl):1–15
Rhodin J, Dalhamn (1956) Electron microscopy of the tracheal ciliated mucosa in rat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat 44(4):345–412
Romanov RA, Rogachevskaja OA, Bystrova MF, Jiang P, Margolskee RF, Kolesnikov SS (2007) Afferent neurotransmission mediated by hemichannels in mammalian taste cells. EMBO J 26(3):657–667
Rossler P, Kroner C, Freitag J, Noe J, Breer H (1998) Identification of a phospholipase C beta subtype in rat taste cells. Eur J Cell Biol 77:253–261
Rossler P, Boekhoff I, Tareilus E, Beck S, Breer H, Freitag J (2000) G protein betagamma complexes in circumvallate taste cells involved in bitter transduction. Chem Senses 25(4):413–421
Ruiz-Avila L, McLaughlin SK, Wildman D, McKinnon PJ, Robichon A, Spickofsky N, Margolskee RF (1995) Coupling of bitter receptor to phosphodiesterase through transducin in taste receptor cells. Nature 376(6535):80–85
Saunders CJ, Reynolds SD, Finger TE (2011) Solitary chemosensory cells turnover in tracheal epithelium, in vivo and in vitro models. A Chem S:67–68 (Abstract)
Sbarbati A, Osculati F (2005) A new fate for old cells: brush cells and related elements. J Anat 06(4):349–358
Sbarbati A, Osculati F (2006) Allelochemical communication in vertebrates: kairomones, allomones and synomones. Cells Tissues Organs 183(4):206–219
Sbarbati A, Merigo F, Benati D, Tizzano M, Bernardi P, Osculati F (2004a) Laryngeal chemosensory clusters. Chem Senses 29(8):683–692
Sbarbati A, Merigo F, Benati D, Tizzano M, Bernardi P, Crescimanno C, Osculati F (2004b) Identification and characterization of a specific sensory epithelium in the rat larynx. J Comp Neurol 475(2):188–201
Sekerková G, Zheng L, Loomis PA, Changyaleket B, Whitlon DS, Mugnaini E, Bartles JR (2004) Espins are multifunctional actin cytoskeletal regulatory proteins in the microvilli of chemosensory and mechanosensory cells. J Neurosci 24(23):5445–5456
Shah AS, Ben-Shahar Y, Moninger TO, Kline JN, Welsh MJ (2009) Motile cilia of human airway epithelia are chemosensory. Science 325(5944):1131–1134
Shum WW, Da Silva N, McKee M, Smith PJ, Brown D, Breton S (2008) Transepithelial projections from basal cells are luminal sensors in pseudostratified epithelia. Cell 135(6):1108–1117
Silver WL, Finger TE (2009) The anatomical and electrophysiological basis of peripheral nasal trigeminal chemoreception. Ann NY Acad Sci 1170:202–205
Silver WL, Maruniak JA (1981) Trigeminal chemoreception in the nasal and oral cavities. Chem Senses 6(4):295–305
Souma T (1987) The distribution and surface ultrastructure of airway epithelial cells in the rat lung: a scanning electron microscopic study. Arch Histol Jpn 50(4):419–436
Taira K, Shibasaki S (1978) A fine structure study of the non-ciliated cells in the mouse tracheal epithelium with special reference to the relation of “brush cells” and “endocrine cells”. Arch Histol Jpn 41(4):351–366
Tizzano M, Merigo F, Sbarbati A (2006) Evidence of solitary chemosensory cells in a large mammal: the diffuse chemosensory system in Bos taurus airways. J Anat 209(3):333–337
Tizzano M, Gulbransen BD, Vandenbeuch A, Clapp TR, Herman JP, Sibhatu HM, Churchill ME, Silver WL, Kinnamon SC, Finger TE (2010) Nasal chemosensory cells use bitter taste signaling to detect irritants and bacterial signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(7):3210–3215
Tizzano M, Cristofoletti M, Sbarbati A, Finger TE (2011) Expression of taste receptors in solitary chemosensory cells of rodent airways. BMC Pulm Med 11:3
Tomchik SM, Berg S, Kim JW, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2007) Breadth of tuning and taste coding in mammalian taste buds. J Neurosci 27(40):10840–10848
Voynow JA, Rubin BK (2009) Mucins, mucus, and sputum. Chest 35(2):505–512
Watson JH, Brinkmann GL (1964) Electron microscopy of the epithelial cells of normal and bronchitic human bronchus. Am Rev Respir Dis 90:851–866
Wessler I, Roth E, Deutsch C, Brockerhoff P, Bittinger F, Kirkpatrick CJ, Kilbinger H (2001) Release of non-neuronal acetylcholine from the isolated human placenta is mediated by organic cation transporters. Br J Pharmacol 134(5):951–956
Widdicombe JG (1992) Chemoreceptor control of the airways. Respir Physiol 87(3):373–381
Wong GT, Gannon KS, Margolskee RF (1996) Transduction of bitter and sweet taste by gustducin. Nature 381(6585):796–800
Yabumoto Y, Watanabe M, Ito Y, Maemura K, Otsuki Y, Nakamura Y, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Watanabe K (2008) Expression of GABAergic system in pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and airway epithelial cells in GAD67-GFP knock-in mice. Med Mol Morphol 41(1):20–27
Yang R, Stoick CL, Kinnamon JC (2004) Synaptobrevin-2-like immunoreactivity is associated with vesicles at synapses in rat circumvallate taste buds. J Comp Neurol 471:59–71
Zancanaro C, Caretta CM, Merigo F, Cavaggioni A, Osculati F (1999) alpha-Gustducin expression in the vomeronasal organ of the mouse. Eur J Neurosci 11(12):4473–4475
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. E. Weibel, Bern, CH, for providing Fig. 3a, and Drs. B. Canning, (Baltimore, MA, USA), T.E Finger (Denver, CO, USA), S.C. Kinnamon (Denver, CO, USA) and M. Tizzano (Denver, CO, USA) for stimulating discussions related to that field during the past years. We appreciate the skillful assistance in artwork figures of Ms Karola Michael. Our studies reviewed here were supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, the German Center for Lung Research, and by HMWK through the LOEWE Center University of Giessen and Marburg Lung Center and the LOEWE Research Focus Non-neuronal Cholinergic Systems.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krasteva, G., Kummer, W. “Tasting” the airway lining fluid. Histochem Cell Biol 138, 365–383 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0993-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0993-5