Abstract
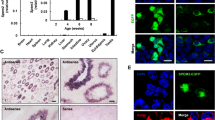
In mouse testis, claudin-11 is responsible for the formation of specific parallel TJ strands of the blood–testis barrier (BTB). Concerning the human BTB, there is no information about the transmembrane TJ proteins. We recently demonstrated the loss of functional integrity of the BTB in testicular intraepithelial neoplasia (TIN), associated with a dislocation of the peripheral TJ proteins ZO-1 and ZO-2. Here, we determined the expression and distribution of claudin-11 at the human BTB in seminiferous tubules with normal spermatogenesis (NSP) and TIN. Immunostaining of claudin-11 revealed intense signals at the basal BTB region in seminiferous epithelium with NSP. Within TIN tubules, claudin-11 immunostaining became diffuse and cytoplasmic. Double immunogold labeling demonstrated a co-localization of claudin-11 and ZO-1 at the inter-Sertoli cell junctions. Real-time RT-PCR of laser microdissected tubules showed an up-regulation of claudin-11 mRNA in TIN. Additionally, increased claudin-11 protein was observed by Western blot. We conclude that claudin-11 constitutes a TJ protein at the human BTB. In TIN tubules, claudin-11 is up-regulated and dislocated from the BTB. Therefore, the disruption of the BTB is related to a dysfunction of claudin-11 and not to a failure of its expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JM, Van Itallie CM (1995) Tight junctions and the molecular basis for regulation of paracellular permeability. Am J Physiol 269:G467–G475
Bazzoni G, Martinez-Estrada OM, Orsenigo F, Cordenonsi M, Citi S, Dejana E (2000) Interaction of junctional adhesion molecule with the tight junction components ZO-1, cingulin, and occludin. J Biol Chem 275:20520–20526
Beckstead JH (1983) Alkaline phosphatase histochemistry in human germ cell neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol 7:341–349
Bergmann M (1987) Photoperiod and testicular function in Phodopus sungorus. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 105:1–76
Bergmann M (2006) Evaluation of testicular biopsy samples from the clinical perspective. In: Schill W-B, Comhaire FH, Hargreave TB (eds) Andrology for the clinician. Springer, Berlin, pp 454–461
Brehm R, Marks A, Rey R, Kliesch S, Bergmann M, Steger K (2002) Altered expression of connexins 26 and 43 in Sertoli cells in seminiferous tubules infiltrated with carcinoma-in situ or seminoma. J Pathol 197:647–653
Brehm R, Rüttinger C, Fischer P, Gashaw I, Winterhager E, Kliesch S, Bohle RM, Steger K, Bergmann M (2006) Transition from preinvasive carcinoma in situ to seminoma is accompanied by a reduction of connexin 43 expression in Sertoli cells and germ cells. Neoplasia 8:499–509
Bronstein JM, Micevych PE, Chen K (1997) Oligodendrocyte-specific protein (OSP) is a major component of CNS myelin. J Neurosci Res 50:713–720
Chung NP, Cheng CY (2001) Is cadmium chloride-induced inter-sertoli tight junction permeability barrier disruption a suitable in vitro model to study the events of junction disassembly during spermatogenesis in the rat testis? Endocrinology 142:1878–1888
Clark MA, Hirst BH (2002) Expression of junction-associated proteins differentiates mouse intestinal M cells from enterocytes. Histochem Cell Biol 118:137–147
Cyr DG, Hermo L, Egenberger N, Mertineit C, Trasler JM, Laird DW (1999) Cellular immunolocalization of occludin during embryonic and postnatal development of the mouse testis and epididymis. Endocrinology 140:3815–3825
Fanning AS, Jameson BJ, Jesaitis LA, Anderson JM (1998) The tight junction protein ZO-1 establishes a link between the transmembrane protein occludin and the actin cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem 273:29745–29753
Fanning AS, Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1999) Transmembrane proteins in the tight junction barrier (review). J Am Soc Nephrol 10:1337–1345
Fink L, Bohle RM (2002) Internal standards for laser microdissection. Methods Enzymol 356:99–113
Fink L, Kinfe T, Seeger W, Ermert L, Kummer W, Bohle RM (2000) Immunostaining for cell picking and real-time mRNA quantitation. Am J Pathol 157:1459–1466
Fink C, Weigel R, Hembes T, Lauke-Wettwer H, Kliesch S, Bergmann M, Brehm RH (2006a) Altered expression of ZO-1 and -2 in Sertoli cells and loss of the blood–testis barrier integrity in testicular carcinoma-in situ. Neoplasia 8:1019–1027
Fink L, Kwapiszewska G, Wilhelm J, Bohle RM (2006b) Laser microdissection for cell type- and compartment-specific analyses on genomic and proteomic level. Exp Toxicol Pathol 57(suppl 2):25–29
Florin A, Maire M, Bozec A, Hellani A, Chater S, Bars R, Chuzel F, Benahmed M (2005) Androgens and postmeitoic germ cells regulate claudin-11 expression in rat Sertoli cells. Endocrinology 146:1532–1540
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi K, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junction with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141:1539–1550
Furuse M, Sasaki H, Tsukita S (1999) Manner of interaction of heterogeneous claudin species within and between tight junction strands. J Cell Biol 147:891–903
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Nava P (2005) Tight junctions, from tight intercellular seals to sophisticated protein complexes involved in drug delivery, pathogens interaction and cell proliferation. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 57:811–814
Gow A, Southwood CM, Li JS, Pariali M, Riordan GP, Brodie SE, Danias J, Bronstein JM, Kachar B, Lazzarini RA (1999) CNS myelin and Sertoli cell tight junction strands are absent in Osp/claudin-11 null mice. Cell 99:649–659
Griswold MD (1995) Interactions between germ cells and Sertoli cells in the testis. Biol Reprod 52:211–216
Hellani A, Ji J, Mauduit C, Deschildre C, Tabone E, Benahmed M (2000) Developmental and hormonal regulation of the expression of oligodendrocyte-specific protein/claudin-11 in mouse testis. Endocrinology 141:3012–3019
Hewitt KJ, Agarwal R, Morin PJ (2006) The claudin gene family: expression in normal and neoplastic tissues. BMC Cancer 6:186–193
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Kliesch S, Behre HM, Hertle L, Bergmann M (1998) Alteration of Sertoli cell differentiation in the presence of carcinoma-in situ in human testis. J Urol 160:1894–1898
Lee NP, Cheng CY (2004) Adaptors, junction dynamics, and spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 71:392–404
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Lui W, Cheng CY (2007) Regulation of cell junction dynamics by cytokines in the testis—a molecular and biochemical perspective. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 18:299–311
Martin TA, Jiang WG (2001) Tight junctions and their role in cancer metastasis. Histol Histopathol 16:1183–1195
Matsuda Y, Semba S, Ueda J, Fuku T, Hasuo T, Chiba H, Sawada N, Kuroda Y, Yokozaki H (2007) Gastric and intestinal claudin expression at the invasive front of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Sci 98:1014–1019
Morin PJ (2005) Claudin proteins in human cancer: promising new targets for diagnosis and therapy. Cancer Res 65:9603–9606
Morita K, Furuse M, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1999a) Claudin multigene family encoding four-transmembrane domain protein components of tight junction strands. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:511–516
Morita K, Sasaki H, Fujimoto K, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999b) Claudin-11/OSP-based tight junctions of myelin sheats in brain and Sertoli cells in testis. J Cell Biol 145:579–588
Moroi S, Saitou M, Fujimoto K, Sakakibara A, Furuse M, Yoshida O, Tsukita S (1998) Occludin is concentrated at tight junctions of mouse/rat but not human/guinea pig Sertoli cells in testes. Am J Physiol 274:C1708–C1717
Neuvians TP, Gashaw I, Hasenfus A, Hacherhäcker A, Winterhager E, Grobholz R (2005a) Differential expression of IGF components and insulin receptor isoforms in human seminoma versus normal testicular tissue. Neoplasia 7:446–456
Neuvians TP, Gashaw I, Sauer CG, von Ostau C, Kliesch S, Bergmann M, Häcker A, Grobholz R (2005b) Standardisation strategy for quantitative PCR in human seminoma and normal testis. J Biotechnol 117:163–171
Oliveira SS, Morgado-Díaz JA (2007) Claudins: multifunctional players in epithelial tight junctions and their role in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:17–28
Rajpert-De Meyts E, Skakkebaek NE (1993) The possible role of sex hormones in the development of testicular cancer. Eur Urol 23:54–59
Riesen FK, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Wunderli-Allenspach H (2002) A ZO1-GFP fusion protein to study the dynamics of tight junctions in living cells. Histochem Cell Biol 117:307–315
Saitou M, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Itoh M, Furuse M, Inazawa J, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1997) Mammalian occludin in epithelial cells: its expression and subcellular distribution. Eur J Cell Biol 73:222–231
Sharpe RM, McKinnell C, Kivlin C, Fisher JS (2003) Proliferation and functional maturation of Sertoli cells, and their relevance to disorders of testis function in adulthood. Reproduction 125:769–784
Sheehan GM, Kallakury BV, Sheehan CE, Fisher HA, Kaufman RP Jr, Ross JS (2007) Loss of claudins-1 and -7 and expression of claudins-3 and -4 correlate with prognostic variables in prostatic adenocarcinomas. Hum Pathol 38: 564–569
Shima JE, McLean DJ, McCarrey JR, Griswold MD (2004) The murine testicular transcriptome: characterizing gene expression in the testis during the progression of spermatogenesis. Biol Reprod 71:319–330
Skakkebaek NE (1972) Possible carcinoma-in situ of the testis. Lancet 2:516–517
Skakkebaek NE, Berthelsen JG, Giwercman A, Müller J (1987) Carcinoma in situ of the testis: possible origin from gonocytes and precursor of all types of germ cell tumours except spermatocytoma. Int J Androl 10:19–28
Skakkebaek NE, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Jorgensen N, Carlsen E, Petersen PM, Giwercman A, Andersen AG, Jensen TK, Anderson AM, Müller J (1998) Germ cell cancer and disorders of spermatogenesis: an environmental connection? APMIS 106:3–12
Soini Y (2005) Expression of claudins 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 7 in various types of tumours. Histopathology 46:551–560
Sonoda N, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Yonemura S, Katahira J, Horiguchi Y, Tsukita S (1999) Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin fragment removes specific claudins from tight junction strands: Evidence for direct involvement of claudins in tight junction barrier. J Cell Biol 147:195–204
Stevenson BR, Siliciano JD, Mooseker MS, Goodenough DA (1986) Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol 103:755–766
Tarulli GA, Stanton PG, Lerchl A, Meachem SJ (2006) Adult Sertoli cells are not terminally differentiated in the Djungarian Hamster: Effect of FSH on proliferation and junction protein organization. Biol Reprod 74:798–806
Tarulli GA, Meachem SJ, Schlatt S, Stanton PG (2008) Regulation of testicular tight junctions by gonadotrophins in the adult Djungarian Hamster in vivo. Reproduction 135:867–877
Tsukita S, Furuse M (2000) Pores in the wall: claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous pores. J Cell Biol 149:13–16
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itho M (1999) Structural and signalling molecules come together at tight junctions. Curr Opin Cell Biol 11:628–633
Tsukita S, Furuse M, Itoh M (2001) Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:285–293
Umeda K, Ikenouchi J, Katahira-Tayama S, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Nakayama M, Matsui T, Tsukita S, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2006) ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 126:741–754
Van Itallie CM, Anderson JM (2006) Claudins and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev 68:403–429
Wong C, Mruk DD, Lui W, Cheng CY (2004) Regulation of blood–testis barrier dynamics: an in vivo study. J Cell Sci 117:783–798
Xia W, Mruk DD, Lee WM, Cheng CY (2006) Differential interactions between transforming growth factor-beta3/TbetaR1, TAB 1, and CD2AP disrupt blood–testis barrier and sertoli-germ cell adhesion. J Biol Chem 281:16799–16813
Zahraoui A, Louvard D, Galli T (2000) Tight junction, a platform for trafficking and signaling protein complexes. J Cell Biol 151:31–36
Acknowledgments
The excellent technical assistance of Marlene Stein and Anne Hild is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fink, C., Weigel, R., Fink, L. et al. Claudin-11 is over-expressed and dislocated from the blood–testis barrier in Sertoli cells associated with testicular intraepithelial neoplasia in men. Histochem Cell Biol 131, 755–764 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0576-2
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0576-2