Abstract
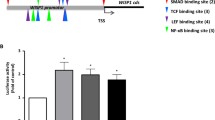
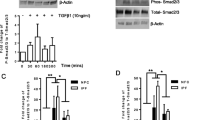
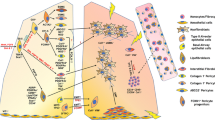
Infectious diseases can be cofactors in idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP) pathogenesis; recent data suggests that toll-like receptors 9 (TLR9) ligands contribute to experimental chronic tissue remodeling. Real-time TAQMAN and immunohistochemical analysis of IIP normal surgical lung biopsies (SLBs), primary fibroblast lines grown from both IIP and normal SLBs indicate that TLR9 is prominently and differentially expressed in a disease-specific manner. TLR9 expression was increased in biopsies from patients with IIP compared with normal lung biopsies and its expression is localized to areas of marked interstitial fibrosis. TLR9 in fibroblasts appeared to be increased by profibrotic Th2 cytokines (IL-4 and IL-13) and this was true in fibroblasts cultured from the most severe form of IIP, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) SLBs, in non-specific interstitial pneumonia fibroblast lines, and in normal fibroblasts. Finally, confocal microscopy studies have shown that TLR9 activation by its synthetic agonist CpG-ODN significantly increased the expression of alpha smooth muscle actin, the main marker of myofibroblast differentiation. These data indicate that TLR9 expression may drive the abnormal tissue healing response in severe forms of IIP and its activation can have a key role in myofibroblast differentiation promoting the progression of disease during the terminal phase of IPF.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akira S, Hemmi H (2003) Recognition of pathogen-associated molecular patterns by TLR family. Immunol Lett 85:85–95
Akira M, Hamada H, Sakatani M, Kobayashi C, Nishioka M, Yamamoto S (1997) CT findings during phase of accelerated deterioration in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 168:79–83
American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias (2002). This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:277–304
Andersen JM, Al-Khairy D, Ingalls RR (2006) Innate immunity at the mucosal surface: role of toll-like receptor 3 and toll-like receptor 9 in cervical epithelial cell responses to microbial pathogens. Biol Reprod 74:824–831
Bauer S, Kirschning CJ, Hacker H, Redecke V, Hausmann S, Akira S, Wagner H, Lipford GB (2001) Human TLR9 confers responsiveness to bacterial DNA via species-specific CpG motif recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9237–9242
Bernasconi NL, Onai N, Lanzavecchia A (2003) A role for Toll-like receptors in acquired immunity: up-regulation of TLR9 by BCR triggering in naive B cells and constitutive expression in memory B cells. Blood 101:4500–4504
Bowman CC, Rasley A, Tranguch SL, Marriott I (2003) Cultured astrocytes express toll-like receptors for bacterial products. Glia 43:281–291
Darby I, Skalli O, Gabbiani G (1990) Alpha-smooth muscle actin is transiently expressed by myofibroblasts during experimental wound healing. Lab Invest 63:21–29
Desmouliere A, Geinoz A, Gabbiani F, Gabbiani G (1993) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces alpha-smooth muscle actin expression in granulation tissue myofibroblasts and in quiescent and growing cultured fibroblasts. J Cell Biol 122:103–111
Droemann D, Albrecht D, Gerdes J, Ulmer AJ, Branscheid D, Vollmer E, Dalhoff K, Zabel P, Goldmann T (2005) Human lung cancer cells express functionally active Toll-like receptor 9. Respir Res 6:1
Ewaschuk JB, Backer JL, Churchill TA, Obermeier F, Krause DO, Madsen KL (2007) Surface expression of Toll-like receptor 9 is upregulated on intestinal epithelial cells in response to pathogenic bacterial DNA. Infect Immun 75:2572–2579
Fenhalls G, Squires GR, Stevens-Muller L, Bezuidenhout J, Amphlett G, Duncan K, Lukey PT (2003) Associations between toll-like receptors and interleukin-4 in the lungs of patients with tuberculosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:28–38
Fine A, Goldstein RH (1987) The effect of transforming growth factor-beta on cell proliferation and collagen formation by lung fibroblasts. J Biol Chem 262:3897–3902
Fischer SF, Rehm M, Bauer A, Hofling F, Kirschnek S, Rutz M, Bauer S, Wagner H, Hacker G (2005) Toll-like receptor 9 signaling can sensitize fibroblasts for apoptosis. Immunol Lett 97:115–122
Flaherty KR, Martinez FJ, Travis W, Lynch JP 3rd (2001a) Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). Semin Respir Crit Care Med 22:423–434
Flaherty KR, Travis WD, Colby TV, Toews GB, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Jain A, Strawderman RL, Flint A, Lynch JP, Martinez FJ (2001b) Histopathologic variability in usual and nonspecific interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1722–1727
Hashimoto S, Gon Y, Takeshita I, Maruoka S, Horie T (2001) IL-4 and IL-13 induce myofibroblastic phenotype of human lung fibroblasts through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-dependent pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol 107:1001–1008
Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K, Akira S (2000) A Toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature 408:740–745
Hinz B (2007) Formation and function of the myofibroblast during tissue repair. J Invest Dermatol 127:526–537
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007) The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 170:1807–1816
Hogaboam CM, Carpenter KJ, Evanoff H, Kunkel SL (2005) Approaches to evaluation of fibrogenic pathways in surgical lung biopsy specimens. Methods Mol Med 117:209–221
Ilvesaro JM, Merrell MA, Swain TM, Davidson J, Zayzafoon M, Harris KW, Selander KS (2007) Toll like receptor-9 agonists stimulate prostate cancer invasion in vitro. Prostate 67:774–781
Ishii KJ, Akira S (2006) Innate immune recognition of, and regulation by, DNA. Trends Immunol 27:525–532
Jakubzick C, Choi ES, Kunkel SL, Evanoff H, Martinez FJ, Puri RK, Flaherty KR, Toews GB, Colby TV, Kazerooni EA, Gross BH, Travis WD, Hogaboam CM (2004) Augmented pulmonary IL-4 and IL-13 receptor subunit expression in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. J Clin Pathol 57:477–486
Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R (2002) Innate immune recognition. Annu Rev Immunol 20:197–216
Katzenstein AL, Zisman DA, Litzky LA, Nguyen BT, Kotloff RM (2002) Usual interstitial pneumonia: histologic study of biopsy and explant specimens. Am J Surg Pathol 26:1567–1577
Kelly BG, Lok SS, Hasleton PS, Egan JJ, Stewart JP (2002) A rearranged form of Epstein–Barr virus DNA is associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166:510–513
Khalil N, Bereznay O, Sporn M, Greenberg AH (1989) Macrophage production of transforming growth factor beta and fibroblast collagen synthesis in chronic pulmonary inflammation. J Exp Med 170:727–737
Kim DS, Park JH, Park BK, Lee JS, Nicholson AG, Colby T (2006) Acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: frequency and clinical features. Eur Respir J 27:143–150
Krieg AM (2002) CpG motifs in bacterial DNA and their immune effects. Annu Rev Immunol 20:709–760
Kuwano K, Nomoto Y, Kunitake R, Hagimoto N, Matsuba T, Nakanishi Y, Hara N (1997) Detection of adenovirus E1A DNA in pulmonary fibrosis using nested polymerase chain reaction. Eur Respir J 10:1445–1449
Latz E, Schoenemeyer A, Visintin A, Fitzgerald KA, Monks BG, Knetter CF, Lien E, Nilsen NJ, Espevik T, Golenbock DT (2004) TLR9 signals after translocating from the ER to CpG DNA in the lysosome. Nat Immunol 5:190–198
Lee JW, Choi JJ, Seo ES, Kim MJ, Kim WY, Choi CH, Kim TJ, Kim BG, Song SY, Bae DS (2007) Increased toll-like receptor 9 expression in cervical neoplasia. Mol Carcinog 46:941–947
Leifer CA, Kennedy MN, Mazzoni A, Lee C, Kruhlak MJ, Segal DM (2004) TLR9 is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum prior to stimulation. J Immunol 173:1179–1183
Lund J, Sato A, Akira S, Medzhitov R, Iwasaki A (2003) Toll-like receptor 9-mediated recognition of Herpes simplex virus-2 by plasmacytoid dendritic cells. J Exp Med 198:513–520
Meneghin A, Hogaboam CM (2007) Infectious disease, the innate immune response, and fibrosis. J Clin Invest 117:530–538
Merrell MA, Ilvesaro JM, Lehtonen N, Sorsa T, Gehrs B, Rosenthal E, Chen D, Shackley B, Harris KW, Selander KS (2006) Toll-like receptor 9 agonists promote cellular invasion by increasing matrix metalloproteinase activity. Mol Cancer Res 4:437–447
Mitchell J, Woodcock-Mitchell J, Reynolds S, Low R, Leslie K, Adler K, Gabbiani G, Skalli O (1989) Alpha-smooth muscle actin in parenchymal cells of bleomycin-injured rat lung. Lab Invest 60:643–650
Mueller T, Terada T, Rosenberg IM, Shibolet O, Podolsky DK (2006) Th2 cytokines down-regulate TLR expression and function in human intestinal epithelial cells. J Immunol 176:5805–5814
Noble PW, Homer RJ (2005) Back to the future: historical perspective on the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:113–120
Parambil JG, Myers JL, Ryu JH (2005) Histopathologic features and outcome of patients with acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis undergoing surgical lung biopsy. Chest 128:3310–3315
Parilla NW, Hughes VS, Lierl KM, Wong HR, Page K (2006) CpG DNA modulates interleukin 1beta-induced interleukin-8 expression in human bronchial epithelial (16HBE14o-) cells. Respir Res 7:84
Platz J, Beisswenger C, Dalpke A, Koczulla R, Pinkenburg O, Vogelmeier C, Bals R (2004) Microbial DNA induces a host defense reaction of human respiratory epithelial cells. J Immunol 173:1219–1223
Schaefer TM, Desouza K, Fahey JV, Beagley KW, Wira CR (2004) Toll-like receptor (TLR) expression and TLR-mediated cytokine/chemokine production by human uterine epithelial cells. Immunology 112:428–436
Schmausser B, Andrulis M, Endrich S, Lee SK, Josenhans C, Muller-Hermelink HK, Eck M (2004) Expression and subcellular distribution of toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on the gastric epithelium in Helicobacter pylori infection. Clin Exp Immunol 136:521–526
Schmausser B, Andrulis M, Endrich S, Muller-Hermelink HK, Eck M (2005) Toll-like receptors TLR4, TLR5 and TLR9 on gastric carcinoma cells: an implication for interaction with Helicobacter pylori. Int J Med Microbiol 295:179–185
Selman M, Pardo A (2003) The epithelial/fibroblastic pathway in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 29:S93–S97
Sempowski GD, Derdak S, Phipps RP (1996) Interleukin-4 and interferon-gamma discordantly regulate collagen biosynthesis by functionally distinct lung fibroblast subsets. J Cell Physiol 167:290–296
Skalli O, Schurch W, Seemayer T, Lagace R, Montandon D, Pittet B, Gabbiani G (1989) Myofibroblasts from diverse pathologic settings are heterogeneous in their content of actin isoforms and intermediate filament proteins. Lab Invest 60:275–285
Stewart JP, Egan JJ, Ross AJ, Kelly BG, Lok SS, Hasleton PS, Woodcock AA (1999) The detection of Epstein–Barr virus DNA in lung tissue from patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:1336–1341
Tajima S, Oshikawa K, Tominaga S, Sugiyama Y (2003) The increase in serum soluble ST2 protein upon acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest 124:1206–1214
Takeshita F, Leifer CA, Gursel I, Ishii KJ, Takeshita S, Gursel M, Klinman DM (2001) Cutting edge: role of Toll-like receptor 9 in CpG DNA-induced activation of human cells. J Immunol 167:3555–3558
Tang YW, Johnson JE, Browning PJ, Cruz-Gervis RA, Davis A, Graham BS, Brigham KL, Oates JA Jr, Loyd JE, Stecenko AA (2003) Herpesvirus DNA is consistently detected in lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Microbiol 41:2633–2640
Ueda T, Ohta K, Suzuki N, Yamaguchi M, Hirai K, Horiuchi T, Watanabe J, Miyamoto T, Ito K (1992) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and high prevalence of serum antibodies to hepatitis C virus. Am Rev Respir Dis 146:266–268
Watanabe A, Hashmi A, Gomes DA, Town T, Badou A, Flavell RA, Mehal WZ (2007) Apoptotic hepatocyte DNA inhibits hepatic stellate cell chemotaxis via toll-like receptor 9. Hepatology 46:1509–1518
Zhang HY, Gharaee-Kermani M, Zhang K, Karmiol S, Phan SH (1996) Lung fibroblast alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and contractile phenotype in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Pathol 148:527–537
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the National Heart Lung and Blood Institute P50 HL56402 (CMH, SLK, KRF, FJM, and GBT), for financial support. We also thank Ms. Robin G. Kunkel for her artistic assistance in the preparation of the manuscript, as well as Dr. Judith Connett for her critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Figure 1.
Double immunofluorescence for TLR9 (red) and α-SMA (green) primary UIP/IPF fibroblasts. DAPI (blue) was used as a nuclear counter stain. Original magnifications, x400. In the left panel: higher magnification of the cell on the bottom. Scale bars as indicated. (DTD File 30 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meneghin, A., Choi, E.S., Evanoff, H.L. et al. TLR9 is expressed in idiopathic interstitial pneumonia and its activation promotes in vitro myofibroblast differentiation. Histochem Cell Biol 130, 979–992 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0466-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-008-0466-z