Abstract
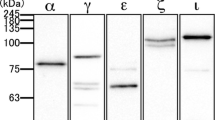
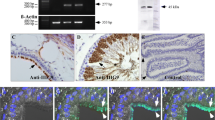
Paralemmin-1 is a phosphoprotein, lipid-anchored to the cytoplasmic face of membranes and implicated in plasma membrane dynamics and cell process formation. We report an immunoperoxidase histochemical analysis of the cellular and subcellular localization of paralemmin-1 in the rat tissues where its expression is highest: the brain, the adrenal gland and the kidney. Paralemmin-1 is detected throughout the brain, in neuronal perikarya, axons and dendrites including dendritic spines and also in glial processes. In the adrenal gland, paralemmin-1 is highly expressed in the medulla. The kidney displays a pattern of differential paralemmin-1 expression in various structures and cell types, with high concentrations in cells of the parietal epithelium of Bowman’s capsule, intermediate tubules, distal tubules and principal cells of outer medullary collecting ducts. Mosaics of paralemmin-positive and paralemmin-negative cells are observed in proximal tubules, the parietal epithelium of Bowman’s capsule and the endothelium of many blood vessels. Plasma membrane association in epithelia is often polarized: paralemmin-1 concentrates at the apical membranes of adrenal chromaffin cells, but at the basolateral plasma membranes of proximal and distal tubule cells in the kidney. Paralemmin-1 immunoreactivity exhibits a spotted pattern and can be seen both at plasma membranes and within the cytoplasm, where it is often associated with endomembranes. This discontinuous distribution and the detergent extraction properties of paralemmin-1 suggest an association with lipid microdomains. The findings are consistent with a role for paralemmin-1 in the formation and stabilization of plasma membrane elaborations, in neurons as well as in other cell types.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann S, Kriz W, Kuhn C, Franke WW (1983) Differentiation of cell types in the mammalian kidney by immunofluorescence microscopy using antibodies to intermediate filament proteins and desmoplakins. Histochemistry 77:365–395
Bagchi M, Katar M, Lo WK, Maisel H (2003) Paralemmin of the lens. J Cell Biochem 89:917–921
Basile M, Lin R, Kabbani N, Karpa K, Kilimann M, Simpson I, Kester M (2006) Paralemmin interacts with D3 dopamine receptors: implications for membrane localization and cAMP signaling. Arch Biochem Biophys 446:60–68
Castellini M, Wolf LV, Chauhan BK, Galileo DS, Kilimann MW, Cvekl A, Duncan MK (2005) Palm is expressed in both developing and adult mouse lens and retina. BMC Ophthalmol 5:14
Chauhan BK, Reed NA, Zhang W, Duncan MK, Kilimann MW, Cvekl A (2002) Identification of genes downstream of Pax6 in the mouse lens using cDNA microarrays. J Biol Chem 277:11539–11548
Cornish JA, Kloc M, Decker GL, Reddy BA, Etkin LD (1992) Xlcaax-1 is localized to the basolateral membrane of kidney tubule and other polarized epithelia during Xenopus development. Dev Biol 150:108–120
Elger M, Schnabel E, Kriz W (2001) Structure of the kidney. In: Massry SG, Glassock RJ (eds) Massry & Glassock’s textbook of nephrology, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 13–36, chapter 1, part 3
El-Husseini AE, Craven SE, Brock SC, Bredt DS (2001) Polarized targeting of peripheral membrane proteins in neurons. J Biol Chem 276:44984–44992
Gauthier-Campbell C, Bredt DS, Murphy TH, El-Husseini AE (2004) Regulation of dendritic branching and filopodia formation in hippocampal neurons by specific acylated protein motifs. Mol Biol Cell 15:2205–2217
Grant NJ, Konig F, Deloulme JC, Aunis D, Langley K (1992) Noradrenergic, but not adrenergic chromaffin cells in the adrenal gland express neuromodulin (GAP-43). Eur J Neurosci 4:1257–1263
Hu B, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Kilimann MW (2001) The paralemmin protein family: identification of paralemmin-2, an isoform differentially spliced to AKAP2/AKAP-KL, and of palmdelphin, a more distant cytosolic relative. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285:1369–1376
Hu B, Petrasch-Parwez E, Laue MM, Kilimann MW (2005) Molecular characterization and immunohistochemical localization of palmdelphin, a cytosolic isoform of the paralemmin protein family implicated in membrane dynamics. Eur J Cell Biol 84:853–866
Kutzleb C, Sanders G, Yamamoto R, Wang X, Lichte B, Petrasch-Parwez E, Kilimann MW (1998) Paralemmin, a prenyl-palmitoyl-anchored phosphoprotein abundant in neurons and implicated in plasma membrane dynamics and cell process formation. J Cell Biol 143:795–813
Lopez Costa JJ, Averill S, Ching YP, Priestley JV (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of a growth-associated protein (GAP-43) in rat adrenal gland. Cell Tissue Res 275:555–566
McGuire CB, Snipes GJ, Norden JJ (1988) Light-microscopic immunolocalization of the growth- and plasticity-associated protein GAP-43 in the developing rat brain. Dev Brain Res 41:277–291
Oestreicher AB, Gispen WH (1986) Comparison of the immunocytochemical distribution of the phosphoprotein B-50 in the cerebellum and hippocampus of immature and adult rat brain. Brain Res 375:267–279
Reilly RF, Ellison DH (2000) Mammalian distal tubule: physiology, pathophysiology, and molecular anatomy. Physiol Rev 80:277–313
Acknowledgements
We thank Wolfgang Witt and Bin Hu for Fig. 11, Marlen Löbbecke-Schumacher and Hans-Werner Habbes for excellent technical assistance, Prof. Monika von Düring for advice and Greta Hultqvist for figure editing. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kutzleb, C., Petrasch-Parwez, E. & Kilimann, M.W. Cellular and subcellular localization of paralemmin-1, a protein involved in cell shape control, in the rat brain, adrenal gland and kidney. Histochem Cell Biol 127, 13–30 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-006-0209-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-006-0209-y