Abstract
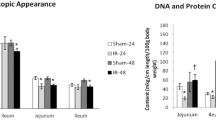
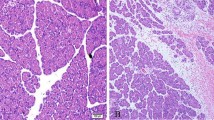
Although ischemia reperfusion (I/R) induces apoptotic damage of mammalian small intestine, the molecular mechanism is largely unknown. We investigated the appearance of apoptosis at various time-points (0–24 h) of reperfusion after 1-h ischemia and the expression of various apoptosis-related proteins, such as Bcl-2, Bax, Fas, Fas ligand (FasL), activated caspase-3, and cytochrome c, immunohistochemically in rat small intestine. As assessed by TUNEL and electron microscopy, apoptotic cells were increased at 3 h of reperfusion in all intestinal parts (villous epithelium, crypt epithelium, and stroma of intestine). Moreover, the TUNEL-positive cells in the stroma were later identified as T cells. The expression of Fas and FasL as well as activated caspase-3 was markedly increased at 3 h of reperfusion in the stroma. In the villous epithelium, a transient decrease in Bcl-2 expression was found while in the crypt epithelium, Fas expression was induced. Finally, intraperitoneal injection of leupeptin (an SH-protease inhibitor) after I/R resulted in a significant inhibition of the induction of apoptosis in the stroma and crypt epithelium. Our results indicate that the triggering molecules of apoptosis in the I/R rat small intestine may vary depending on cell type and that the use of a broad-spectrum protease inhibitor may reduce intestinal damage.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (1981) Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem 29:775
Baba N, Koji T, Itoh M, Mizuno A (1999) Reciprocal changes in the expression of Bcl-2 and Bax in hypoglossal nucleus after axotomy in adult rats: possible involvement in the induction of neuronal cell death. Brain Res 827:122–129
Cohen GM (1997) Caspases: the executioners of apoptosis. Biochem J 326:1–16
Coopersmith CM, O’Donnell D, Gordon JI (1999) Bcl-2 inhibits ischemia-reperfusion-induced apoptosis in the intestinal epithelium of transgenic mice. Am J Physiol 276:G677–G686
Cotran RS, Kumar V, Robbins SL (1994) Cellular injury and cellular death. In: Cotran RS, Kumar V, Robbins SL, Schoen FJ (eds) Pathologic basis of disease, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 1–33
Damavandi E, Hishikawa Y, Izumi S, Shin M, Koji T (2002) Involvement of Bax redistribution in the induction of germ cell apoptosis in neonatal mouse testes. Acta Histochem Cytochem 35:449–459
Eskes R, Antonsson B, Osen-Sand A, Montessuit S, Richter C, Sadoul R, Mazzei G, Nichols A, Martinou JC (1998) Bax-induced cytochrome C release from mitochondria is independent of the permeability transition pore but highly dependent on Mg2+ ions. J Cell Biol 143:217–224
French LE, Hahne M, Viard I, Radlgruber G, Zanone R, Becker K, Muller C, Tschopp J (1996) Fas and Fas ligand in embryos and adult mice: ligand expression in several immune-privileged tissues and coexpression in adult tissues characterized by apoptotic cell turnover. J Cell Biol 133:335–343
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119:493–501
Genesca M, Sola A, Miquel R, Pi F, Xaus C, Alfaro V, Hotter G (2002) Role of changes in tissular nucleotides on the development of apoptosis during ischemia/reperfusion in rat small bowel. Am J Pathol 161:1839–1847
Gottlieb RA, Burleson KO, Kloner RA, Babior BM, Engler RL (1994) Reperfusion injury induces apoptosis in rabbit cardiomyocytes. J Clin Invest 94:1621–1628
Granger DN, Korthuis RJ (1995) Physiologic mechanisms of postischemic tissue injury. Annu Rev Physiol 57:311–332
Green DR (1998) Apoptotic pathways: the roads to ruin. Cell 94:695–698
Hakuno N, Koji T, Yano T, Kobayashi N, Tsutsumi O, Taketani Y, Nakane PK (1996) Fas/APO-1/CD95 system as a mediator of granulosa cell apoptosis in ovarian follicle atresia. Endocrinology 137:1938–1948
Hashimoto S, Koji T, Niu J, Kanematsu T, Nakane PK (1995) Differential staining of DNA strand breaks in dying cells by non-radioactive in situ nick translation. Arch Histol Cytol 58:161–170
Hassoun HT, Zou L, Moore FA, Kozar RA, Weisbrodt NW, Kone BC (2002) Alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone protects against mesenteric ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 282:G1059–G1068
Itoh H, Yagi M, Fushida S, Tani T, Hashimoto T, Shimizu K, Miwa K (2000) Activation of immediate early gene, c-fos, and c-jun in the rat small intestine after ischemia/reperfusion. Transplantation 69:598–604
Kawano N, Koji T, Hishikawa Y, Murase K, Murata I, Kohno S (2004) Identification and localization of estrogen receptor alpha- and beta-positive cells in adult male and female mouse intestine at various estrogen levels. Histochem Cell Biol 121:399–405
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Koji T, Kobayashi N, Nakanishi Y, Yoshii A, Hashimoto S, Shibata Y, Anjiki N, Yamamoto R, Aoki A, Ueda T, Kanazawa S, Nakane PK (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of Fas antigen in paraffin sections with rabbit antibodies against human synthetic Fas peptides. Acta Histochem Cytochem 27:459–463
Koji T, Hishikawa Y, Ando H, Nakanishi Y, Kobayashi N (2001) Expression of Fas and Fas ligand in normal and ischemia-reperfusion testes: involvement of the Fas system in the induction of germ cell apoptosis in the damaged mouse testis. Biol Reprod 64:946–954
Krajewski S, Krajewska M, Shabaik A, Miyashita T, Wang HG, Reed JC (1994) Immunohistochemical determination of in vivo distribution of Bax, a dominant inhibitor of Bcl-2. Am J Pathol 145:1323–1336
Kuida K, Haydar TF, Kuan CY, Gu Y, Taya C, Karasuyama H, Su MS, Rakic P, Flavell RA (1998) Reduced apoptosis and cytochrome c-mediated caspase activation in mice lacking caspase 9. Cell 94:325–337
Lin T, Brunner T, Tietz B, Madsen J, Bonfoco E, Reaves M, Huflejt M, Green DR (1998) Fas ligand-mediated killing by intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes. Participation in intestinal graft-versus-host disease. J Clin Invest 101:570–577
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J, Jemmerson R, Wang X (1996) Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 86:147–157
Megison SM, Horton JW, Chao H, Walker PB (1990) A new model for intestinal ischemia in the rat. J Surg Res 49:168–173
Nagata S, Golstein P (1995) The Fas death factor. Science 267:1449–1456
Nakane PK (1968) Simultaneous localization of multiple tissue antigens using the peroxidase-labeled antibody method: a study on pituitary glands of the rat. J Histochem Cytochem 16:557–560
Nogae S, Miyazaki M, Kobayashi N, Saito T, Abe K, Saito H, Nakane PK, Nakanishi Y, Koji T (1998) Induction of apoptosis in ischemia-reperfusion model of mouse kidney: possible involvement of Fas. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:620–631
Nomura M, Shimizu S, Ito T, Narita M, Matsuda H, Tsujimoto Y (1999) Apoptotic cytosol facilitates Bax translocation to mitochondria that involves cytosolic factor regulated by Bcl-2. Cancer Res 59:5542–5548
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL, Korsmeyer SJ (1993) Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that accelerates programmed cell death. Cell 74:609–619
Potten CS, Merritt A, Hickman J, Hall P, Faranda A (1994) Characterization of radiation-induced apoptosis in the small intestine and its biological implications. Int J Radiat Biol 65:71–78
Potten CS, Wilson JW, Booth C (1997) Regulation and significance of apoptosis in the stem cells of the gastrointestinal epithelium. Stem Cells 15:82–93
Suda T, Takahashi T, Golstein P, Nagata S (1993) Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell 75:1169–1178
Sun F, Akazawa S, Sugahara K, Kamihira S, Kawasaki E, Eguchi K, Koji T (2002) Apoptosis in normal rat embryo tissues during early organogenesis: the possible involvement of Bax and Bcl-2. Arch Histol Cytol 65:145–157
Wang RA, Nakane PK, Koji T (1998) Autonomous cell death of mouse male germ cells during fetal and postnatal period. Biol Reprod 58:1250–1256
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Itoh N, Yonehara S, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Nagata S (1992) The cDNA structure, expression, and chromosomal assignment of the mouse Fas antigen. J Immunol 148:1274–1279
Wolf BB, Green DR (1999) Suicidal tendencies: apoptotic cell death by caspase family proteinases. J Biol Chem 274:20049–20052
Wu B, Iwakiri R, Tsunada S, Utsumi H, Kojima M, Fujise T, Ootani A, Fujimoto K (2002) iNOS enhances rat intestinal apoptosis after ischemia-reperfusion. Free Radic Biol Med 33:649–658
Zou H, Henzel WJ, Liu X, Lutschg A, Wang X (1997) Apaf-1, a human protein homologous to C. elegans CED-4, participates in cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3. Cell 90:405–413
Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Japanese Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture (no. 15390058 to T.K.). The authors thank Mr. Takashi Suematsu for this excellent ME techniques assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, S., Hishikawa, Y. & Koji, T. Induction of cell death in rat small intestine by ischemia reperfusion: differential roles of Fas/Fas ligand and Bcl-2/Bax systems depending upon cell types. Histochem Cell Biol 123, 249–261 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0765-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0765-6