Abstract
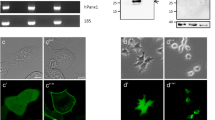
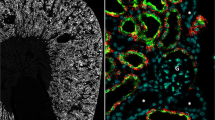
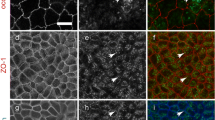
The PDZ domain-containing protein zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), a well-established component of tight junctions, has recently been shown to interact with various connexin proteins that form gap junctions. We investigated the association of connexin36 (Cx36) with ZO-1 in various cultured cells and tissues. Punctate immunofluorescence labeling for Cx36 was detected in Cx36-transfected HeLa cells, βTC-3 cells, pancreatic islets, and adrenal medulla. Immunofluorescence for ZO-1 was also punctate in cells and tissues, and was colocalized with Cx36 at points of cell–cell contact. Immunoprecipitation of either Cx36 or ZO-1 from cell lysates and tissue homogenates resulted in immunoblot detection of ZO-1 or Cx36, respectively, in immunoprecipitates. A 14-amino acid peptide corresponding to the carboxy-terminus of Cx36 showed binding capacity to the PDZ1 domain of ZO-1, which was eliminated after removal of the last 4 carboxy-terminus amino acids. Low micromolar concentrations of the 14-amino acid peptide produced up to 85% inhibition of Cx36 interaction with the PDZ1 domain of ZO-1. These results provide evidence for molecular interaction between Cx36 and ZO-1 in vitro, and in vivo, and suggest that the interference with Cx36/ZO-1 interaction by short carboxy-terminus peptides of Cx36 may be of value for functional studies of this interaction.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balda MS, Matter K (2000) The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression. EMBO J 19:2024–2033
Balda MS, Anderson JM, Matter K (1996) The SH3 domain of the tight junction protein ZO-1 binds to a serine protein kinase that phosphorylates a region C-terminal to this domain. FEBS Lett 399:326–332
Becamel C, Gavarini S, Chanrion B, Alonso G, Galeotti N, Dumuis A, Bockaert J, Marin P (2004) The serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors interact with specific sets of PDZ proteins. J Biol Chem 279:20257–20266
Bischof LJ, Martin CC, Svitek CA, Stadelmaier BT, Hornbuckle LA, Goldman JK, Oeser JK, Hutton JC, O’Brien RM (2001) Characterization of the mouse islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein gene promoter by in situ footprinting: correlation with fusion gene expression in the islet-derived βTC-3 and hamster insulinoma tumor cell lines. Diabetes 50:502–514
Calabrese A, Güldenagel M, Charollais A, Mas C, Caton D, Bauquis J, Serre-Beinier V, Caille D, Söhl G, Teubner B, Le Gurun S, Trovato-Salinaro A, Condorelli DF, Haefliger JA, Willecke K, Meda P (2001) Cx36 and the function of endocrine pancreas. Cell Commun Adhes 8:387–391
Calabrese A, Zhang M, Serre-Beinier V, Caton D, Mas C, Satin LS, Meda P (2003) Connexin36 controls synchronization of Ca2+ oscillations and insulin secretion in MIN6 cells. Diabetes 52:417–424
Calabrese A, Caton D, Meda P (2004) Differentiating the effects of Cx36 and E-cadherin for proper insulin secretion of MIN6 cells. Exp Cell Res 294:379–391
Chen ML, Pothoulakis C, LaMont JT (2002) Protein kinase C signaling regulates ZO-1 translocation and increased paracellular flux of T84 colonocytes exposed to Clostridium difficile toxin A. J Biol Chem 277:4247–4254
Condorelli DF, Parenti R, Spinella F, Trovato-Salinare A, Belluardo N, Cardile V, Cicirata F (1998) Cloning of a new gap junction gene (Cx36) highly expressed in mammalian brain neurons. Eur J Neurosci 10:1202–1208
Condorelli DF, Belluardo N, Trovato-Salinaro A, Mudo G (2000) Expression of Cx36 in mammalian neurons. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 32:72–85
Deans MR, Gibson JR, Sellitto C, Connors BW, Paul DL (2001) Synchronous activity of inhibitory networks in neocortex requires electrical synapses containing connexin36. Neuron 16:477–485
Denker BM, Saha C, Khawaja S, Nigam SK (1996) Involvement of a heterotrimeric G protein alpha subunit in tight junction biogenesis. J Biol Chem 271:25750–25753
Dodane V, Kachar B (1996) Identification of isoforms of G proteins and PKC that colocalize with tight junctions. J Membr Biol 149:199–209
Doyle JP, Stempak JG, Cowin P, Colman DR, D’Urso D (1995) Protein zero, a nervous system adhesion molecule, triggers epithelial reversion in host carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 131:465–482
Giepmans BN, Moolenaar WH (1998) The gap junction protein connexin43 interacts with the second PDZ domain of the zona occludens-1 protein. Curr Biol 8:931–934
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Avila-Flores A (2000) MAGUK proteins: structure and role in the tight junction. Semin Cell Dev Biol 11:315–324
Gonzalez-Mariscal L, Betanzos A, Nava P, Jaramillo BE (2003) Tight junction proteins. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 81:1–44
Goodenough DA, Goliger JA, Paul DL (1996) Connexins, connexons, and intercellular communication. Annu Rev Biochem 65:475–502
Grynszpan-Wynograd O, Nicolas G (1980) Intercellular junctions in the adrenal medulla: a comparative freeze-fracture study. Tissue Cell 12:661–672
Howarth AG, Hughes MR, Stevenson BR (1992) Detection of the tight junction-associated protein ZO-1 in astrocytes and other nonepithelial cell types. Am J Physiol 262:C461–C469
In’t Veld PA, Pipeleers DG, Gepts W (1984) Evidence against the presence of tight junctions in normal endocrine pancreas. Diabetes 33:101–104
Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Kitani-Yasuda T, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) The 220-kD protein colocalizing with cadherins in non-epithelial cells is identical to ZO-1, a tight junction-associated protein in epithelial cells: cDNA cloning and immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol 121:491–502
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2 and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Kausalya PJ, Reichert M, Hunziker W (2001) Connexin45 directly binds to ZO-1 and localizes to the tight junction region in epithelial MDCK cells. FEBS Lett 505:92–96
Kleeff J, Shi X, Bode HP, Hoover K, Shrikhande S, Bryant PJ, Korc M, Buchler MW, Friess H (2001) Altered expression and localization of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in primary and metastatic pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 23:259–265
Kojima T, Kokai Y, Chiba H, Yamamoto M, Mochizuki Y, Sawada N (2001) Cx32 but not Cx26 is associated with tight junctions in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Exp Cell Res 263:193–201
Kumar NM, Gilula NB (1996) The gap junction communication channel. Cell 84:381–388
Laing JG, Manley-Markowski RN, Koval M, Civitelli R, Steinberg TH (2001a) Connexin45 interacts with zonula occludens-1 and connexin43 in osteoblastic cells. J Biol Chem 276:23051–23055
Laing JG, Manley-Markowski RN, Koval M, Civitelli R, Steinberg TH (2001b) Connexin45 interacts with zonula occludens-1 in osteoblastic cells. Cell Commun Adhes 8:209–212
Le Gurun S, Martin D, Formenton A, Maeschler P, Caille D, Waeber G, Meda P, Haefliger JA (2003) Connexin36 contributes to control function of insulin-producing cells. J Biol Chem 278:37690–37697
Li X, Lynn BD, Olson C, Meier C, Davidson KG, Yasumura T, Rash JE, Nagy JI (2002) Connexin29 expression, immunocytochemistry and freeze-fracture replica immunogold labelling (FRIL) in sciatic nerve. Eur J Neurosci 16:795–806
Li X, Ionescu AV, Lynn BD, Lu S, Kamasawa N, Morita M, Davidson KGV, Yasumura T, Rash JE, Nagy JI (2004a) Connexin47, connexin29 and connexin32 co-expression in oligodendrocytes and Cx47 association with zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) in mouse brain. Neuroscience 126:611–630
Li X, Olson C, Lu S, Kamasawa N, Yasumura T, Rash JE, Nagy JI (2004b) Neuronal connexin36 association with zonula occludens-1 protein (ZO-1) in mouse brain and interaction with the first PDZ domain of ZO-1. Eur J Neurosci 19:2132–2146
Lynn BD, Li X, Cattini PA, Turley EA, Nagy JI (2001) Identification of sequence, protein isoforms, and distribution of the hyaluronan-binding protein RHAMM in adult and developing rat brain. J Comp Neurol 439:315–330
Martin AQ, Mathieu MN, Chevillard C, Guerineau NC (2001) Gap junctions mediate electrical signaling and ensuing cytosolic Ca2+ increases between chromaffin cells in adrenal slices: a role in catecholamine release. J Neurosci 21:5397–5405
Martin AQ, Mathieu MN, Guerineau NC (2003) Evidence for long-lasting cholinergic control of gap junctional communication between adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurosci 23:3669–3678
Matter K, Balda MS (2003) Signalling to and from tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:225–236
Meda P, Pepper MS, Traub O, Willecke K, Gros D, Beyer E, Nicholson B, Paul D, Orci L (1993) Differential expression of gap junction connexins in endocrine and exocrine glands. Endocrinology 133:2371–2378
Meyer TN, Schwesinger C, Denker BM (2002) Zonula occludens-1 is a scaffolding protein for signaling molecules. Galpha(12) directly binds to the Src homology 3 domain and regulates paracellular permeability in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 277:24855–24858
Mitic LL, Anderson JM (1998) Molecular architecture of tight junctions. Annu Rev Physiol 60:121–142
Moser T (1998) Low-conductance intercellular coupling between mouse chromaffin cells in situ. J Physiol 506:195–205
Murray SA, Davis K, Gay V (2003) ACTH and adrenocortical gap junctions. Microsc Res Tech 61:240–246
Nagy JI, Li X, Rempel J, Stelmack G, Patel D, Staines WA, Yasumura T, Rash JE (2001) Connexin26 in adult rodent central nervous system: demonstration at astrocytic gap junctions and co-localization with connexin30 and connexin43. J Comp Neurol 441:302–323
Nielsen PA, Baruch A, Giepmans BN, Kumar NM (2001) Characterization of the association of connexins and ZO-1 in the lens. Cell Commun Adhes 8:213–217
Nielsen PA, Beahm DL, Giepmans BN, Baruch A, Hall JE, Kumar NM (2002) Molecular cloning, functional expression, and tissue distribution of a novel human gap junction-forming protein, connexin-31.9. Interaction with zona occludens protein-1. J Biol Chem 277:38272–38283
Nielsen PA, Baruch A, Shestopalov VI, Giepmans BN, Benedetti EI, Kumar NM (2003) Lens connexins Cx46 and CxCHCHx50 interact with zonula occludens protein-1 (ZO-1). Mol Biol Cell 14:2470–2481
Orci L (1974) A portrait of the pancreatic B-cell. Diabetologia 10:163–187
Orci L, Malaisse-Lagae F, Amherdt M, Ravazzola M, Weisswange A, Dobbs R, Perrelet A, Unger R (1975a) Cell contacts in human islets of Langerhans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 41:841–844
Orci L, Malaisse-Lagae F, Ravazzola M, Rouiller D, Renold AE, Perrelet A, Unger R (1975b) A morphological basis for intercellular communication between alpha- and beta-cells in the endocrine pancreas. J Clin Invest 56:1066–1070
Rash JE, Staines WA, Yasumura T, Patel D, Furman CS, Stelmack GL, Nagy JI (2000) Immunogold evidence that neuronal gap junctions in adult rat brain and spinal cord contain connexin-36 but not connexin-32 or connexin-43. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:7573–7578
Rash JE, Yasumura T, Dudek FE, Nagy JI (2001) Cell-specific expression of connexins and evidence of restricted gap junctional coupling between glial cells and between neurons. J Neurosci 15:1983–2000
Scadding JW (1981) Development of ongoing activity, mechanosensitivity, and adrenaline sensitivity in severed peripheral nerve axons. Exp Neurol 73:345–364
Schnabel E, Anderson JM, Farquhar MG (1990) The tight junction protein ZO-1 is concentrated along slit diaphragms of the glomerular epithelium. J Cell Biol 111:1255–1263
Serre-Beinier V, Le Gurun S, Belluardo N, Trovato-Salinaro A, Charollais A, Haefliger JA, Condorelli DF, Meda P (2000) Cx36 preferentially connects beta-cells within pancreatic islets. Diabetes 49:727–734
Serre-Beinier V, Mas C, Calabrese A, Caton D, Bauquis J, Caille D, Charollais A, Cirulli V, Meda P (2002) Connexins and secretion. Biol Cell 94:477–492
Sheng M, Sala C (2001) PDZ domains and the organization of supramolecular complexes. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:1–29
Söhl G, Degen J, Teubner B, Willecke K (1998) The murine gap junction gene connexin36 is highly expressed in mouse retina and regulated during brain development. FEBS Lett 428:27–31
Songyang Z, Fanning AS, Fu C, Xu J, Marfatia SM, Chishti AH, Crompton A, Chan AC, Anderson JM, Cantley LC (1997) Recognition of unique carboxyl-terminal motifs by distinct PDZ domains. Science 275:73–77
Spiryda LB, Colman DR (1998) Protein zero, a myelin IgCAM, induces physiologically operative tight junctions in nonadhesive carcinoma cells. J Neurosci Res 54:282–288
Stevenson BR, Siliciano JD, Mooseker MS, Goodenough DA (1986) Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol 103:755–766
Stuart RQ, Nigam SK (1995) Regulated assembly of tight junctions by protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 20:6072–6076
Theis M, Mas C, Doring B, Degen J, Brink C, Caille D, Charollais A, Krüger O, Plum A, Nepote V, Herrera P, Meda P, Willecke K (2004) Replacement by a lacZ reporter gene assigns mouse connexin36, 45 and 43 to distinct cell types in pancreatic islets. Exp Cell Res 294:18–29
Thomas MA, Huang S, Cokoja A, Riccio O, Staub O, Suter S, Chanson M (2002) Interaction of connexins with protein partners in the control of channel turnover and gating. Biol Cell 94:445–456
Toyofuku T, Yabuki M, Otsu K, Kuzuya T, Hori M, Tada M (1998) Direct association of the gap junction protein connexin-43 with ZO-1 in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 273:12725–12731
Unsicker K, Seidl K, Hofmann HD (1989) The neuro-endocrine ambiguity of sympathoadrenal cells. Int J Dev Neurosci 7:413–417
White TW, Bruzzone R (1996) Multiple connexin proteins in single intercellular channels: connexin compatibility and functional consequences. J Bioenerg Biomembr 28:339–350
White TW, Paul DL (1999) Genetic diseases and gene knockouts reveal diverse connexin functions. Annu Rev Physiol 61:283–310
Willecke K, Eiberger J, Degen J, Eckardt D, Romualdi A, Güldenagel M, Deutsch U, Söhl G (2002) Structural and functional diversity of connexin genes in the mouse and human genome. Biol Chem 383:725–737
Yamagami K, Moritoyo T, Wakamori M, Sorimachi M (2002) Limited intercellular spread of spontaneous Ca2+ signals via gap junctions between mouse chromaffin cells in situ. Neurosci Lett 323:97–100
Yamamoto T, Hertzberg EL, Nagy JI (1995) Differential distribution of connexin43-immunoreactive gap junctions in the rat adrenal cortex. In: Kanno Y (ed) Progress in cell research, vol 4. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 289–292
Yokoyama S, Tachibana K, Nakanishi H , Yamamoto Y, Irie K, Mandai K, Nagafuchi A, Monden M, Takai Y (2001) Alpha-catenin-independent recruitment of ZO-1 to nectin-based cell-cell adhesion sites through afadin. Mol Biol Cell 12:1595–1609
Zhurinsky J, Shtutman M, Ben-Ze’ev A (2000) Differential mechanisms of LEF/TCF family-dependent transcriptional activation by beta-catenin and plakoglobin. Mol Cell Biol 20:4238–4252
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Brett McLean and Nora Nolette for excellent technical assistance. We also thank Dr. David Paul (Department of Neuroscience, Harvard University) for providing heterozygous Cx36/LacZ mice, and Dr. Christopher McIntosh (Department of Physiology, University of British Columbia) for providing βTC-3 cells. This work was supported by grants from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research to J.I.N.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*co-1st authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li*, X., Olson*, C., Lu, S. et al. Association of connexin36 with zonula occludens-1 in HeLa cells, βTC-3 cells, pancreas, and adrenal gland. Histochem Cell Biol 122, 485–498 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0718-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0718-5