Abstract
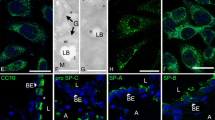
The study of function and regulation of the phenotype of alveolar type I (AT I) epithelial cells is limited by the rareness of suitable cell lines or primary cultures of this cell type. We describe in the present study the type I-like rat epithelial cell line R3/1. This cell line displays in vitro a phenotype with several characteristic features of AT I cells. R3/1 cells were analysed for mRNA and protein content of markers related to the AT I cell type (T1α, ICAM-1, connexin-43, caveolins-1 and -2) and AT II phenotypes [surfactant proteins (SPs) A, B, C and D]. The mRNAs for SPs were found to be at a low level. Moderate protein levels for SP-A and SP-B were found, and SP-C and SP-D proteins were not detectable. R3/1 cells are positive for CD44s, E-cadherin, cytokeratin, vimentin and RAGE, and bind the lectins BPA and SBA. For demonstration of the suitability of R3/1 cells for in vitro studies on epithelial injury, the cells were treated with bleomycin. As shown by real-time RT-PCR and immunoblotting, bleomycin-treatment of R3/1 cells resulted in a decrease in mRNA and protein for both caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 in comparison with controls. The AT I-like cell line R3/1 may serve as a promising tool for the study of lung cell biology.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham V, Chou ML, DeBolt KM, Koval M (1999) Phenotypic control of gap junctional communication by cultured alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 276:L825–L834
Adamson IY, Bowden DH (1975) Derivation of type 1 epithelium from type 2 cells in the developing rat lung. Lab Invest 32:736–745
Bankston PW, Porter GA, Milici AJ, Palade GE (1991) Differential and specific labeling of epithelial and vascular endothelial cells of the rat lung by Lycopersicon esculentum and Griffonia simplicifolia I lectins. Eur J Cell Biol 54:187–195
Borok Z, Danto SI, Dimen LL, Zhang XL, Lubman RL (1998a) Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase expression in alveolar epithelial cells: upregulation of active ion transport by KGF. Am J Physiol 274:L149–L158
Borok Z, Danto SI, Lubman RL, Cao Y, Williams MC, Crandall ED (1998b) Modulation of t1alpha expression with alveolar epithelial cell phenotype in vitro. Am J Physiol 275:L155–L164
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Campbell L, Hollins AJ, Al-Eid A, Newman GR, von Ruhland C, Gumbleton M (1999) Caveolin-1 expression and caveolae biogenesis during cell transdifferentiation in lung alveolar epithelial primary cultures. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 262:744–751
Cao YX, Williams, M.C. (2002) Hyperoxia increases expression of endogenous alveolar type I cell mRNAs in the E10/C10 murine lung epithelial cell lines. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 165:A627
Christensen PJ, Kim S, Simon RH, Toews GB, Paine R III (1993) Differentiation-related expression of ICAM-1 by rat alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 8:9–15
Clegg R, Harrison DJ, McElroy MC (2003) The phenotype of cultured alveolar epithelial cells. FASEB J 17:562
Cunningham AC, Milne DS, Wilkes J, Dark JH, Tetley TD, Kirby JA (1994) Constitutive expression of MHC and adhesion molecules by alveolar epithelial cells (type II pneumocytes) isolated from human lung and comparison with immunocytochemical findings. J Cell Sci 107:443–449
Dobbs LG, Williams MC, Gonzalez R (1988) Monoclonal antibodies specific to apical surfaces of rat alveolar type I cells bind to surfaces of cultured, but not freshly isolated, type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 970:146–156
Dobbs LG, Gonzalez R, Matthay MA, Carter EP, Allen L, Verkman AS (1998) Highly water-permeable type I alveolar epithelial cells confer high water permeability between the airspace and vasculature in rat lung. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:2991–2996
Drab M, Verkade P, Elger M, Kasper M, Lohn M, Lauterbach B, Menne J, Lindschau C, Mende F, Luft FC, Schedl A, Haller H, Kurzchalia TV (2001) Loss of caveolae, vascular dysfunction, and pulmonary defects in caveolin-1 gene-disrupted mice. Science 293:2449–2452
Emura M, Riebe M, Ochiai A, Aufderheide M, Germann P, Mohr U (1990) New functional cell-culture approach to pulmonary carcinogenesis and toxicology. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 116:557–562
Fehrenbach H, Kasper M, Tschernig T, Shearman MS, Schuh D, Muller M (1998) Receptor for advanced glycation endproducts (RAGE) exhibits highly differential cellular and subcellular localisation in rat and human lung. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 44:1147–1157
Gargalovic P, Dory L (2003) Cellular apoptosis is associated with increased caveolin-1 expression in macrophages. J Lipid Res 44:1622–1632
Gumbleton M, Hollins AJ, Omidi Y, Campbell L, Taylor G (2003) Targeting caveolae for vesicular drug transport. J Control Release 87:139–151
Gutierrez JA, Gonzalez RF, Dobbs LG (1998) Mechanical distension modulates pulmonary alveolar epithelial phenotypic expression in vitro. Am J Physiol 274:L196–L202
Hamilton RF Jr, Li L, Felder TB, Holian A (1995) Bleomycin induces apoptosis in human alveolar macrophages. Am J Physiol 269:L318–L325
Isakson BE, Lubman RL, Seedorf GJ, Boitano S (2001) Modulation of pulmonary alveolar type II cell phenotype and communication by extracellular matrix and KGF. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1291–C1299
Johnson MD, Widdicombe JH, Allen L, Barbry P, Dobbs LG (2002) Alveolar epithelial type I cells contain transport proteins and transport sodium, supporting an active role for type I cells in regulation of lung liquid homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1966–1971
Kasper M (2003) Pulmonary pathology of knockouts in mice lacking type I antigens. Ann Anat 185(suppl):144
Kasper M, Singh G (1995) Epithelial lung cell marker: current tools for cell typing. Histol Histopathol 10:155–169
Kasper M, Rudolf T, Hahn R, Peterson I, Muller M (1993a) Immuno- and lectin histochemistry of epithelial subtypes and their changes in a radiation-induced lung fibrosis model of the mini pig. Histochemistry 100:367–377
Kasper M, Rudolf T, Verhofstad AA, Schuh D, Muller M (1993b) Heterogeneity in the immunolocalization of cytokeratin-specific monoclonal antibodies in the rat lung: evaluation of three different alveolar epithelial cell types. Histochemistry 100:65–71
Kasper M, Schuh D, Muller M (1994) Bauhinia purpurea lectin (BPA) binding of rat type I pneumocytes: alveolar epithelial alterations after radiation-induced lung injury. Exp Toxicol Pathol 46:361–367
Kasper M, Koslowski R, Luther T, Schuh D, Muller M, Wenzel KW (1995) Immunohistochemical evidence for loss of ICAM-1 by alveolar epithelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem Cell Biol 104:397–405
Kasper M, Traub O, Reimann T, Bjermer L, Grossmann H, Muller M, Wenzel KW (1996) Upregulation of gap junction protein connexin43 in alveolar epithelial cells of rats with radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Histochem Cell Biol 106:419–424
Kasper M, Reimann T, Hempel U, Wenzel KW, Bierhaus A, Schuh D, Dimmer V, Haroske G, Muller M (1998) Loss of caveolin expression in type I pneumocytes as an indicator of subcellular alterations during lung fibrogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 109:41–48
Kasper M, Seidel D, Knels L, Morishima N, Neisser A, Bramke S, Koslowski R (2004) Early signs of lung fibrosis after in vitro treatment of rat lung slices with CdCl2 and TGF-beta1. Histochem Cell Biol 121:131–140
Katsuoka F, Kawakami Y, Arai T, Imuta H, Fujiwara M, Kanma H, Yamashita K (1997) Type II alveolar epithelial cells in lung express receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:512–516
Knebel JW, Aufderheide M, Emura M (1994) Comparison of biological effects of different polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in lung cells of hamster and rat in vitro. Toxicol Lett 72:65–72
Koslowski R, Dobbs LG, Wenzel KW, Schuh D, Muller M, Kasper M (1998) Loss of immunoreactivity for RTI40, a type I cell-specific protein in the alveolar epithelium of rat lungs with bleomycin-induced fibrosis. Eur Respir J 12:1397–1403
Koval M (2002) Sharing signals: connecting lung epithelial cells with gap junction channels. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 283:L875–L893
Kuwano K, Hagimoto N, Tanaka T, Kawasaki M, Kunitake R, Miyazaki H, Kaneko Y, Matsuba T, Maeyama T, Hara N (2000) Expression of apoptosis-regulatory genes in epithelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis in mice. J Pathol 190:221–229
Lee YC, Yellowley CE, Li Z, Donahue HJ, Rannels DE (1997) Expression of functional gap junctions in cultured pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol 272:L1105–L1114
Liliensiek BWM, Bierhaus A, Nicklas W, Kasper M, Hofer S, Plachky J, Gröne H-J, Schmidt AM, Shi Du Yan, Martin E, Schleicher E, Stern DM, Hämmerling GJ, Nawroth PP, Arnold B (2004) Receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) regulating sepsis but not the adaptive immune response. J Clin Invest (in press)
Liu J, Lee P, Galbiati F, Kitsis RN, Lisanti MP (2001) Caveolin-1 expression sensitizes fibroblastic and epithelial cells to apoptotic stimulation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280:C823–C835
Liu P, Rudick M, Anderson RG (2002) Multiple functions of caveolin-1. J Biol Chem 277:41295–41298
Matthay MA, Folkesson HG, Clerici C (2002) Lung epithelial fluid transport and the resolution of pulmonary edema. Physiol Rev 82:569–600
Nakanishi K, Maruyama M, Shibata T, Morishima N (2001) Identification of a caspase-9 substrate and detection of its cleavage in programmed cell death during mouse development. J Biol Chem 276:41237–41244
Paine R, Ben-Ze’ev A, Farmer SR, Brody JS (1988) The pattern of cytokeratin synthesis is a marker of type 2 cell differentiation in adult and maturing fetal lung alveolar cells. Dev Biol 129:505–515
Paine R III, Christensen P, Toews GB, Simon RH (1994) Regulation of alveolar epithelial cell ICAM-1 expression by cell shape and cell-cell interactions. Am J Physiol 266:L476–L484
Pan T, Mason RJ, Westcott JY, Shannon JM (2001) Rat alveolar type II cells inhibit lung fibroblast proliferation in vitro. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:353–361
Parton RG (1996) Caveolae and caveolins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:542–548
Ramaekers FC, Haag D, Kant A, Moesker O, Jap PH, Vooijs GP (1983) Coexpression of keratin- and vimentin-type intermediate filaments in human metastatic carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 80:2618–2622
Razani B, Lisanti MP (2001) Caveolin-deficient mice: insights into caveolar function human disease. J Clin Invest 108:1553–1561
Razani B, Engelman JA, Wang XB, Schubert W, Zhang XL, Marks CB, Macaluso F, Russell RG, Li M, Pestell RG, Di Vizio D, Hou H Jr, Kneitz B, Lagaud G, Christ GJ, Edelmann W, Lisanti MP (2001) Caveolin-1 null mice are viable but show evidence of hyperproliferative and vascular abnormalities. J Biol Chem 276:38121–38138
Razani B, Wang XB, Engelman JA, Battista M, Lagaud G, Zhang XL, Kneitz B, Hou H Jr, Christ GJ, Edelmann W, Lisanti MP (2002) Caveolin-2-deficient mice show evidence of severe pulmonary dysfunction without disruption of caveolae. Mol Cell Biol 22:2329–2344
Reid LCM (1979) Cloning. In: Jacoby WBAPIH (ed) Methods in enzymology: cell culture. Academic, San Diego, pp 152–163
Roehlecke C, Kuhnt AK, Fehrenbach H, Werner C, Funk RH, Kasper M (2000) Resistance of L132 lung cell clusters to glyoxal-induced apoptosis. Histochem Cell Biol 114:283–292
Shannon JM, Jennings SD, Nielsen LD (1992) Modulation of alveolar type II cell differentiated function in vitro. Am J Physiol 262:L427–L436
Shirasawa M, Fujiwara N, Hirabayashi S, Ohno H, Iida J, Makita K, Hata Y (2004) Receptor for advanced glycation end-products is a marker of type I lung alveolar cells. Genes Cells 9:165–174
Slack RS, Belliveau DJ, Rosenberg M, Atwal J, Lochmuller H, Aloyz R, Haghighi A, Lach B, Seth P, Cooper E, Miller FD (1996) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the tumor suppressor, p53, induces apoptosis in postmitotic neurons. J Cell Biol 135:1085–1096
Wang R, Ibarra-Sunga O, Verlinski L, Pick R, Uhal BD (2000) Abrogation of bleomycin-induced epithelial apoptosis and lung fibrosis by captopril or by a caspase inhibitor. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 279:L143–L151
Williams MC (2003) Alveolar type I cells: molecular phenotype and development. Annu Rev Physiol 65:669–695
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. M.C. Williams (Boston) for helpful discussion prior to the submission of the manuscript. The authors wish to thank P. Peche, B. Rost, K. Pehlke, S. Bramke and D. Streichert for their excellent technical assistance and E. Kuhlisch, Institute of Medical Informatics and Biometrics, for performing the statistical analysis. The technical support of T. Schwalm for preparation of figures is acknowledged with gratitude.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Roland Koslowski and Kathrin Barth contributed equally to the study
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koslowski, R., Barth, K., Augstein, A. et al. A new rat type I-like alveolar epithelial cell line R3/1: bleomycin effects on caveolin expression. Histochem Cell Biol 121, 509–519 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0662-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-004-0662-4