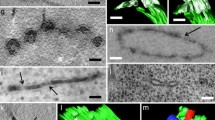
Abstract
Cargo selection and export from the endoplasmic reticulum occurs at specialized sites in cells. Export complexes consist of transitional elements of the endoplasmic reticulum and pre-Golgi intermediates. It is generally assumed that 60 to 80 nm initially COPII-coated vesicles derived from the transitional endoplasmic reticulum are the main carriers for transport of cargo to the Golgi apparatus. We have analyzed on serial ultrathin sections the transitional endoplasmic reticulum and pre-Golgi intermediates of beta cells of islets of Langerhans in mouse pancreas. In addition to Golgi-associated complexes, others were observed in the periphery of the cells or close to the nuclear envelope. Upon three-dimensional reconstruction, non-coated ribosome-free tubules with an average diameter of 115 nm (range 60–195 nm) and a length of up to 500 nm were detected in the pre-Golgi intermediates in addition to small vesiculo-tubular elements. Furthermore, evidence was found that the large tubular elements may directly arise from transitional elements of the endoplasmic reticulum. In a given cell, pre-Golgi intermediates were found to be composed solely of small vesiculo-tubular elements or additionally of tubules or solely of tubules. Immunogold labeling for proinsulin indicated that the large tubular elements contained cargo and thus appear to take part in ER-to-Golgi transport.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antonny B, Schekman R (2001) ER export: public transportation by the COPII coach. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:438–443
Aridor M, Fish KN, Bannykh S, Weissman J, Roberts TH, Lippincott-Schwartz J, Balch WE (2001) The Sar1 GTPase coordinates biosynthetic cargo selection with endoplasmic reticulum export site assembly. J Cell Biol 152:213–229
Bannykh SI, Balch WE (1997) Membrane dynamics at the endoplasmic reticulum Golgi interface. J Cell Biol 138:1–4
Bannykh SI, Rowe T, Balch WE (1996) The organization of endoplasmic reticulum export complexes. J Cell Biol 135:19–35
Bednarek SY, Ravazzola M, Hosobuchi M, Amherdt M, Perrelet A, Schekman R, Orci L (1995) COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles bud directly from the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. Cell 83:1183–1196
Belden WJ, Barlowe C (1996) Erv25p, a component of COPII-coated vesicles, forms a complex with emp24p that is required for efficient endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi transport. J Biol Chem 271:26939–26946
Blum R, Feick P, Puype M, Vandekerckhove J, Klengel R, Nastainczyk W, Schulz I (1996) Tmp21 and p24A, two type I proteins enriched in pancreatic microsomal membranes, are members of a protein family involved in vesicular trafficking. J Biol Chem 271:17183–17189
Bonfanti L, Mironov AA, Martinez-Menarguez JA, Martella O, Fusella A, Baldassarre M, Buccione R, Geuze HJ, Mironov AA, Luini A (1998) Procollagen traverses the Golgi stack without leaving the lumen of cisternae: evidence for cisternal maturation. Cell 95:993–1003
Fiedler K, Rothman JE (1997) Sorting determinants in the transmembrane domain of p24 proteins. J Biol Chem 272:24739–24742
Fiedler K, Veit M, Stamnes MA, Rothman JE (1996) Bimodal interaction of coatomer with the p24 family of putative cargo receptors. Science 273:1396–1399
Hammond AT, Glick BS (2000) Dynamics of transitional endoplasmic reticulum sites in vertebrate cells. Mol Biol Cell 11:3013–3030
Hauri HP, Kappeler F, Andersson H, Appenzeller C (2000) ERGIC-53 and traffic in the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 113:587–596
Horstmann H, Ng CP, Tang BL, Hong WJ (2002) Ultrastructural characterization of endoplasmic reticulum–Golgi transport containers (EGTC). J Cell Sci 115:4263–4273
Kaiser C, Ferro-Novick S (1998) Transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10:477–482
Klumperman J (2000) Transport between ER and Golgi. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:445–449
Kuehn MJ, Schekman R (1997) COPII and secretory cargo capture into transport vesicles. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9:477–483
Ladinsky MS, Mastronarde DN, McIntosh JR, Howell KE, Staehelin LA (1999) Golgi structure in three dimensions: functional insights from the normal rat kidney cell. J Cell Biol 144:1135–1149
Lahtinen U, Dahllof B, Saraste J (1992) Characterization of a 58-kDa cis-Golgi protein in pancreatic exocrine cells. J Cell Sci 103:321–333
Lippincott-Schwartz J (2001) The secretory membrane system studied in real-time. Histochem Cell Biol 116:97–107
Lippincott-Schwartz J, Roberts TH, Hirschberg K (2000) Secretory protein trafficking and organelle dynamics in living cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 16:557–589
Muniz M, Nuoffer C, Hauri HP, Riezman H (2000) The Emp24 complex recruits a specific cargo molecule into endoplasmic reticulum-derived vesicles. J Cell Biol 148:925–930
Orci L, Ravazzola M, Amherdt M, Madsen O, Vassalli JD, Perrelet A (1985) Direct identification of prohormone conversion site in insulin-secreting cells. Cell 42:671–681
Orci L, Ravazzola M, Storch M-J, Anderson RGW, Vassalli J-D, Perrelet A (1987) Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles. Cell 49:865–868
Palade G (1975) Intracellular aspects of the process of protein biosynthesis. Science 189:347–358
Palokangas H, Ying M, Vaananen K, Saraste J (1998) Retrograde transport from the pre-Golgi intermediate compartment and the Golgi complex is affected by the vacuolar H+-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1. Mol Biol Cell 9:3561–3578
Presley J, Cole N, Schroer T, Hirschberg K, Zaal K, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1997) ER-to-Golgi transport visualized in living cells. Nature 389:81–85
Roth J, Kasper M, Heitz PU, Labat F (1985) What’s new in light and electron microscopic immunocytochemistry? Application of the protein A-gold technique to routinely processed tissue. Pathol Res Pract 180:711–717
Roth J, Ziak M, Guhl B (2000) Non-heating antigen retrieval techniques for light and electron microscopic immunolabeling. In: Taylor CR, Shi S-R (eds) Antigen retrieval technique: a revolutionary approach to routine immunohistochemistry. Eaton, Natick, MA, pp 275–285
Saraste J, Kuismanen E (1984) Pre- and post-Golgi vacuoles operate in the transport of Semliki Forest virus membrane glycoproteins to the cell surface. Cell 38:535–549
Saraste J, Kuismanen E (1992) Pathways of protein sorting and membrane traffic between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. Semin Cell Biol 3:343–355
Saraste J, Svensson K (1991) Distribution of intermediate elements operating in ER to Golgi transport. J Cell Sci 100:415–430
Scales SJ, Pepperkok R, Kreis TE (1997) Visualization of ER-to-Golgi transport in living cells reveals a sequential mode of action for COPII and COPI. Cell 90:1137–1148
Sesso A, Defaria FP, Iwamura ESM, Correa H (1994) A 3-dimensional reconstruction study of the rough ER-Golgi interface in serial thin sections of the pancreatic acinar cell of the rat. J Cell Sci 107:517–528
Stephens DJ, LinMarq N, Pagano A, Pepperkok R, Paccaud JP (2000) COPI-coated ER-to-Golgi transport complexes segregate from COPII in close proximity to ER exit sites. J Cell Sci 113:2177–2185
Stinchcombe J, Nomoto H, Cutler D, Hopkins C (1995) Anterograde and retrograde traffic between the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol 131:1387–1401
Ying M, Flatmark T, Saraste J (2000) The p58-positive pre-Golgi intermediates consist of distinct subpopulations of particles that show differential binding of COPI and COPII coats and contain vacuolar H+-ATPase. J Cell Sci 113:3623–3638
Zuber C, Fan JY, Guhl B, Parodi A, Fessler JH, Parker C, Roth J (2001) Immunolocalization of UDP-glucose: glycoprotein glucosyltransferase indicates involvement of pre-Golgi intermediates in protein quality control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10710–10715
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Bruno Guhl for skilled technical assistance, N. Wey for help in preparing the photographs, and Antoinette Schumacher for help in preparing the manuscript. This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation and the Canton of Zurich.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Presented at the 43rd Symposium of the Society for Histochemistry, Vienna, Austria, 27–29 September 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, JY., Roth, J. & Zuber, C. Ultrastructural analysis of transitional endoplasmic reticulum and pre-Golgi intermediates: a highway for cars and trucks. Histochem Cell Biol 120, 455–463 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0597-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0597-1