Abstract
Purpose
This paper aimed to determine the involvement of Na+/H+ exchanger regulatory factor 1 (NHERF1) in experimental murine corneal neovascularization (NV), and to study the effect of NHERF1 on the biological properties of HUVEC and related mechanisms.
Methods
Using loss- and gain-function, we investigated the biological effects of NHERF1 on HUVEC. Western blotting was used to detect the expression of NHERF1 in cells. A carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) labeling assay and scarification test were used to measure the proliferation and migration activity, respectively, of HUVEC. The cell cycle distribution of the cells was assessed by flow cytometry analysis. The effect of NHERF1 on the phosphorylation levels of Akt and the changes of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 and MMP-9 levels were detected by western blotting analysis. Change in the NHERF1 expression in the alkali burn-induced corneal NV model was detected by microarray, real-time PCR, and immunofluorescence.
Results
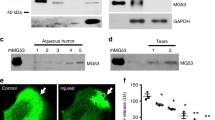
Overexpression of exogenous NHERF1 in HUVEC slightly inhibited the proliferation and significantly reduced the migration of the cells. NHERF1 also significantly downregulated Akt1 phosphorylation induced by platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGF-BB) and the secretion of MMP-2 and MMP-9 compared with control cells. NHERF1 was upregulated in corneas challenged with alkali burns.
Conclusions
Our results indicated that NHERF1 might serve as a potential target for manipulating neovascularization-related diseases. This discovery contributes to a better understanding of the bioactivity of NHERF1 in angiogenesis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Usui T, Sugisaki K, Iriyama A, Yokoo S, Yamagami S, Nagai N, Ishida S, Amano S (2008) Inhibition of corneal neovascularization by blocking the angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:4370–4376
Mochimaru H, Usui T, Yaguchi T, Nagahama Y, Hasegawa G, Usui Y, Shimmura S, Tsubota K, Amano S, Kawakami Y, Ishida S (2008) Suppression of alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization by dendritic cell vaccination targeting VEGF receptor 2. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:2172–2177
Lai LJ, Xiao X, Wu JH (2007) Inhibition of corneal neovascularization with endostatin delivered by adeno-associated viral (AAV) vector in a mouse corneal injury model. J Biomed Sci 14:313–322
Dai JL, Wang L, Sahin AA, Broemeling LD, Schutte M, Pan Y (2004) NHERF (Na+/H + exchanger regulatory factor) gene mutations in human breast cancer. Oncogene 23:8681–8687
Cardone RA, Bellizzi A, Busco G, Weinman EJ, Dell'Aquila ME, Casavola V, Azzariti A, Mangia A, Paradiso A, Reshkin SJ (2007) The NHERF1 PDZ2 domain regulates PKA-RhoA-p38-mediated NHE1 activation and invasion in breast tumor cells. Mol Biol Cell 18:1768–1780
Burgering BM, Coffer PJ (1995) Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 376:599–602
Welsh GI, Wilson C, Proud CG (1996) GSK3: a SHAGGY frog story. Trends Cell Biol 6:274–279
Simoncini T, Scorticati C, Mannella P, Fadiel A, Giretti MS, Fu XD, Baldacci C, Garibaldi S, Caruso A, Fornari L, Naftolin F, Genazzani AR (2006) Estrogen receptor alpha interacts with Galpha13 to drive actin remodeling and endothelial cell migration via the RhoA/Rho kinase/moesin pathway. Mol Endocrinol 20:1756–1771
Takahashi Y, Morales FC, Kreimann EL, Georgescu MM (2006) PTEN tumor suppressor associates with NHERF proteins to attenuate PDGF receptor signaling. EMBO J 25:910–920
Reczek D, Berryman M, Bretscher A (1997) Identification of EBP50: a PDZ-containing phosphoprotein that associates with members of the ezrin-radixin-moesin family. J Cell Biol 139:169–179
Weinman EJ, Steplock D, Tate K, Hall RA, Spurney RF, Shenolikar S (1998) Structure-function of recombinant Na/H exchanger regulatory factor (NHE-RF). J Clin Invest 101:2199–2206
Ladias JA (2003) Structural insights into the CFTR-NHERF interaction. J Membr Biol 192:79–88
Cao TT, Deacon HW, Reczek D, Bretscher A, von Zastrow M (1999) A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the beta2-adrenergic receptor. Nature 401:286–290
Maudsley S, Zamah AM, Rahman N, Blitzer JT, Luttrell LM, Lefkowitz RJ, Hall RA (2000) Platelet-derived growth factor receptor association with Na(+)/H(+) exchanger regulatory factor potentiates receptor activity. Mol Cell Biol 20:8352–8363
Suh PG, Hwang JI, Ryu SH, Donowitz M, Kim JH (2001) The roles of PDZ-containing proteins in PLC-beta-mediated signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 288:1–7
James MF, Beauchamp RL, Manchanda N, Kazlauskas A, Ramesh V (2004) A NHERF binding site links the betaPDGFR to the cytoskeleton and regulates cell spreading and migration. J Cell Sci 117:2951–2961
Demoulin JB, Seo JK, Ekman S, Grapengiesser E, Hellman U, Ronnstrand L, Heldin CH (2003) Ligand-induced recruitment of Na+/H + -exchanger regulatory factor to the PDGF (platelet-derived growth factor) receptor regulates actin cytoskeleton reorganization by PDGF. Biochem J 376:505–510
Georgescu MM, Morales FC, Molina JR, Hayashi Y (2008) Roles of NHERF1/EBP50 in cancer. Curr Mol Med 8:459–468
Song GJ, Barrick S, Leslie KL, Sicari B, Fiaschi-Taesch NM, Bisello (2010) A EBP50 inhibits the anti-mitogenic action of the parathyroid hormone type 1 receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 49:1012–1021
Ediger TR, Kraus WL, Weinman EJ, Katzenellenbogen BS (1999) Estrogen receptor regulation of the Na+/H + exchange regulatory factor. Endocrinology 140:2976–2982
Baeyens N, Horman S, Vertommen D, Rider M, Morel N (2010) Identification and functional implication of a Rho kinase-dependent moesin-EBP50 interaction in noradrenaline-stimulated artery. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299:C1530–1540
Chen J, Somanath PR, Razorenova O, Chen WS, Hay N, Bornstein P, Byzova TV (2005) Akt1 regulates pathological angiogenesis, vascular maturation and permeability in vivo. Nat Med 11:1188–1196
Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe’er J, Stone J, Keshet E (1995) Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med 1:1024–1028
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, Yan M, Keyt BA, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase/Akt signal transduction pathway. Requirement for Flk-1/KDR activation. J Biol Chem 273:30336–30343
Fujio Y, Walsh K (1999) Akt mediates cytoprotection of endothelial cells by vascular endothelial growth factor in an anchorage-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 274:16349–16354
Shiojima I, Walsh K (2002) Role of Akt signaling in vascular homeostasis and angiogenesis. Circ Res 90:1243–1250
Morales-Ruiz M, Fulton D, Sowa G, Languino LR, Fujio Y, Walsh K, Sessa WC (2000) Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated actin reorganization and migration of endothelial cells is regulated via the serine/threonine kinase Akt. Circ Res 86:892–896
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ, Hemmings BA (2004) Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts. Trends Biochem Sci 29:233–242
Raffetto JD, Khalil RA (2008) Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in vascular remodeling and vascular disease. Biochem Pharmacol 75:346–359
Rundhaug JE (2005) Matrix metalloproteinases and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med 9:267–285
Fingleton B (2006) Matrix metalloproteinases: roles in cancer and metastasis. Front Biosci 11:479–491
Opdenakker G, Van den Steen PE, Van Damme J (2001) Gelatinase B: a tuner and amplifier of immune functions. Trends Immunol 22:571–579
Ma DH, Chen JK, Kim WS, Hao YX, Wu HC, Tsai RJ, Hwang DG, Zhang F (2001) Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1 and 2 in inflammation-induced corneal neovascularization. Ophthalmic Res 33:353–362
Samolov B, Steen B, Seregard S, van der Ploeg I, Montan P, Kvanta A (2005) Delayed inflammation-associated corneal neovascularization in MMP-2-deficient mice. Exp Eye Res 80:159–166
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the State Key Basic Research Project (2007CB516705) and Shandong Sci-Tec Foundation (2006GG1102020). Yiqiang Wang is partially supported by the Taishan Scholar Program (QDU-EYE) of China.
Financial support
There is no financial relationship with the organization that sponsored the research. The authors have full control of all primary data and we agree to allow Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology to review our data upon request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Wang, Y., Yang, L. et al. Novel bioactivity of NHERF1 in corneal neovascularization. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250, 1615–1625 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-2094-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-012-2094-5