Abstract
Background
The aim of this work is to assess the repeatability of spectral-domain-OCT (SD-OCT) retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFL) thickness measurements in a non-glaucoma group and patients with glaucoma and to compare these results to conventional time-domain-OCT (TD-OCT).
Methods
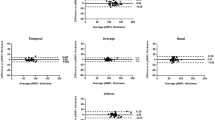
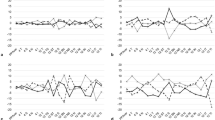
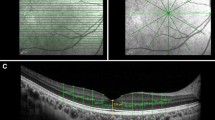
In a prospective, comparative, observational case-control study, 50 eyes of 25 non-glaucoma and 22 eyes of 11 patients with primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) were included. SD-OCT and TD-OCT circle scans were centered on the optic disc. In each eye, OCT scans were performed three times by two independent observers. RNFL thickness was measured in four quadrants around the optic disc. In addition, the overall mean RNFL thickness was assessed. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and coefficients of variation (COV) were calculated. Inter-observer and inter-OCT repeatability was visualized by using Bland–Altman analysis.
Results
Intra-observer repeatability for TD- OCT was good with an ICCmean RNFL thickness of 0.939 in non-glaucomas and 0.980 in glaucomatous eyes. For SD-OCT, intra-observer repeatability was higher with an ICC of 0.989 for non-glaucomas and 0.997 for glaucomatous eyes. COVs for TD-OCT ranged from 2.9–7.7% in non-glaucomas and from 6.0–13.3% in glaucoma patients. COVs for SD-OCT ranged from 0.3–1% in non-glaucomas and from 0.9–2.3% in glaucomatous eyes. COVs were influenced by various factors. In the glaucoma group, COVs were significantly higher (p < 0.001) compared to the non-glaucoma group. COVs increased by a mean of 5.1% when TD-OCT was used instead of SD-OCT (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
SD-OCT RNFL thickness measurements in healthy volunteers and glaucoma patients showed good intra- and inter-observer repeatability. Especially in glaucomatous eyes, repeatability of SD-OCT was superior to TD-OCT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen TC, Zeng A, Sun W, Mujat M, de Boer JF (2008) Spectral domain optical coherence tomography and glaucoma. Int Ophthalmol Clin 48:29–45
Cho JW, Sung KR, Hong JT, Um TW, Kang SY, Kook MS (2011)Detection of glaucoma by spectral domain-scanning laser ophthalmoscopy/optical coherence tomography (SD-SLO/OCT) and time domain optical coherence tomography. J Glaucoma 20:15–20
Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, Qiu K, Liu S, Li H, Xu G, Fan N, Pang CP, Tse KK, Lam DS (2010) Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer progression in glaucoma: a study on optical coherence tomography guided progression analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:217–222
Park SB, Sung KR, Kang SY, Kim KR, Kook MS (2009) Comparison of glaucoma diagnostic capabilities of cirrus HD and stratus optical coherence tomography. Arch Ophthalmol 127:1603–1609
Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Weinreb RN (2000) Evaluating the optic disc and retinal nerve fiber layer in glaucoma. II: optical image analysis. Semin Ophthalmol 15:206–220
Schuman JS, Hee MR, Arya AV, Pedut-Kloizman T, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG, Swanson EA (1995) Optical coherence tomography: a new tool for glaucoma diagnosis. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 6:89–95
Blumenthal EZ, Williams JM, Weinreb RN, Girkin CA, Berry CC, Zangwill LM (2000) Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements by use of optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 107:2278–2282
Bourne RR, Medeiros FA, Bowd C, Jahanbakhsh K, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN (2005) Comparability of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurements of optical coherence tomography instruments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:1280–1285
Budenz DL, Chang RT, Huang X, Knighton RW, Tielsch JM (2005) Reproducibility of retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements using the stratus OCT in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:2440–2443
Budenz DL, Fredette MJ, Feuer WJ, Anderson DR (2008) Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber thickness measurements with stratus OCT in glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmology 115(661–666):e664
Carpineto P, Ciancaglini M, Zuppardi E, Falconio G, Doronzo E, Mastropasqua L (2003) Reliability of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography in normal and glaucomatous eyes. Ophthalmology 110:190–195
Krist R, Hoffmann EM, Schwenn O (2005) Reproducibility of measurements of the peripapillary retinal nerve fibre layer thickness. Optical coherence tomography versus retinal thickness analyzer. Ophthalmologe 102(1175–1178):1180
Paunescu LA, Schuman JS, Price LL, Stark PC, Beaton S, Ishikawa H, Wollstein G, Fujimoto JG (2004) Reproducibility of nerve fiber thickness, macular thickness, and optic nerve head measurements using StratusOCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1716–1724
Choma M, Sarunic M, Yang C, Izatt J (2003) Sensitivity advantage of swept source and Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Express 11:2183–2189
Wojtkowski M, Srinivasan V, Fujimoto JG, Ko T, Schuman JS, Kowalczyk A, Duker JS (2005) Three-dimensional retinal imaging with high-speed ultrahigh-resolution optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 112:1734–1746
Wojtkowski M, Srinivasan V, Ko T, et al (2005) High-speed, ultrahigh resolution retinal imaging using spectral/Fourier domain OCTConf Lasers Electrooptics, pp. 2058–2060
Wojtkowski M, Srinivasan V, Ko T, Fujimoto J, Kowalczyk A, Duker J (2004) Ultrahigh-resolution, high-speed, Fourier domain optical coherence tomography and methods for dispersion compensation. Opt Express 12:2404–2422
Bendschneider D, Tornow RP, Horn FK, Laemmer R, Roessler CW, Juenemann AG, Kruse FE, Mardin CY (2010) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in normals measured by spectral domain OCT. J Glaucoma 19:475–482
Gabriele ML, Ishikawa H, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Kagemann L, Wojtkowski M, Srinivasan VJ, Fujimoto JG, Duker JS, Schuman JS (2007) Peripapillary nerve fiber layer thickness profile determined with high speed, ultrahigh resolution optical coherence tomography high-density scanning. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:3154–3160
Hong S, Kim CY, Lee WS, Seong GJ (2010) Reproducibility of peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer thickness with spectral domain cirrus high-definition optical coherence tomography in normal eyes. Jpn J Ophthalmol 54:43–47
Menke MN, Knecht P, Sturm V, Dabov S, Funk J (2008) Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using 3D Fourier-domain OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:5386–5391
Rabe-Hesketh S, Skrondal A (2008) Estimation using xtmixed in Multilevel and Longitudinal Modeling Using STATA, pp. 433–436
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Bland JM, Altman DG (1999) Measuring agreement in method comparison studies. Stat Methods Med Res 8:135–160
Gonzalez-Garcia AO, Vizzeri G, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN (2009) Reproducibility of RTVue retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disc measurements and agreement with Stratus optical coherence tomography measurements. Am J Ophthalmol 147:1067–1074, 1074 e1061
Johnson DE, El-Defrawy SR, Almeida DR, Campbell RJ (2009) Comparison of retinal nerve fibre layer measurements from time domain and spectral domain optical coherence tomography systems. Can J Ophthalmol 44:562–566
Kim JS, Ishikawa H, Sung KR, Xu J, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Gabriele ML, Kagemann L, Duker JS, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS (2009) Retinal nerve fibre layer thickness measurement reproducibility improved with spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Br J Ophthalmol 93:1057–1063
Knight OJ, Chang RT, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL (2009) Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer measurements using time domain and spectral domain optical coherent tomography. Ophthalmology 116:1271–1277
Sung KR, Kim DY, Park SB, Kook MS (2009) Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by Cirrus HD and Stratus optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 116:1264–1270, 1270 e1261
Vizzeri G, Weinreb RN, Gonzalez-Garcia AO, Bowd C, Medeiros FA, Sample PA, Zangwill LM (2009) Agreement between spectral-domain and time-domain OCT for measuring RNFL thickness. Br J Ophthalmol 93:775–781
Leite MT, Zangwill LM, Weinreb RN, Rao HL, Alencar LM, Sample PA, Medeiros FA (2010) Effect of disease severity on the performance of Cirrus spectral-domain OCT for glaucoma diagnosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:4104–4109
Jones AL, Sheen NJ, North RV, Morgan JE (2001) The Humphrey optical coherence tomography scanner: quantitative analysis and reproducibility study of the normal human retinal nerve fibre layer. Br J Ophthalmol 85:673–677
Schuman JS, Pedut-Kloizman T, Hertzmark E, Hee MR, Wilkins JR, Coker JG, Puliafito CA, Fujimoto JG, Swanson EA (1996) Reproducibility of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements using optical coherence tomography. Ophthalmology 103:1889–1898
Chang RT, Knight OJ, Feuer WJ, Budenz DL (2009) Sensitivity and specificity of time-domain versus spectral-domain optical coherence tomography in diagnosing early to moderate glaucoma. Ophthalmology 116:2294–2299
Kim JS, Ishikawa H, Gabriele ML, Wollstein G, Bilonick RA, Kagemann L, Fujimoto JG, Schuman JS (2010) Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measurement comparability between time domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) and spectral domain OCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:896–902
Leung CK, Cheung CY, Weinreb RN, Qiu Q, Liu S, Li H, Xu G, Fan N, Huang L, Pang CP, Lam DS (2009) Retinal nerve fiber layer imaging with spectral-domain optical coherence tomography: a variability and diagnostic performance study. Ophthalmology 116:1257–1263, 1263 e1251–1252
Schuman JS (2008) Spectral domain optical coherence tomography for glaucoma (an AOS thesis). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 106:426–458
Knighton RW, Qian C (2000) An optical model of the human retinal nerve fiber layer: implications of directional reflectance for variability of clinical measurements. J Glaucoma 9:56–62
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any financial interest in any product described in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The study is registered in the registrar of the U.S. National Institute of Health (http://www.clinicaltrials.gov, NCT 01273285).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Töteberg-Harms, M., Sturm, V., Knecht, P.B. et al. Repeatability of nerve fiber layer thickness measurements in patients with glaucoma and without glaucoma using spectral-domain and time-domain OCT. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 250, 279–287 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1811-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-011-1811-9