Abstract
Purpose
To describe the clinical characteristics of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV) in a large number of Chinese patients.
Methods
This study enrolled 204 consecutive patients (246 eyes) in our department who were diagnosed as having polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy PCV. Patients underwent ophthalmologic examinations including best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) testing, ophthalmoscopy, fundus photography, fluorescein angiography, indocyanine green angiography, and optic coherence tomography.
Results
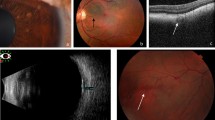
Mean patient age was 66.1 years and 60.3% were men. Of the cases, 79.4% were unilateral and 51.2% of BCVA was less than 35 letters. In 171 eyes (69.5%), polypoidal lesions were located in the macula area. Among them, polypoidal lesions were located in the foveal area in 29 eyes (11.8%), in the parafoveal area in 50 eyes (20.3%), and in the extrafoveal area in 88 eyes (35.8%), in both the foveal and parafoveal area in three eyes (1.2%), and in both the parafoveal and extrafoveal area in one eye (0.4%). In 37 eyes (15.0%), PCV lesions were under the temporal retinal vascular arcade; in 11 eyes (4.5%), PCV lesions were found peripapillary. PCV lesion formation was single in 88 eyes (35.8%), cluster in 145 eyes (59.0%), string in two eyes (0.8%), and branch in two eyes (0.8%). In nine eyes (3.6%), the formation of PCV lesions showed both single and cluster shape in the same eye. There were 54.5% with drusen, 44.7% with serous PED, 20.7% with hemorrhagic PED, and 39.0% with neuroretinal detachment.
Conclusions
The majority of Chinese PCV patients were male, unilateral, and showed macular polyps. Drusen, serous PED, hemorrhagic PED, and neuroretinal detachment on OCT were commonly seen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yannuzzi LA, Sorenson J, Spaide RF, Lipson B (1990) Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (IPCV). Retina 10:1–8
Yannuzzi LA, Ciardella A, Spaide RF, Rabb M, Freund KB, Orlach DA (1997) The expanding clinical spectrum of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Archives of Ophthalmology 115:478–485
Laude A, Cackett PD, Vithana EN, Yeo IY, Wong D, Koh AH, Wong TY, Aung T (2010) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and neovascular age-related macular degeneration: same or different disease? Progress in Retinal and Eye Research 29:19–29
Ciardella AP, Donsoff IM, Huang SJ, Costa DL, Yannuzzi LA (2004) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Survey of Ophthalmology 49:25–37
Guyer DR, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Sorenson JA, Hanutsaha P, Spaide RF, Schwartz SG, Hirschfeld JM, Orlock DA (1996) Classification of choroidal neovascularization by digital indocyanine green videoangiography. Ophthalmology 103:2054–2060
Spaide RF, Yannuzzi LA, Slakter JS, Sorenson J, Orlach DA (1995) Indocyanine green videoangiography of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Retina 15:100–110
Stanga PE, Lim JI, Hamilton P (2003) Indocyanine green angiography in chorioretinal diseases: indications and interpretation: an evidence-based update. Ophthalmology 110(15–21):22–13
Kwok AK, Lai TY, Chan CW, Neoh EL, Lam DS (2002) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Chinese patients. The British Journal of Ophthalmology 86:892–897
Wen F, Chen C, Wu D, Li H (2004) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in elderly Chinese patients. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fűr Klinische und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie 242:625–629
Yamaoka S, Okada AA, Sugahara M, Hida T (2009) Clinical features of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy and visual outcomes in the absence of classic choroidal neovascularization. Ophthalmologica Journal International d’Ophtalmologie (International Journal of Ophthalmology) 224:147–152
Uyama M, Matsubara T, Fukushima I, Matsunaga H, Iwashita K, Nagai Y, Takahashi K (1999) Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Japanese patients. Archives of Ophthalmology 117:1035–1042
Scassellati-Sforzolini B, Mariotti C, Bryan R, Yannuzzi LA, Giuliani M, Giovannini A (2001) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Italy. Retina 21:121–125
Lafaut BA, Leys AM, Snyers B, Rasquin F, De Laey JJ (2000) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Caucasians. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fűr Klinische und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie) 238:752–759
Hwang DK, Yang CS, Lee FL, Hsu WM (2007) Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. J Chin Med Assoc 70:84–88
Liu Y, Wen F, Huang S, Luo G, Yan H, Sun Z, Wu D (2007) Subtype lesions of neovascular age-related macular degeneration in Chinese patients. Graefe’s Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology (Albrecht von Graefes Archiv fűr Klinische und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie) 245:1441–1445
Yi C, Ou J, Yian H, Mai G, Yu Q (2001) A case report of idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Yan ke xue bao = Eye science / “Yan ke xue bao” bian ji bu 17: 126–129
(2005) Criteria for diagnosis of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Nippon Ganka Gakkai zasshi 109:417–427
Maruko I, Iida T, Saito M, Nagayama D, Saito K (2007) Clinical characteristics of exudative age-related macular degeneration in Japanese patients. American Journal of Ophthalmology 144:15–22
Yeung L, Chen SN (2004) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Taiwan. Chang Gung Medical Journal 27:366–372
Ahuja RM, Stanga PE, Vingerling JR, Reck AC, Bird AC (2000) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in exudative and haemorrhagic pigment epithelial detachments. The British Journal of Ophthalmology 84:479–484
Squirrell DM, Bacon JF, Brand CS (2009) To investigate the prevalence of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in presumed age-related peripapillary subretinal neovascular membranes. Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology 37:368–372
Moorthy RS, Lyon AT, Rabb MF, Spaide RF, Yannuzzi LA, Jampol LM (1998) Idiopathic polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy of the macula. Ophthalmology 105:1380–1385
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (No:2005CB724307), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No:30901639), the Beijing Novel Program (No:2009B04), Special Funds for Central Health research projects (No.B2009B041; China:MWZ) and the Epidemiological Survey and Consultation Network Construction of Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy in the Beijing Region.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jing Hou and Yong Tao contributed equally to the work.
Proprietary interest: None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, J., Tao, Y., Li, Xx. et al. Clinical characteristics of polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy in Chinese patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 249, 975–979 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-010-1575-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-010-1575-7