Abstract
Background
To evaluate the haemodynamic features of young healthy myopes and emmetropes, in order to ascertain the perfusion profile of human myopia and its relationship with axial length prior to reaching a degenerative state.
Methods
The retrobulbar, microretinal and pulsatile ocular blood flow (POBF) of one eye of each of twenty-two high myopes (N = 22, mean spherical equivalent (MSE) ≤−5.00D), low myopes (N = 22, MSE−1.00 to−4.50D) and emmetropes (N = 22, MSE ± 0.50D) was analyzed using color Doppler Imaging, Heidelberg retinal flowmetry and ocular blood flow analyser (OBF) respectively. Intraocular pressure, axial length (AL), systemic blood pressure, and body mass index were measured.
Results
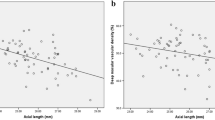
When compared to the emmetropes and low myopes, the AL was greater in high myopia (p < 0.0001). High myopes showed higher central retinal artery resistance index (CRA RI) (p = 0.004), higher peak systolic to end diastolic velocities ratio (CRA ratio) and lower end diastolic velocity (CRA EDv) compared to low myopes (p = 0.014, p = 0.037). Compared to emmetropes, high myopes showed lower OBFamplitude (OBFa) (p = 0.016). The POBF correlated significantly with the systolic and diastolic blood velocities of the CRA (p = 0.016, p = 0.036). MSE and AL correlated negatively with OBFa (p = 0.03, p = 0.003), OBF volume (p = 0.02, p < 0.001), POBF (p = 0.01, p < 0.001) and positively with CRA RI (p = 0.007, p = 0.05).
Conclusion
High myopes exhibited significantly reduced pulse amplitude and CRA blood velocity, the first of which may be due to an OBF measurement artefact or real decreased ocular blood flow pulsatility. Axial length and refractive error correlated moderately with the ocular pulse and with the resistance index of the CRA, which in turn correlated amongst themselves. It is hypothesized that the compromised pulsatile and CRA haemodynamics observed in young healthy myopes is an early feature of the decrease in ocular blood flow reported in pathological myopia. Such vascular features would increase the susceptibility for vascular and age-related eye diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fitzgerald M, Wildsoet C, Anton R (2001) Temporal relationship of choroidal blood flow and thickness changes during recovery from form deprivation myopia in chicks. Exp Eye Res 74:561–570
Troilo D, Nickla DL, Wildsoet CF (2000) Choroidal thickness changes during altered eye growth and refractive state in a primate. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:1249–1258
Shih Y-F, Fitzgerald MEC, Norton TT, Gamlin PDR, Hodos W, Reiner A (1993) Reduction in choroidal blood flow occurs in chicks wearing goggles that induce eye growth toward myopia. Curr Eye Res 3:219–227
Hirata A, Negi A (1998) Lacquer crack lesions in experimental chick myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 236:138–145
Hirata A, Negi A (1998) Morphological changes of choriocapillaris in experimentally induced chick myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 236:132–137
Dimitrova G, Tamaki Y, Kato S, Nagahara M (2002) Retrobulbar circulation in myopic patients with or without myopic choroidal neovascularisation. Br J Ophthalmol 86:771–773
Akyol N, Kukner A, Ozdemir T, Esmerligil S (1996) Choroidal and retinal blood flow changes in degenerative myopia. Can J Ophthalmol 31:113–119
Ravalico G, Pastori G, Croce M, Toffoli G (1997) Pulsatile ocular blood flow variations with axial length and refractive error. Ophthalmologica 211:271–273
Tano Y (2002) Pathologic myopia: where are we now? Am J Ophthalmol 134:645–660
Schumann J, Orgül S, Gugleta K, Dubler B, Flammer J (2000) Interocular difference in progression of glaucoma correlates with interocular differences in retrobulbar circulation. Am J Ophthalmol 129:728–733
Kaiser HJ, Schötzau A, Stümpfig D, Flammer J (1997) Blood-flow velocities of the extraocular vessels in patients with high-tension and normal-tension primary open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 123:320–327
Lam A, Chan S, Chan B, Chan H (2003) The effect of axial length on ocular blood flow assessment in anisometropes. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 23:315–320
Logan NS, Gilmartin B, Cox W (2002) Ocular Volume and Blood Flow. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:ARVO E-Abstract 199
Harris A, Harris M, Biller J, Garzozi H, Zarfty D, Ciulla TA, Martin B (2000) Aging affects the retrobulbar circulation differently in women and men. Arch Ophthalmol 118:1076–1080
Yang Y, Hulbert M, Batterbury M, Clearkin L (1997) Pulsatile ocular blood flow measurements in healthy eyes: reproducibility and reference values. J Glaucoma 6:175–179
Domino EF, Minoshima S, Guthrie S, Ohl L, Ni L, Koeppe R, Zubieta JK (2000) Nicotine effects on regional cerebral blood flow in awake, resting tobacco smokers. Synapse 38:313–321
Gdovinova Z (2001) Blood flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery in heavy alcohol drinkers. Alcohol Alcohol 36:346–348
Silver D, Geyer O (2000) Pressure-volume relation for the living human eye. Curr Eye Res 20:115–120
Baxter G, Williamson T (1995) Colour Doppler Imaging of the eye: normal ranges, reproducibility and observer variation. J Ultrasound Med 14:91–96
Michelson G, Schmauss B, Langhans M, Harazny J, Groh M (1996) Principle, validity, and reliability of scanning laser Doppler flowmetry. J Glaucoma 5:99–105
Hosking S, Embleton S, Kagemann L, Chabra A, Jonescu-Cuypers C, Harris A (2001) Detector sensitivity influences blood flow sampling in scanning laser Doppler flowmetry. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 239(6):407–410
Hosking S, Embleton S, Cunliffe I (2001) Application of a local search strategy improves the detection of blood flow deficits in the neuroretinal rim of glaucoma patients using scanning laser Doppler flowmetry. Br J Ophthalmol 85:1298–1302
Boothe WA, Lee DA, Panek WC, Pettit TH (1988) The tonopen: a manometric and clinical study. Arch Ophthalmol 106:1214–1247
Logan NS, Davies LN, Mallen EA, Gilmartin B (2005) Ametropia and ocular biometry in a UK university student population. Optom Vis Sci 82:261–266
Saw SM, Chua WH, Gazzard G, Koh D, Tan D, Stone R (2005) Eye growth changes in myopic children in Singapore. Br J Ophthalmol 89:1489–1494
Tong L, Saw SM, Chua WH, Luu C, Cheng B, Yeo I, Wong E, Tan D, Koh A (2004) Optic disk and retinal characteristics in myopic children. Am J Ophthalmol 138:160–162
Zadnik K, Manny RE, Yu JA, Mitchell GL, Cotter SA, Quiralte JC, Shipp M, Friedman NE, Kleinstein RN, Walker TW, Jones LA, Moeschberger ML, Mutti DO (2003) Ocular component data in schoolchildren as a function of age and gender. Collaborative Longitudinal Evaluation of Ethnicity and Refractive Error (CLEERE) Study Group. Optom Vis Sci 80:226–236
Patton N, Maini R, MacGillivary T, Aslam TM, Deary IJ, Dhillon B (2005) Effect of axial length on retinal vascular network geometry. Am J Ophthalmol 140:641–648
Polska E, Kircher K, Ehrlich P, Vecsei P, Schmetterer L (2001) RI in central retinal artery as assessed by CDI does not correspond to retinal vascular resistance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 280:1442–1447
Harris A, Ishii Y, Chung HS, Jonescu-Cuypers CP, McCranor LJ, Kagemann L, Garzozi HJ (2003) Blood flow per unit retinal nerve fibre tissue volume is lower in the human inferior retina. Br J Ophthalmol 87:184–188
Shimada N, Ohno-Matsui K, Harino S, Yoshida T, Yasuzumi K, Kojima A, Kobayashi K, Futagami S, Tokoro K, Mochizuki M (2004) Reduction of retinal blood flow in high myopia. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:284–288
Hosking SL, Harris A, Chung HS, Jonescu-Cuypers CP, Kagemann L, Roff Hilton EJ, Garzozi H (2004) Ocular haemodynamic responses to induced hypercapnia and hyperoxia in glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol 88:406–411
Jonescu-Cuypers CP, Harris A, Bartz-Schmidt KU, Kagemann L, Boros AS, Heimann UE, Lenz BH, Hilgers RD, Krieglstein GK (2004) Reproducibility of circadian retinal and optic nerve head blood flow measurements by Heidelberg retina flowmetry. Br J Ophthalmol 88:348–353
Zion IB, Harris A, Siesky B, Shulman S, McCranor L, Garzozi HJ (2007) Pulsatile ocular blood flow: relationship with flow velocities in vessels supplying the retina and choroid. Br J Ophthalmol 91:882–884
Mitchell P, Hourihan F, Sandbach J, Wang J (1999) The relationship between glaucoma and myopia. The Blue Mountains Eye Study. Ophthalmology 106:2010–2015
Gherghel D, Orgül S, Gugleta K, Gekkieva M, Flammer J (2000) Relationship between ocular perfusion pressure and retrobulbar blood flow in patients with glaucoma with progressive damage. Am J Ophthalmol 130:597–605
Findl O, Rainer G, Dallinger S, Dorner G, Polak K, Kiss B, Georgopoulos M, Vass C, Schmetterer L (2000) Assessment of optic disk blood flow in patients with open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 130:589–596
Ehrlich R, Kheradiya NS, Winston DM, Moore DB, Wirostko B, Harris A (2009) Age-related ocular vascular changes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247:583–591
Gilmartin B (2004) Myopia: precedents for research in the twenty-first century. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 32:305–324
Nemeth J, Knezy K, Tapaszto B, Kovacs R, Harkanyi Z (2002) Different autoregulation response to dynamic exercise in ophthalmic and central retinal arteries: a color Doppler study in healthy subjects. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 240:835–840
Riva C, Hero M, Titze P, Petrig B (1997) Autoregulation of human optic nerve head blood flow in response to acute changes in ocular perfusion pressure. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 235:618–626
Roff E, Harris A, Sung-Chung H, Hosking S, Morrison A, Halter P, Jagemann L (1999) Comprehensive assessment of retinal, choroidal and retrobulbar haemodynamics during blood gas perturbation. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 237:984–990
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Dheeraj Bansal for his invaluable technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No financial relationship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benavente-Pérez, A., Hosking, S.L., Logan, N.S. et al. Ocular blood flow measurements in healthy human myopic eyes. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 248, 1587–1594 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-010-1407-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-010-1407-9