Abstract
Background
Double filling (DF) with perfluorohexyloctane (F6H8) and silicone oil (SIL) has been recently proposed and tested clinically as a means to improve the tamponade properties of single components. This in vitro study investigated (1) the kinetics of the mixing process of F6H8 with SIL (1,000 mPa s) and (2) the contact and emulsification behaviour of DF as compared with pure liquids, with the aim of assessing the tamponade efficiency and its evolution with time.
Methods
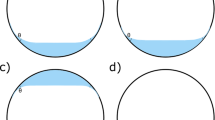
(1) The velocity of the mixing process for F6H8+SIL was estimated by monitoring the position of the interphase in a rectangular cell kept at constant temperature. (2) The surface contact and the tendency to emulsification of DF and of SIL and F6H8 were visually examined by using a Perspex eye model.
Results
(1) The mixing process for F6H8+SIL is slow. In the absence of stirring, equilibrium is reached no earlier than 1 month at 37°C. (2) F6H8 was found to show close contact with the eye model and dispersion into droplets; SIL showed poor contact with the cell surface and no dispersion; DF exhibited poor contact with the superior cell surface and little evidence of dispersion.
Conclusions
F6H8 dissolves slowly in SIL and equilibrium is only reached after 1 month. The final ratio of the DF phases differs from the initial ratio. An initial F6H8/SIL ratio of 70%:30% vol results in 25% vol of pure F6H8 (density, 1.33 g/cm3) and 75% vol of a solution containing F6H8, viz. 60% vol F6H8 in SIL (density 1.17 g/cm3). Because of its density and contact properties, the investigated DF has a tamponade effectiveness better than that of SIL on the inferior retina. Compared with using F6H8 alone, DF reduces emulsification.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Genovesi-Ebert F, Rizzo S, Figus M, Ferretti C, Nardi M (2000) Combination of silicone solvent (F6H8) and PDMS in complex retinal detachment. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41 (Suppl):663
Herbert E, Stappler T, Wetterqvist C, Williams R, Wong D (2003) Tamponade properties of double-filling with perfluorohexyloctane and silicone oil in a model eye chamber. Graefe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 242:250–254
Hoerauf H, Kobuch K, Dresp J, Menz DH (2001) Combined use of partially fluorinated alkanes, perfluorocarbon liquids and silicone oil: an experimental study. Graefe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 239:373–381
Lepori L, Matteoli E, Spanedda A (2004) Liquid–liquid equilibria for mixtures of a partially fluorinated alkane with a polydimethylsiloxane. 18th IUPAC International Conference on Chemical Thermodynamics, August 17–21, Beijing, China, 01-P-17, p 65
Meinert H, Roy T (2000) Semifluorinated alkanes a new class of with outstanding properties for use in ophthalmology. Eur J Ophthalmol 10:189–197
Novak JP, Matous J, Pick J (1986) Liquid liquid equilibria. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Rizzo S, Zenoni S, Genovesi-Ebert F, Belting C, Borgioli M, Zuccarini S (2002) Long-term vitreous replacement with perfluorohexyloctane (F6H8) and silicone oil. Ophthalmol Sci 5–10
Rizzo S, Genovesi-Ebert F, Belting C (2004) The combined use of perfluorohexyloctane (F6H8) and silicone oil as an intraocular tamponade in the treatment of severe retinal detachment. Graefe Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol (in press)
Sparrow JR, Jayakumar A, Berrocal M, Ozmert E, Chang S (1992) Experimental studies of the combined use of vitreous substitutes of high and low specific gravity. Retina 12:134–140
Wetterqvist C, Wong D, Williams R, Stappler T, Herbert E, Freeburn S (2004) Tamponade efficiency of perfluorohexyloctane and silicone oil solutions in a model eye chamber. Br J Ophthalmol 88:692–696
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepori, L., Matteoli, E., Spanedda, A. et al. Combined use of perfluorohexyloctane and silicone oil as intraocular tamponade: an in vitro study. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmo 244, 79–82 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-005-0003-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-005-0003-x