Abstract
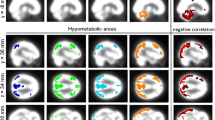
Fluorodopa (FDOPA) and fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET was performed in six patients in early stages of corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and compared to Parkinson’s disease (PD) patients with a similar degree of bradykinesia and rigidity and to healthy controls. Statistical parametric mapping analysis comparing CBD to controls showed metabolic decrease in premotor, primary motor, supplementary motor, primary sensory, prefrontal, and parietal associative cortices, and in caudate and thalamus contralateral to the side of clinical signs. Except for the prefrontal regions a similar metabolic pattern was observed when CBD was compared to PD. Putamen FDOPA uptake was decreased in both CBD and PD. Caudate FDOPA uptake in CBD patients was decreased contralateral to clinical signs when compared to controls, but was higher than in PD. In early stages of CBD, FDOPA and FDG PET patterns differed from those observed in PD. In CBD the asymmetry in FDOPA uptake was less pronounced than that of clinical signs or metabolic impairment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 19 January 1999 Received in revised form: 2 July 1999 Accepted: 14 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Laureys, S., Salmon, E., Garraux, G. et al. Fluorodopa uptake and glucose metabolism in early stages of corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol 246, 1151–1158 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050534
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004150050534