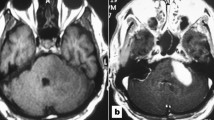
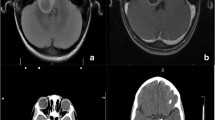
Abstract
Background
Brainstem gliomas are rare in adults. The diagnosis is often difficult, as some teams still consider brainstem biopsies dangerous and often avoid this procedure. The aim of this study was to describe differential diagnoses that can mimic brainstem glioma, to help clinicians avoid diagnostic and therapeutic mistakes, and to propose a diagnostic algorithm according to radiological presentations.
Methods
The French network of adult brainstem gliomas (GLITRAD) retrospectively collected all reported cases of differential diagnoses between 2006 and 2017. The inclusion criteria were as follows: age over 18 years, lesion epicenter in the brainstem, radiological pattern suggestive of a glioma and diagnostic confirmation (histopathological or not, depending on the disease).
Results
We identified a total of 68 cases. Most cases (58/68, 85%) presented as contrast-enhancing lesions. The most frequent final diagnosis in this group was metastases in 24/58 (41%), followed by central nervous system lymphoma in 8/58 (14%). Conversely, MRI findings revealed 10/68 nonenhancing lesions. The most frequent diagnosis in this group was demyelinating disease (3/10, 30%).
Conclusion
The risk of diagnostic mistakes illustrates the need to consider the more systematic use of a brainstem biopsy when reasonably possible. However, we propose an MRI-based approach to the differential diagnosis of gliomas to limit the risk of misdiagnosis in cases where a biopsy is not a reasonable option.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisele S, Reardon D (2016) Adult brainstem gliomas. Cancer 122(18):2799–2809. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29920
Hu J, Western S, Kesari S (2016) Brainstem glioma in adults. Front Oncol 6:180. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2016.00180
Dellaretti M, Touzet G, Reyns N et al (2012) Correlation between magnetic resonance imaging findings and histological diagnosis of intrinsic brainstem lesions in adults. Neuro Oncol. 3:381–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nor215
Rachinger W, Grau S, Holtmannspötter M, Herms J et al (2009) Serial stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions in adults improves diagnostic accuracy compared with MRI only. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1134–1139
Nicolas Massager, Philippe David, Serge Goldman, Benoite Pirotte et al (2000) Combined magnetic resonance imaging and positron emission tomography-guided sterotactic biopsy in brainstem mass lesions: diagnostic yield in a series of 30 patients. J Nuerosurg 93:951–957
Chad D, Abernathey CD, Camacho A, Kelly PJ (1989) Stereotaxic suboccipital transcerebellar biopsy of pontine mass lesions. J Neurosurg. 70(2):195–200. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1989.70.2.0195
Gonçalves-Ferreira AJ, Herculano-Carvalho M, Pimentel J (2003) Stereotactic biopsies of focal brainstem lesions. Surg Neurol. 4:311–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0090-3019(03)00379-3
Samadani U, Stein S, Moonis G, Sonnad SS, Bonura P, Judy KD (2006) Stereotactic biopsy of brain stem masses: Decision analysis and literature review. Surg Neurol. 5:484–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surneu.2006.05.056
Kickingereder P, Willeit P, Simon T, Ruge MI (2013) Diagnostic value and safety of stereotactic biopsy of brainstem tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 1480 cases. Neurosurgery 72:873–881
Rajshekhar V, Chandy MJ (1995) Computerized tomography-guided stereotactic surgery for brainstem masses: a risk-benefit analysis in 71 patients. J. Neurosurg. 82:976–981
Boviatsis EJ, Kouyialis AT, Stranjalis G, Korfias S, Sakas D (2003) CT-guided stereotactic biopsies of brain stem lesions: personal experience and literature review. Neurol Sci 24:97–102
Friedman WA, Sceats J, Nestok B et al (1989) The incidence of unexpected pathological findings in an image-guided biopsy series: a review of 100 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 25:180–184
Mehta VS, Chandra PS, Singh PK, Garg A, Rath GK (2009) Surgical considerations for “intrinsic” brainstem gliomas: proposal of a modification in classification. Neurology India 3:274–281
Chen SY, Chen CH, Sun MH, Lee HT, Shen CC (2011) Stereotactic biopsy for brainstem lesion: comparison of approaches and reports of 10 cases. J Chin Med Assoc 74(3):110–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2011.01.024
Mathon B (2021) Stereotactic biopsies of brainstem lesions: dilemma on the best trajectory. Acta Neurochir 164(3):745–746
Jung IH (2021) Stereotactic biopsy for adult brainstem lesions: a surgical approach and its diagnostic value according to the 2016 World Health Organization Classification. Cancer Med 10:7514–7524
Jaradat A (2021) Stereotactic biopsy for adult brainstem lesions: which approach? Acta Neurochir 163:1957–1964
Pafundi D (2013) Biopsy validation of 18F-DOPA PET and biodistribution in gliomas for neurosurgical planning and radiotherapy target delineation: results of a prospective pilot study. Neuro-Oncology 15(8):1058–1067. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/not002
Zukotynski K (2017) (2017) Correlation of 18 F-FDG PET and MRI apparent diffusion coefficient histogram metrics with survival in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: a report from the Pediatric Brain Tumor Consortium. J Nucl Med 58(8):1264–1269. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.116.185389
Morana G (2020) Correlation of multimodal 18F-DOPA PET and conventional MRI with treatment response and survival in children with diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. Theranostics 10(26):11881–11891. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.5059
Tinkle C (2019) Evaluation of 11C-methionine PET and anatomic MRI associations in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Nucl Med 60(3):312–319
Abdullah A (2018) Value of 18 F-FET PET in adult brainstem glioma. Clin Imaging 51:68–75
Abdelaziz O, Eshra M, Belal A (2016) Diagnostic value of magnetic resonance spectroscopy compared with sterotactic biospy of intra axial brain lesions. J. Neurol Sur A Cent Eur Neurosurg 4:283–290
Psimaras D, Bonnet C, Heinzmann A, Cárdenas G, Hernández José Luis S, Tungaria A, Behari S, Lacrois D, Mokhtari K, Karantoni E, Sokrab Tag E, Idris Mohamed N, Sönmez G, Caumes E, Roze E (2014) Solitary tuberculous brain lesions: 24 new cases and a review of the literature. Rev Neurol (Paris). 170(6–7):454–63
Sadashiva N, Tiwari S, Shukla D, Bhat D, Saini J, Somanna S, Devi BI (2017) Isolated brainstem tuberculomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 159(5):889–897
Fuentes S, Delsanti C, Metellus P et al (2006) Brainstem metastases: management using gamma knife radiosurgery. Neurosurgery 58(1):37–4
Yoo TW, Park ES, Kwon DH, Kim CJ (2011) Gamma knife radiosurgery for brainstem metastasis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 4:299–303
Yen CP, Sheehan J, Patterson G, Steiner L (2006) Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brainstem tumors. J Neurosurg 105(2):213–9
Patel A, Mohammadi H, Dong T, Shiue KR, Frye D, Le Y, Ansari S, Watson GA, Miller JC, Lautenschlaeger T (2018) Brainstem metastases treated with Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery: the Indiana University Health experience. CNS Oncol 1:15–23. https://doi.org/10.2217/cns-2017-0029
Duc NM (2020) The role of diffusion tensor imaging metrics in the discrimination between cerebellar medulloblastoma and brainstem glioma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 67(9):e28468. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.28468
Minh TP (2020) The role of apparent diffusion coefficient in the differentiation between cerebellar medulloblastoma and brainstem glioma. Neurol Int 12(3):34–40. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurolint12030009
Duc NM (2020) The effects of applying apparent diffusion coefficient parameters on the differentiation between fourth ventricular ependymoma and diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J Child Sci 10:e169–e174
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Laura Rozenblum, from the Department of Nuclear Medicine of Pitie-Salpetriere Hospital, for her expertise and for her help in improving our manuscript.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All investigations were carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Additional information
on behalf of the GLITRAD network (RENOCLIP LOC)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duran-Peña, A., Ducray, F., Ramirez, C. et al. Adult brainstem glioma differential diagnoses: an MRI-based approach in a series of 68 patients. J Neurol 269, 4349–4362 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11070-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11070-6