Abstract
Objective
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is a rare, autoimmune-inflammatory disease of the peripheral nervous system. Recently, various immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) type auto-antibodies have been described in patients with CIDP which can effectively be removed by immunoadsorption (IA). Therefore, we prospectively evaluated the therapeutic effect of IA in 17 patients with progressive CIDP not responding to other treatment.
Methods
We prospectively evaluated the course of disease of 17 patients with CIDP who had insufficiently responded to steroids and/or IVIg previously and who received at least one cycle of IA. As clinical outcome parameter, we used a combined CIDP score of three validated scales comprising disability, motor score, and sensitivity. Seven patients received repeated treatments in regular intervals over a prolonged period up to 46 months.
Results
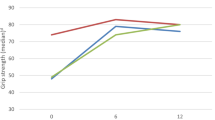
We observed a small, but significant improvement of the overall score after 2 weeks that mainly reflected an improvement of muscle strength. The median value of the combined CIDP score was 308.0 (266.0–374.5) points before IA and 330.0 (290.0–393.5) points 2 weeks after IA (p = 0.019). More importantly, all but one of seven progressive patients who received long-term immunoadsorption in regular intervals stabilized almost completely. Before IA, these patients lost 6.7 (3.0–13.1) points of combined CIDP score per month. During IA, they lost − 0.1 (0.0–0.8) points per month (p < 0.0001).
Interpretation
Our results suggest that IA might constitute a promising and well-tolerated therapeutic alternative in CIDP for short-term and long-term treatment. We showed that long-term treatment with IA in regular intervals can stabilize the course of disease at least in a subgroup of patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van den Bergh PY, Hadden RD, Bouche P, Cornblath DR, Hahn A, Illa I, Koski CL, Leger JM, Nobile-Orazio E, Pollard J, Sommer C, van Doorn PA, van Schaik IN (2010) European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—first revision. Eur J Neurol 17(3):356–363
Querol L, Devaux J, Rojas-Garcia R, Illa I (2017) Autoantibodies in chronic inflammatory neuropathies: diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Nat Rev Neurol 13(9):533–547
Illa I (2017) ARTHUR ASBURY LECTURE: Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: clinical aspects and new animal models of auto-immunity to nodal components. J Peripher Nerv Syst 22(4):418–424
Jacob S, Rajabally YA (2009) Current proposed mechanisms of action of intravenous immunoglobulins in inflammatory neuropathies. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(4):337–342
Zollner S, Pablik E, Druml W, Derfler K, Rees A, Biesenbach P (2014) Fibrinogen reduction and bleeding complications in plasma exchange, immunoadsorption and a combination of the two. Blood Purif 38(2):160–166. https://doi.org/10.1159/000367682
Kohler W, Bucka C, Klingel R (2011) A randomized and controlled study comparing immunoadsorption and plasma exchange in myasthenic crisis. J Clin Apher 26(6):347–355. https://doi.org/10.1002/jca.20317
Lieker I, Slowinski T, Harms L, Hahn K, Klehmet J (2017) A prospective study comparing tryptophan immunoadsorption with therapeutic plasma exchange for the treatment of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. J Clin Apher 32(6):486–493
Klingel R, Heibges A, Fassbender C (2009) Plasma exchange and immunoadsorption for autoimmune neurologic diseases—current guidelines and future perspectives. Atheroscler Suppl 10(5):129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1567-5688(09)71827-6
Merkies IS, Schmitz PI, van der Meche FG, Samijn JP, van Doorn PA (2002) Clinimetric evaluation of a new overall disability scale in immune mediated polyneuropathies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72(5):596–601
Breiner A, Barnett C, Bril V (2014) INCAT disability score: a critical analysis of its measurement properties. Muscle Nerve 50(2):164–169
Merkies IS, Hughes RA, Donofrio P, Bril V, Dalakas MC, Hanna K, Hartung HP, Latov N, van Doorn PA, Deng C (2010) Understanding the consequences of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy from impairments to activity and participation restrictions and reduced quality of life: the ICE study. J Peripher Nerv Syst 15(3):208–215
Galldiks N, Burghaus L, Dohmen C, Teschner S, Pollok M, Leebmann J, Frischmuth N, Hollinger P, Nazli N, Fassbender C, Klingel R, Benzing T, Fink GR, Haupt WF (2011) Immunoadsorption in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy with unsatisfactory response to first-line treatment. Eur Neurol 66(4):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1159/000331011
Zinman LH, Sutton D, Ng E, Nwe P, Ngo M, Bril V (2005) A pilot study to compare the use of the Excorim staphylococcal protein immunoadsorption system and IVIG in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Transfus Apher Sci 33(3):317–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transci.2005.07.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JD did the scientific literature search, data collection, and analysis of data. JD, HT, and MS were involved in study conception and design. All authors participated in data interpretation. JD wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors reviewed and critiqued the manuscript. HT and MS contributed equally to this work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
JD reports personal fees from Fresenius Medical Care GmbH and Fresenius Medical Care Deutschland GmbH, outside the submitted work. JD and HT report research and sponsoring grants from Fresenius Medical Care GmbH and Fresenius Medical Care Deutschland GmbH, outside the submitted work. MS has received honoraria for speaking and/or travel grants from Bayer, Biogen, and TEVA, and research funding from the Hertha-Nathorff-Program and University of Ulm; none related to this study. All other authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The study has been approved by the local ethics committee and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All patients were extensively informed about the procedure, its risks, and possible therapeutic alternatives, and gave their written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorst, J., Ludolph, A.C., Senel, M. et al. Short-term and long-term effects of immunoadsorption in refractory chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: a prospective study in 17 patients. J Neurol 265, 2906–2915 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9082-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-018-9082-6