Abstract
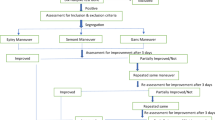
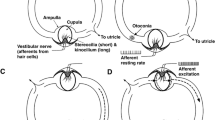
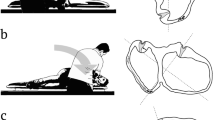
Although the efficacy of Semont (SM) and Epley maneuvers (EM) for treatment of posterior canal benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is well established, data comparing SM and EM regarding maneuver-induced canal switch are lacking. We prospectively investigated 102 posterior canal BPPV patients after application of the Semont or the Epley maneuver and looked for the appearance of ipsilateral horizontal canal BPPV symptoms. Although treatment success was similar for SM and EM (67 and 76 %, respectively), there was a significant difference in posterior-to-horizontal canal switch rates. In particular, 4 of 51 patients (7.8 %) of the EM group converted to the geotropic type of horizontal canal BPPV, whereas none of the 51 SM patients exhibited a canal switch. All four patients were cleared with a single barbecue maneuver. Our data suggest a small but significant difference in canal switch rate between EM and SM, which could be partly explained by the higher number of maneuver steps during which the head is in the dependent position throughout the EM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F et al (2007) Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:710–715
Semont A, Freyss G, Vitte E (1988) Curing the BPPV with a liberatory maneuver. Adv Otolaryngol 42:290–293
Epley JM (1992) The canalith repositioning procedure for treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 107:399–404
White J, Savvides P, Cherian N, Oas J (2005) Canalith repositioning for benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. Otol Neurotol 26:704–710
Helminski JO, Zee DS, Janssen I, Hain TC (2010) Effectiveness of particle repositioning maneuvers in the treatment of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a systematic review. Phys Ther 90:663–678
Toupet M, Ferrary E, Bozorg Grayeli A (2012) Effect of repositioning maneuver type and postmaneuver restrictions on vertigo and dizziness in benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. Sci World J 2012:162123
Foster CA, Zaccaro K, Strong D (2012) Canal conversion and reentry: a risk of Dix-Hallpike during canalith repositioning procedures. Otol Neurotol 33:199–203
White JA, Oas JG (2005) Diagnosis and management of lateral semicircular canal conversions during particle repositioning therapy. Laryngoscope 115:1895–1897
Yimtae K, Srirompotong S, Srirompotong S, Sae-Seaw P (2003) A randomized trial of the canalith repositioning procedure. Laryngoscope 113:828–832
Brocchetti F, Garaventa G, Ameli F, Baricalla F, Chiarlone M, Peirano M, Presta A, Fibbi A (2003) Effect of repetition of Semont’s manoeuvre on benign paroxysmal positional vertigo of posterior semicircular canal. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 23:428–435
Steenerson RL, Cronin GW, Marbach PM (2005) Effectiveness of treatment techniques in 923 cases of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Laryngoscope 115:226–231
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
All patients gave written informed consent for participation in the study, which was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by our institution’s Ethics Committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anagnostou, E., Stamboulis, E. & Kararizou, E. Canal conversion after repositioning procedures: comparison of Semont and Epley maneuver. J Neurol 261, 866–869 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7290-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-014-7290-2