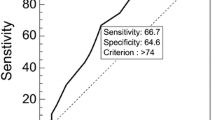
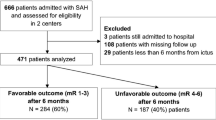
Abstract
The number of elderly patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is increasing with the aging of the population. However, management recommendations based on long-term outcome data and analyses of prognostic factors are scarce. Our study focused exclusively on elderly patients aged ≥60 years at the onset of SAH. Patients were selected from an in-house database and compared in cohorts of age 60–69, 70–79, and ≥80, regarding pre-existing medical conditions, treatment, clinical course including complications, and outcome. A multivariate analysis was conducted to identify prognostic factors for death and disability. A total of 256 patients (138 aged 60–69, 93 aged 70–79, 25 aged ≥80) with putative aneurysmal SAH who had been admitted to our hospital between January 1, 1996 and June 30, 2007 were extracted. The median follow-up of our total cohort was 35.5 months (range <1–154 months). Endovascular or conservative aneurysm treatment was applied more often with increasing age (p < 0.006). The 1-year survival rate was 78, 65, and 38 % in the three age groups, respectively (p = 0.0002); most of the patients died from the initial hemorrhage or from medical complications. Patients aged <70 with an initial World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies (WFNS) score of I–III showed the best clinical recovery. WFNS score, age, and clipping/coiling were extracted as prognostic factors from the Cox model. Elderly patients who get admitted with a good WFNS score (I–III) seem to benefit from aggressive treatment whereas caution seems to be warranted particularly in patients ≥70 years of age who get admitted in a WFNS score of IV and V because of their limited short- and long-term prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano S, Watanabe T, Shinohara T, Takanashi S, Ogawa A, Fujii N, Tanaka J, Naito Y, Furuya K, Ueno T, Nakagomi T (2011) Importance of the initial grade of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the patients with the age of 80 years and older from a single center analysis. Acta Neurol Belg 111:213–216
Brilstra EH, Algra A, Rinkel GJ, Tulleken CA, van Gijn J (2002) Effectiveness of neurosurgical clip application in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg 97:1036–1041
Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJ, Algra A, van Gijn J (2000) Rebleeding, secondary ischemia, and timing of operation in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurology 55:1656–1660
Chung RY, Carter BS, Norbash A, Budzik R, Putnam C, Ogilvy CS (2000) Management outcomes for ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in the elderly. Neurosurgery 47:827–832
de Rooij NK, Linn FH, van der Plas JA, Algra A, Rinkel GJ (2007) Incidence of subarachnoid haemorrhage: a systematic review with emphasis on region, age, gender and time trends. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1365–1372
Ferch R, Pasqualin A, Barone G, Pinna G, Bricolo A (2003) Surgical management of ruptured aneurysms in the eighth and ninth decades. Acta Neurochir 145:439–445
Fisher CM, Kistler JP, Davis JM (1980) Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning. Neurosurgery 6:1–9
Fortuny LA, Adams CB, Briggs M (1980) Surgical mortality in an aneurysm population: effects of age, blood pressure and preoperative neurological state. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 43:879–882
Fridriksson SM, Hillman J, Saveland H, Brandt L (1995) Intracranial aneurysm surgery in the 8th and 9th decades of life: impact on population-based management outcome. Neurosurgery 37:627–631
Garbossa D, Panciani PP, Fornaro R, Crobeddu E, Marengo N, Fronda C, Ducati A, Bergui M, Fontanella M (2011) Subarachnoid hemorrhage in elderly: advantages of the endovascular treatment. Geriatr Gerontol Int 12(1):46–49
Inagawa T (1992) Cerebral vasospasm in elderly patients treated by early operation for ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Acta Neurochir 115:79–85
Inagawa T (1991) Cerebral vasospasm in elderly patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms. Surg Neurol 36:91–98
Inagawa T (2001) Trends in incidence and case fatality rates of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Izumo City, Japan, between 1980–1989 and 1990–1998. Stroke 32:1499–1507
Jain R, Deveikis J, Thompson BG (2004) Endovascular management of poor-grade aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the geriatric population. Am J Neuroradiol 25:596–600
Jennett B, Bond M (1975) Assessment of outcome after severe brain damage. Lancet 1:480–484
Johansson M, Cesarini KG, Contant CF, Persson L, Enblad P (2001) Changes in intervention and outcome in elderly patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke 32:2845–2949
Karamanakos PN, Koivisto T, Vanninen R, Khallaf M, Ronkainen A, Parviainen I, Manninen H, Zu FM, Morgan MK, Jaaskelainen JE, Hernesniemi J, Rinne J (2010) The impact of endovascular management on the outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the elderly in eastern Finland. Acta Neurochir 152:1493–1502
Lanzino G, Kassell NF, Germanson TP, Kongable GL, Truskowski LL, Torner JC, Jane JA (1996) Age and outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: why do older patients fare worse? J Neurosurg 85:410–418
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R (2002) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomized trial. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 11:304–314
Nieuwkamp DJ, Rinkel GJ, Silva R, Greebe P, Schokking DA, Ferro JM (2006) Subarachnoid haemorrhage in patients > or = 75 years: clinical course, treatment and outcome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 77:933–937
Proust F, Gerardin E, Derrey S, Lesveque S, Ramos S, Langlois O, Tollard E, Benichou J, Chassagne P, Clavier E, Freger P (2010) Interdisciplinary treatment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms in elderly patients. J Neurosurg 112:1200–1207
Ryttlefors M, Enblad P, Ronne-Engstrom E, Persson L, Ilodigwe D, Macdonald RL (2010) Patient age and vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 67:911–917
Stocchetti N, Paterno R, Citerio G, Beretta L, Colombo A (2012) Traumatic brain injury in an aging population. J Neurotrauma 29:1119–1125
Teasdale GM, Drake CG, Hunt W, Kassell N, Sano K, Pertuiset B, De Villiers JC (1988) A universal subarachnoid hemorrhage scale: report of a committee of the World Federation of Neurosurgical Societies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:1457
Timiras PS (1994) Disuse and aging: same problem, different outcomes. J Gravit Physiol 1:5–7
van Gijn J, Rinkel GJ (2001) Subarachnoid haemorrhage: diagnosis, causes and management. Brain 124:249–278
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Katja Laspe (Department of Neurosurgery, University of Giessen Medical Center) for proofreading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical standard
All human studies must state that they have been approved by the appropriate ethics committee and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schöller, K., Massmann, M., Markl, G. et al. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in elderly patients: long-term outcome and prognostic factors in an interdisciplinary treatment approach. J Neurol 260, 1052–1060 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6758-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-012-6758-1