Abstract
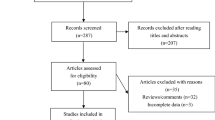
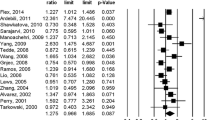
Studies of the relationship between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and polymorphism in the promoter region of Interleukin 6 (IL-6) -174 G/C have reported inconsistent results. To assess the association between IL-6 -174 G/C promoter polymorphism and AD risk, a meta-analysis containing 3,101 AD cases and 3,860 controls from 18 case–control studies was performed. There were 16 studies involving Europeans and 2 studies involving non-Europeans. The combined results showed significant differences in recessive model [CC versus GC + GG, odds ratio (OR) = 0.70, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 0.54–0.90] and heterozygote comparison (CC versus GC, OR = 0.76, 95% CI = 0.60–0.96) on the basis of all studies. On subgroup analysis by ethnicity, similarly significant differences in recessive model (CC versus GC + GG) were found in both Europeans and non-Europeans, but significant difference in heterozygote comparison (CC versus GC) was found only in non-Europeans. In conclusion, there were statistically significant differences in genotype distribution of IL-6 -174 G/C between AD cases and controls in recessive model (CC versus GC + GG). Genotype CC of IL-6 -174 G/C could decrease the risk of AD. Further studies with large sample size, especially in subgroup analysis, should be done.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arosio B, Trabattoni D, Galimberti L, Bucciarelli P, Fasano F, Calabresi C, Cazzullo CL, Vergani C, Annoni G, Clerici M (2004) Interleukin-10 and interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 25:1009–1015
Bagli M, Papassotiropoulos A, Knapp M, Jessen F, Luise Rao M, Maier W, Heun R (2000) Association between an interleukin-6 promoter and 3′ flanking region haplotype and reduced Alzheimer’s disease risk in a German population. Neurosci Lett 283:109–112
Bhojak TJ, DeKosky ST, Ganguli M, Kamboh MI (2000) Genetic polymorphisms in the cathespin D and interleukin-6 genes and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 288:21–24
Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM (2007) Forecasting the global burden of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement 3:186–191
Campbell IL, Stalder AK, Chiang CS, Bellinger R, Heyser CJ, Steffensen S, Masliah E, Powell HC, Gold LH, Henriksen SJ, Siggins GR (1997) Transgenic models to assess the pathogenic actions of cytokines in the central nervous system. Mol Psychiatry 2:125–129
Capurso C, Solfrizzi V, Colacicco AM, D’Introno A, Frisardi V, Imbimbo BP, Lorusso M, Vendemiale G, Denitto M, Santamato A, Seripa D, Pilotto A, Fiore P, Capurso A, Panza F (2010) Interleukin 6-174 G/C promoter and variable number of tandem repeats (VNTR) gene polymorphisms in sporadic Alzheimer’s disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:177–182
Capurso C, Solfrizzi V, D’Introno A, Colacicco AM, Capurso SA, Capurso A, Panza F (2004) Interleukin 6-174 G/C promoter gene polymorphism and sporadic Alzheimer’s disease: geographic allele and genotype variations in Europe. Exp Gerontol 39:1567–1573
Combarros O, Infante J, Llorca J, Pena N, Fernandez-Viadero C, Berciano J (2005) Interaction between interleukin-6 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 genes and Alzheimer’s disease risk. J Neurol 252:485–487
Depboylu C, Lohmuller F, Gocke P, Du Y, Zimmer R, Gasser T, Klockgether T, Dodel RC (2004) An interleukin-6 promoter variant is not associated with an increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 17:170–173
Faltraco F, Burger K, Zill P, Teipel SJ, Moller HJ, Hampel H, Bondy B, Ackenheil M (2003) Interleukin-6-174 G/C promoter gene polymorphism C allele reduces Alzheimer’s disease risk. J Am Geriatr Soc 51:578–579
Fontalba A, Gutierrez O, Llorca J, Mateo I, Vazquez-Higuera JL, Berciano J, Fernandez-Luna JL, Combarros O (2009) Gene–gene interaction between CARD8 and interleukin-6 reduces Alzheimer’s disease risk. J Neurol 256:1184–1186
Infante J, Sanz C, Fernandez-Luna JL, Llorca J, Berciano J, Combarros O (2004) Gene–gene interaction between interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 reduces AD risk. Neurology 63:1135–1136
Klimkowicz-Mrowiec A, Wolkow P, Spisak K, Maruszak A, Styczynska M, Barcikowska M, Szczudlik A, Slowik A (2010) Interleukin-6 gene–174 C/G and apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms and the risk of Alzheimer disease in a Polish population. Neurol Neurochir Pol 44:537–541
Koivisto AM, Helisalmi S, Pihlajamaki J, Moilanen L, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Hiltunen M, Keijo K, Hanninen T, Helkala EL, Kervinen K, Kesaniemi YA, Soininen H (2005) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Finnish population. J Neurogenet 19:155–161
Licastro F, Grimaldi LM, Bonafe M, Martina C, Olivieri F, Cavallone L, Giovanietti S, Masliah E, Franceschi C (2003) Interleukin-6 gene alleles affect the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and levels of the cytokine in blood and brain. Neurobiol Aging 24:921–926
Mansoori N, Tripathi M, Alam R, Luthra K, Ramakrishnan L, Parveen S, Mukhopadhyay AK (2010) IL-6-174 G/C and ApoE gene polymorphisms in Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia patients attending the cognitive disorder clinic of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 30:461–468
Papassotiropoulos A, Hock C, Nitsch RM (2001) Genetics of interleukin 6: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobio Aging 22:863–871
Paradowski B, Celczynska D, Dodosz T, Noga L (2008) Polymorphism 174 G/C of interleukin 6 gene in Alzheimer’s disease—preliminary report. Neurol Neurochir Pol 42:312–315
Pola R, Flex A, Gaetani E, Lago AD, Gerardino L, Pola P, Bernabei R (2002) The -174 G/C polymorphism of the interleukin-6 gene promoter is associated with Alzheimer’s disease in an Italian population. Neuroreport 13:1645–1647
Ribizzi G, Fiordoro S, Barocci S, Ferrari E, Megna M (2010) Cytokine polymorphisms and Alzheimer disease: possible associations. Neurol Sci 31:321–325
Shawkatova I, Javor J, Parnicka Z, Vrazda L, Novak M, Buc M (2010) No association between cytokine gene polymorphism and risk of Alzheimer’s disease in Slovaks. Acta Neurobiol Exp 70:303–307
Shibata N, Ohnuma T, Takahashi T, Baba H, Ishizuka T, Ohtsuka M, Ueki A, Nagao M, Arai H (2002) Effect of IL-6 polymorphism on risk of Alzheimer disease: genotype–phenotype association study in Japanese cases. Am J Med Genet 114:436–439
van Oijen M, Arp PP, de Jong FJ, Hofman A, Koudstaal PJ, Uitterlinden AG, Breteler MM (2006) Polymorphisms in the interleukin 6 and transforming growth factor beta1 gene and risk of dementia. The Rotterdam Study. Neurosci Lett 402:113–117
Vural P, Degirmencioglu S, Parildar-Karpuzoglu H, Dogru-Abbasoglu S, Hanagasi HA, Karadag B, Gurvit H, Emre M, Uysal M (2009) The combinations of TNFalpha-308 and IL-6-174 or IL-10-1082 genes polymorphisms suggest an association with susceptibility to sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand 120:396–401
Wilson CJ, Finch CE, Cohen HJ (2002) Cytokines and cognition–the case for a head-to-toe inflammatory paradigm. J Am Geriatr Soc 50:2041–2056
Zhang Y, Hayes A, Pritchard A, Thaker U, Haque MS, Lemmon H, Harris J, Cumming A, Lambert JC, Chartier-Harlin MC, St Clair D, Iwatsubo T, Mann DM, Lendon CL (2004) Interleukin-6 promoter polymorphism: risk and pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 362:99–102
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China grant 30800441.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, L., Liu, D., Guo, H. et al. Association between polymorphism in the promoter region of Interleukin 6 (-174 G/C) and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Neurol 259, 414–419 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6164-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-011-6164-0