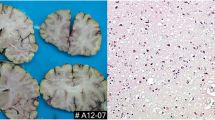
Abstract
We assessed the prevalence of Wernicke encephalopathy (WE) in all 657 cases suspected of Creutzfeldt-Jakob (CJD) referred from 2001 to 2006 to the French Neuropathology Network of CJD. Clinical, biological and imaging data were reviewed when the diagnosis of WE was made at autopsy. No CJD was found in five cases suspected of sporadic CJD. In these five cases, myoclonus had been observed in four, CSF 14-3-3 protein in two. In 14 other cases, WE was combined with CJD, 13 of which were sporadic. These belonged mainly to the molecular variants of sporadic CJD associated with a long duration of disease. This stresses the necessity of remaining alert to the diagnosis of WE when CJD is suspected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brandel JP, Delasnerie-Lauprêtre N, Laplanche JL, Hauw JJ, Alpérovitch A (2000) Diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: effect of clinical criteria on incidence estimates. Neurology 54:1095–1994
Brown P (2008) Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy in the 21st century: neuroscience for the clinical neurologist. Neurology 70:713–722
Budka H, Aguzzi A, Brown P et al (1995) Neuropathological diagnostic criteria for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and other human spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases). Brain Pathol 5:459–466
Collins SJ, Sanchez-Juan P, Masters CL et al (2006) Determinants of diagnostic investigation sensitivities across the clinical spectrum of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Brain 129:2278–2287
Gaytan-Garcia S, Gilbert JJ, Deck JHN, Kaufmann JCE (1988) Jakob-Creutzfeldt disease associated with Wernicke encephalopathy. Can J Neurol Sci 15:156–160
Haïk S, Brandel JP, Sazdovitch V et al (2000) Dementia with Lewy bodies in a neuropathologic series of suspected Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurology 55:1401–1404
Harper C, Butterworth R (1997) Nutritional and metabolic disorders. In: Graham DI, Lantos PL (eds) Greenfield’s neuropathology. Arnold, London, pp 601–655
Hauw JJ, de Baecque C, Hausser-Hauw C, Serdaru M (1988) Chromatolysis in alcoholic encephalopathies: Pellagra-like changes in 22 cases. Brain 111:843–857
Hauw JJ, Sazdovitch V, Laplanche JL et al (2000) Neuropathologic variants of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and codon 129 of PrP gene. Neurology 54:1641–1646
Johnson RT, Gonzales G, Frosch MP (2005) Case 27-2005: an 80-year-old man with fatigue, unsteady gait and confusion. New Engl J Med 353:1042–1050
Levavasseur E, Laffont-Proust I, Morain E et al (2008) Regulating factors of PrPres glycosylation in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease—implications for the dissemination and the diagnosis of human prion strains. PLoS ONE 3(7):e2786
Nagashima T, Okawa M, Kitamoto T et al (1999) Wernicke encephalopathy-like symptoms as an early manifestation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in a chronic alcoholic. J Neurol Sci 163:192–198
Ogershok PR, Rahman A, Nestor S, Brick J (2002) Wernicke encephalopathy in nonalcoholic patients. Am J Med Sci 323:107–111
Parchi P, Giese A, Capellari S et al (1999) Classification of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on molecular and phenotypic analysis of 300 subjects. Ann Neurol 46:224–233
Pietrini V (1992) Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease presenting as Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome. J Neurol Sci 108:149–153
Ropper AH, Brown RH (2005) Diseases of the nervous system due to nutritional deficiencies. In: Adam’s and Victor’s principles of neurology. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 983–1039
Russell RWR (1980) Supranuclear palsy of eyelid closure. Brain 103:71–787
Serdaru M, Hausser-Hauw C, Laplane D et al (1988) The clinical spectrum of alcoholic pellagra encephalopathy: a retrospective analysis of 22 cases studied pathologically. Brain 111:829–842
Weidauer S, Nichtweiss M, Lanfermann H, Zanella FE (2003) Wernicke encephalopathy: MR findings and clinical presentation. Eur Radiol 13:1001–1009
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. U. de Girolami for helpful suggestions. The contribution of the members of the French CJD Neuropathology Network and of all the physicians who referred their patients to the Network is gratefully acknowledged. InVS, DGS and DHOS supported this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertrand, A., Brandel, J.P., Grignon, Y. et al. Wernicke encephalopathy and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neurol 256, 904–909 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5038-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5038-1