Abstract
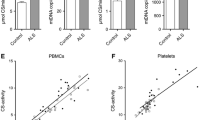
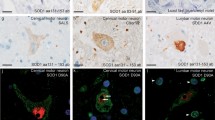
In an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) patient who also had an IgA gammopathy, autopsy studies identified the IgA in the surviving motor neurons. Further, the IgA bound the surface of isolated bovine motor neurons and inhibited neuronal proliferation in culture. To determine the pathologic basis of this IgA interaction with motor neurons, a neuroblastoma cDNA library was generated and screened with the IgA monoclonal antibody. Reactive clones were identified as flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) synthetase. To extend this finding to ALS in general, quantitative RT-PCRs were performed on blood samples from 26 ALS and 30 control blood samples to determine mRNA expression levels of FAD synthetase and other electron transport chain proteins, specifically riboflavin kinase (RFK), cytochrome C1 (CYC1), and succinate dehydrogenase complex subunit B (SDHB). All expression levels were measured against a control enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Expression levels for a non-respiratory chain protein (beta-actin) were also measured. We found that FAD synthetase expression levels were decreased in ALS samples compared to expression levels in controls (P = 0.0151). Expression levels for RFK, CYC1, and SDHB were also significantly decreased in the ALS group (P = 0.0025, P = 0.0002, and P < 0.0001, respectively). As control, expression levels for beta-actin did not show a significant difference between ALS and control groups (P = 0.2118). Our data show that a reduction in electron transport proteins, namely FAD synthetase, RFK, CYC1, and SDHB, is seen in patients with ALS. It is possible that this may have an effect on oxygen-dependent metabolic pathways. Human motor neurons may be particularly susceptible to injury if there is sub-optimal oxidative metabolism.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolski S, Thomas FP, Sadiq SA, Suder F, Cadet JL, Latov N, Hays AP, Mena MA, DeYebenes JG (1990) IgA monoclonal antibody in ALS inhibits proliferation of human neuroblastoma cells. In: Neurology, p 184 Abstr
Appel SH, Engelhardt JI, Henkel JS, Siklos L, Beers DR, Yen AA, Simpson EP, Luo Y, Carrum G, Heslop HE, Brenner MK, Popat U (2008) Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurology 71:1326–1334
Barile M, Passarella S, Bertoldi A, Quagliariello E (1993) Flavin adenine dinucleotide synthesis in isolated rat liver mitochondria caused by imported flavin mononucleotide. Arch Biochem Biophys 305:442–447
Beghi E, Chio A, Inghilleri M, Mazzini L, Micheli A, Mora G, Poloni M, Riva R, Serlenga L, Testa D, Tonali P (2000) A randomized controlled trial of recombinant interferon beta-1a in ALS. Italian Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology 54:469–474
Borthwick GM, Johnson MA, Ince PG, Shaw PJ, Turnbull DM (1999) Mitochondrial enzyme activity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: implications for the role of mitochondria in neuronal cell death. Ann Neurol 46:787–790
Brizio C, Galluccio M, Wait R, Torchetti EM, Bafunno V, Accardi R, Gianazza E, Indiveri C, Barile M (2006) Over-expression in Escherichia coli and characterization of two recombinant isoforms of human FAD synthetase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 344:1008–1016
Comi GP, Bordoni A, Salani S, Franceschina L, Sciacco M, Prelle A, Fortunato F, Zeviani M, Napoli L, Bresolin N, Moggio M, Ausenda CD, Taanman JW, Scarlato G (1998) Cytochrome c oxidase subunit I microdeletion in a patient with motor neuron disease. Ann Neurol 43:110–116
Cookson MR, Menzies FM, Manning P, Eggett CJ, Figlewicz DA, McNeil CJ, Shaw PJ (2002) Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (SOD1) mutations associated with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) affect cellular free radical release in the presence of oxidative stress. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 3:75–85
Deluca C, Kaplan NO (1958) Flavin adenine dinucleotide synthesis in animal tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta 30:6–11
Drachman DB, Chaudhry V, Cornblath D, Kuncl RW, Pestronk A, Clawson L, Mellits ED, Quaskey S, Quinn T, Calkins A et al (1994) Trial of immunosuppression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using total lymphoid irradiation. Ann Neurol 35:142–150
Engelhardt JI, Appel SH, Killian JM (1989) Experimental autoimmune motoneuron disease. Ann Neurol 26:368–376
Hamajima S, Ono S, Hirano H, Obara K (1979) Induction of the FAD synthetase system in rat liver by phenobarbital administration. Int J Vitam Nutr Res 49:59–63
Hays AP, Roxas A, Sadiq SA, Vallejos H, D’Agati V, Thomas FP, Torres R, Sherman WH, Bailey-Braxton D, Hays AG et al (1990) A monoclonal IgA in a patient with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis reacts with neurofilaments and surface antigen on neuroblastoma cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49:383–398
Kong J, Xu Z (1998) Massive mitochondrial degeneration in motor neurons triggers the onset of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in mice expressing a mutant SOD1. J Neurosci 18:3241–3250
Latov N (1990) Neuropathic syndromes associated with monoclonal gammopathies. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis 68:221–232
Manfredi G, Xu Z (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction and its role in motor neuron degeneration in ALS. Mitochondrion 5:77–87
Martin LJ (2006) Mitochondriopathy in Parkinson disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:1103–1110
Martin LJ, Liu Z, Chen K, Price AC, Pan Y, Swaby JA, Golden WC (2007) Motor neuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mutant superoxide dismutase-1 transgenic mice: mechanisms of mitochondriopathy and cell death. J Comp Neurol 500:20–46
Morrison BM, Morrison JH (1999) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis associated with mutations in superoxide dismutase: a putative mechanism of degeneration. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 29:121–135
Rowland LP (1991) Ten central themes in a decade of ALS research. Adv Neurol 56:3–23
Rowland LP (ed), Merritt HH (2005) Merritt’s neurology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Sadiq SA, Latov N (1991) Monoclonal gammopathy and motor neuron disease. Adv Neurol 56:413–420
Sadiq SA, Thomas FP, Kilidireas K, Protopsaltis S, Hays AP, Lee KW, Romas SN, Kumar N, van den Berg L, Santoro M et al (1990) The spectrum of neurologic disease associated with anti-GM1 antibodies. Neurology 40:1067–1072
Sadiq SA, van den Berg LH, Thomas FP, Kilidireas K, Hays AP, Latov N (1991) Human monoclonal antineurofilament antibody cross-reacts with a neuronal surface protein. J Neurosci Res 29:319–325
Shy ME, Rowland LP, Smith T, Trojaborg W, Latov N, Sherman W, Pesce MA, Lovelace RE, Osserman EF (1986) Motor neuron disease and plasma cell dyscrasia. Neurology 36:1429–1436
Tanridag T, Coskun T, Hurdag C, Arbak S, Aktan S, Yegen B (1999) Motor neuron degeneration due to aluminium deposition in the spinal cord: a light microscopical study. Acta Histochem 101:193–201
Vielhaber S, Kunz D, Winkler K, Wiedemann FR, Kirches E, Feistner H, Heinze HJ, Elger CE, Schubert W, Kunz WS (2000) Mitochondrial DNA abnormalities in skeletal muscle of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 123(Pt 7):1339–1348
Vijayvergiya C, Beal MF, Buck J, Manfredi G (2005) Mutant superoxide dismutase 1 forms aggregates in the brain mitochondrial matrix of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. J Neurosci 25:2463–2470
Wong NK, Strong MJ (1998) Nitric oxide synthase expression in cervical spinal cord in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur J Cell Biol 77:338–343
Younger DS, Rowland LP, Latov N, Sherman W, Pesce M, Lange DJ, Trojaborg W, Miller JR, Lovelace RE, Hays AP et al (1990) Motor neuron disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: relation of high CSF protein content to paraproteinemia and clinical syndromes. Neurology 40:595–599
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Diamanduros, A., Chowdhury, S.A. et al. Specific electron transport chain abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 256, 774–782 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5015-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-5015-8