Abstract
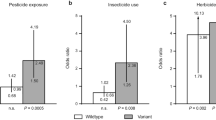
The multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1 or ABCB1) gene encodes a P-glycoprotein that protects the brain against neurotoxicants. Certain MDR1 genetic variants are known to compromise the function of this transporter and may thus be associated with Parkinson disease (PD). We therefore conducted a large case-control study investigating the potential relationship between MDR1 variants and PD. We determined the frequency of three MDR1 variants in 599 European PD patients and controls and further stratified the population by ethnicity, age at onset, and exposure to pesticides. We detected no relevant association in either the entire sample, or when separately investigating by ethnic origin or age at onset. However, the distribution of c.3435C/T differed significantly between PD patients exposed to pesticides compared to those non-exposed (odds ratio = 4.74; confidence interval = [1.009; 22.306]); p = 0.047), suggesting that common MDR1 variants might influence the risk to develop PD in conjunction with exposure to pesticides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arjomand-Nahad F, Diefenbach K, Landt O, Gaikovitch E, Roots I (2004) Genotyping of the triallelic variant G2677T/A in MDR1 using LightCycler with locked-nucleic-acid-modified hybridization probes. Anal Biochem 334:201–203
Ascherio A, Chen H, Weisskopf MG, O’Reilly E, McCullough ML, Calle EE, Schwarzschild MA, Thun MJ (2006) Pesticide exposure and risk for Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 60:197–203
Bagade S, Allen NC, Tanzi R, Bertram L. The PDGene Database. Available at: http://www.pdgene.org/. In: Alz heimer Research Forum
Brown TP, Rumsby PC, Capleton AC, Rushton L, Levy LS (2006) Pesticides and Parkinson’s disease – is there a link? Environ Health Perspect 114: 156–164
Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Johne A, Meisel C, Hoffmeyer S, Schwab M, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U, Roots I (2001) Frequency of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene in white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 69:169–174
Drozdzik M, Bialecka M, Mysliwiec K, Honczarenko K, Stankiewicz J, Sych Z (2003) Polymorphism in the P-glycoprotein drug transporter MDR1 gene: a possible link between environmental and genetic factors in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacogenetics 13:259–263
Elbaz A, Levecque C, Clavel J, Vidal JS, Richard F, Amouyel P, Alperovitch A, Chartier-Harlin MC, Tzourio C (2004) CYP2D6 polymorphism, pesticide exposure, and Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 55:430–434
Furuno T, Landi MT, Ceroni M, Caporaso N, Bernucci I, Nappi G, Martignoni E, Schaeffeler E, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2002) Expression polymorphism of the blood-brain barrier component Pglycoprotein (MDR1) in relation to Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacogenetics 12:529–534
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Hoffmeyer S, Burk O, von Richter O, Arnold HP, Brockmoller J, Johne A, Cascorbi I, Gerloff T, Roots I, Eichelbaum M, Brinkmann U (2000) Functional polymorphisms of the human multidrug-resistance gene: multiple sequence variations and correlation of one allele with P-glycoprotein expression and activity in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3473–3478
Klein C, Schlossmacher MG (2006) The genetics of Parkinson disease: Implications for neurological care. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 2:136–146
Kortekaas R, Leenders KL, van Oostrom JC, Vaalburg W, Bart J, Willemsen AT, Hendrikse NH (2005) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in parkinsonian midbrain in vivo. Ann Neurol 57:176–179
Kraft P, Yen YC, Stram DO, Morrison J, Gauderman WJ (2007) Exploiting gene-environment interaction to detect genetic associations. Hum Hered 63:111–119
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine- analog synthesis. Science 219:979–980
Lee CG, Tang K, Cheung YB, Wong LP, Tan C, Shen H, Zhao Y, Pavanni R, Lee EJ, Wong MC, Chong SS, Tan EK (2004) MDR1, the blood-brain barrier transporter, is associated with Parkinson’s disease in ethnic Chinese. J Med Genet 41:e60
Lee G, Bendayan R (2004) Functional expression and localization of P-glycoprotein in the central nervous system: relevance to the pathogenesis and treatment of neurological disorders. Pharm Res 21:1313–1330
Menegon A, Board PG, Blackburn AC, Mellick GD, Le Couteur DG (1998) Parkinson’s disease, pesticides, and glutathione transferase polymorphisms. Lancet 352:1344–1346
Momose Y, Murata M, Kobayashi K, Tachikawa M, Nakabayashi Y, Kanazawa I, Toda T (2002) Association studies of multiple candidate genes for Parkinson’s disease using single nucleotide polymorphisms. Ann Neurol 51:133–136
Sakaeda T (2005) MDR1 genotyperelated pharmacokinetics: fact or fiction? Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20:391–414
Schaid DJ, Rowland CM, Tines DE, Jacobson RM, Poland GA (2002) Score tests for association between traits and haplotypes when linkage phase is ambiguous. Am J Hum Genet 70:425–434
Seidler A, Hellenbrand W, Robra BP, Vieregge P, Nischan P, Joerg J, Oertel WH, Ulm G, Schneider E (1996) Possible environmental, occupational, and other etiologic factors for Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study in Germany. Neurology 46:1275–1284
Singh C, Ahmad I, Kumar A (2007) Pesticides and metals induced Parkinson’s disease: involvement of free radicals and oxidative stress. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 53:19–28
Takano M, Yumoto R, Murakami T (2006) Expression and function of efflux drug transporters in the intestine. Pharmacol Ther 109:137–161
Tan EK, Chan DK, Ng PW, Woo J, Teo YY, Tang K, Wong LP, Chong SS, Tan C, Shen H, Zhao Y, Lee CG (2005) Effect of MDR1 haplotype on risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 62:460–464
Tan EK, Drozdzik M, Bialecka M, Honczarenko K, Klodowska-Duda G, Teo YY, Tang K, Wong LP, Chong SS, Tan C, Yew K, Zhao Y, Lee CG (2004) Analysis of MDR1 haplotypes in Parkinson’s disease in a white population. Neurosci Lett 372:240–244
Tanner CM, Ottman R, Goldman SM, Ellenberg J, Chan P, Mayeux R, Langston JW (1999) Parkinson disease in twins: an etiologic study. Jama 281:341–346
Thiruchelvam M, Richfield EK, Goodman BM, Baggs RB, Cory-Slechta DA (2002) Developmental exposure to the pesticides paraquat and maneb and the Parkinson’s disease phenotype. Neurotoxicology 23:621–633
Wellek S (2004) Tests for establishing compatibility of an observed genotype distribution with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in the case of a biallelic locus. Biometrics 60:694–703
Wilk JB, Tobin JE, Suchowersky O, Shill HA, Klein C, Wooten GF, Lew MF, Mark MH, Guttman M, Watts RL, Singer C, Growdon JH, Latourelle JC, Saint- Hilaire MH, DeStefano AL, Prakash R, Williamson S, Berg CJ, Sun M, Goldwurm S, Pezzoli G, Racette BA, Perlmutter JS, Parsian A, Baker KB, Giroux ML, Litvan I, Pramstaller PP, Nicholson G, Burn DJ, Chinnery PF, Vieregge P, Slevin JT, Cambi F, MacDonald ME, Gusella JF, Myers RH, Golbe LI (2006) Herbicide exposure modifies GSTP1 haplotype association to Parkinson onset age: the GenePD Study. Neurology 67:2206–2210
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zschiedrich, K., König, I.R., Brüggemann, N. et al. MDR1 variants and risk of Parkinson disease. J Neurol 256, 115–120 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0089-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0089-x