Abstract
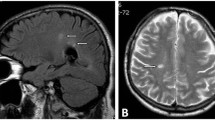
We discuss two cases receiving different anti-tumornecrosis-factor alpha antagonists (anti-TNF-α); one for psoriatic arthritis (PA) and the other for ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Due to neurological symptoms cerebral magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed and cerebral lesions were detected. Our interpretations of these cerebral lesions and the resulting diagnostic and therapeutic consequences are presented in regard of data published in the medical literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkhof F, Filippi M, Miller DH, ScheltensP, Campi A, Polman CH, Comi G,Adèr HJ, Losseff N, Valk J (1997) Comparisonof MRI criteria at first presentationto predict conversion to clinicallydefinite multiple sclerosis. Brain120:2059–2069
Bellesi M, Logullo F, DiBella P, ProvincialiL (2006) CNS demyelination duringanti-tumor necrosis factor alphatherapy. J Neurol 253:668–669
Bensouda-Grimaldi L, Mullemann D,Valat JP, Autret-leca E (2007) Adalimumab-associated Multiple Sclerosis.J Rheumatol 34:239–240
Calin A (1989) Is there an associationbetween ankylosing spondylitis andmultiple sclerosis? Ann Rheum Dis48:971–972
Cellerini M, Gabbrielli S, Bongi SM(2001) Cerebral magnetic resonanceimaging in a patient with ankylosingspondylitis and multiple sclerosis-likesyndrome. Neuroradiology 43:1067–1069
Enayati PJ, Papadakis KA (2005) Associationof anti-tumor necrosis factortherapy with the development ofmultiple sclerosis. J Clin Gastroenterol39:303–306
Foroozan R, Buono LM, Sergott RC,Savino PJ (2002) Retrobulbar opticneuritis associated with infliximab.Arch Ophthalmol 120:985–987
Fox DA (2000) Cytokine blockade as anew strategy to treat rheumatoidarthritis. Inhibition of tumor necrosisfactor. Arch Intern Med 160:437–444
Gupta G, Gelfand JM, Lewis JD (2005)Increased risk for demyelinating diseasesin patients with inflammatorybowel disease. Gastroenterology 129:1117–1120
Hemmer B, Hartung HP (2007)Towards the development of rationaltherapies in multiple sclerosis: What ison the horizon? Ann Neurol 62:314–326
Jarand J, Zochodne DW, Martin LO,Voll C (2006) Neurological complicationsof infliximab. J Rheumatol 33:1018–1020
Kelley RE (2006) Ischemic demyelination.Neurol Res 28:334–340
Kim E, Edgar E, Isenhath S, Blauwelt A,Bourdette D, Whitham R (2008)Successful treatment of pyodermagangrenosum with a TNF-alphablocker in a subject with multiplesclerosis. Neurology 70(Suppl 1):A93
Kimura K, Hunter SF, Thollander MS,Loftus EV Jr, Melton LJ 3rd, O’BrienPC, Rodriguez M, Phillips SF (2000)Concurrence of inflammatory boweldisease and multiple sclerosis. MayoClin Proc 75:802–806
Kodama S, Davis M, Faustmann DL(2005) The therapeutic potential oftumor necrosis factor for autoimmunedisease: a mechanistically basedhypothesis. Cell Mol Lif Sci 62:1850–1862
Magnano MD, Robinson WH, GenoveseMC (2004) Demyelination andinhibition of tumor necrosis factor(TNF). Clin Exp Rheumatol 22(5 Suppl35):S134–S140
Marotte H, Charrin JE, Miossec P(2002) Infliximab-induced asepticmeningitis. Lancet 359:1252
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G,Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD,McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH,Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M,Sibley W, Thompson A, van den NoortS, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001)Recommended diagnostic criteria formultiple sclerosis: guidelines from theInternational Panel on the diagnosis ofmultiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50:121–127
Midgard R, Grønning M, Riise T, KvåleG, Nyland H (1996) Multiple sclerosisand chronic inflammatory diseases. Acase-control study. Acta Neurol Scand93:322–328
Mohan N, Edwards ET, Cupps TR,Oliviero PJ, Sandberg G, Crayton H,Richert JR, Siegel JN (2001) Demyelinationoccuring during anti-tumornecrosis factor alpha therapy forinflammatory arthritides. ArthritisRheum 44:2862–2869
Quispel R, van der Worp HB, PruissenM, Schipper ME, Oldenburg B (2006)Fatal aseptic meningoencephalitisfollowing infliximab treatment for inflammatorybowel disease. Gut 55:1056
Ramagopalan SV, Dyment DA, ValdarW, Herrera BM, Criscuoli M, Yee IM,Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC; CanadianCollaborative Study Group (2007)Autoimmune disease in families withmultiple sclerosis: a population-basedstudy. Lancet Neurol 6:604–610
Ranges GE, Figari IS, Espevik T, PalladinoMA (1987) Inhibition of cytotoxicT cell development by transforminggrowth factor-beta and reversakl byrecombinant tumor necrosis factoralpha. J Exp Med 166:991–999
Reidel MA, Stippich C, Heiland S,Storch-Hagenlocher B, Jansen O,Hähnel S (2003) Differentiation ofmultiple sclerosis plaques, subacutecerebral ischaemic infarcts, focalvasogenic oedema and lesions of subcorticalarteriosclerotic encephalopathyusing magnetisation transfer measurements.Neuroradiology 45:289–294
Selmaj KW, Raine CS (1988) Tumor necrosisfactor mediates myelin and oligodendrocytedamage in vitro. AnnNeurol 23:339–346
Selmaj KW, Raine CS (1995) Experimentalautoimmune encephalomyelitis:immunotherapy with anti-tumornecrosis factor antibodies and solubletumor necrosis factor receptors. Neurology45(Suppl 6):S44–S49
Selmaj KW (2000) Tumour necrosisfactor and anti-tumour necrosis factorapproach to inflammatory demyelinatingdiseases of the central nervous system.Ann Rheum Dis 59(Suppl I):i94–i102
Shin IS, Baer AN, Kwon HJ, PapadopoulosEJ, Siegel JN (2006) Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromesoccurring with tumor necrosis factoralpha antogonist therapy. ArthritisRheum 54:1429–1434
Sicotte NL, Voskuhl RR (2001) Onset ofmultiple sclerosis associated with anti-TNF therapy. Neurology 57:1885–1888
Tan FU, Tellioğlu S, Aydin G,Erdemoğlu AK, Keles¸ I (2004) Ankylosingspondylitis and multiple sclerosisin a HLA-B27 negative patient. ActaNeurol Belg 104:169–172
Tanno M, Nakamura I, Kobayashi S,Kurihara K, Ito K (2006) New-onsetdemyelination induced by infliximabtherapy in two rheumatoid arthritispatients. Clin Rheumatol 25:929–933
The Lenercept Multiple Sclerosis StudyGroup and the University of BritishColumbia MS/MRI Analysis Group(1999) TNF neutralization in multiplesclerosis: results of a randomized,placebo-controlled multicenter study.Neurology 53:457–465
Thomas CW Jr, Weinshenker BG, SandbornWJ (2004) Demyelination duringanti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapywith infliximab for Crohn’s disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis 10:28–31
Titelbaum DS, Degenhardt A, KinkelRP (2005) Anti-tumor necrosis factoralpha-associated Multiple Sclerosis.Am J Neuroradiol 26:1548–1550
Toussirot E, Pertuiset E, Martin A,Melac-Ducamp S, Alcalay M, Grardel B,Seror P, Perdriger A, Wendling D,Mulleman D, Beraneck L, Mariette X;Club Rheumatismes et Inflammation(2006) Association of rheumatoidarthritis with multiple sclerosis: reportof 14 cases and discussion of its significance.J Rheumatol 33:1027–1028
Van Oosten BW, Barkhof F, Truyen L,Boringa JB, Berteslmann FW, vonBolmberg BM, Woody JN, Hartung HP,Polman CH (1996) Increased MRIactivity and immune activation in twomultiple sclerosis patients treated withthe monoclonal anti-tumor necrosisfactor antibody cA2. Neurology 47:1531–1534
Yokota S, Geppert TD, Lipsky PI (1988)Enhancement of antigen-and mitogen-inducedhuman T lymphocyte proliferationby tumor necrosis factor.J Immunol 140:531–538
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of interest We have no conflicts of interest.
Disclosure We have nothing to disclose.
Role of the funding source No funding sources were involved in the preparation of this article or in the decision to submit it for publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winkelmann, A., Patejdl, R., Wagner, S. et al. Cerebral MRI lesions and anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy. J Neurol 255 (Suppl 6), 109–114 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-6020-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-008-6020-z