Abstract
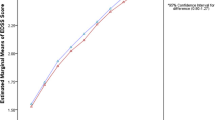
We compared the relative efficacy of interferon beta (IFNβ) products and azathioprine (AZA) in the treatment of relapsing- remitting multiple sclerosis (RRMS). Ninety-four previously untreated patients of short duration with RRMS were randomly allocated to the two treatment groups. The first group received IFNβ products (Betaferon,Avonex or Rebif); the second group received AZA for 12 months. Response to treatment was assessed at 3, 6, and 12 months after starting therapy. The mean number of relapse during one year of the study was lower in the AZA group than in the IFNβ products group (0.28 vs. 0.64, P < 0.05).After 12 months, 57.4% of patients receiving IFNβ products remained relapse free compared with 76.6% of those given AZA. The Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) decreased by 0.30 units in IFNβ-treated patients (P < 0.05) and 0.46 in AZAtreated patients (P < 0.001). Treatment with IFNβ products and AZA significantly reduces the relapse rate and EDSS score in patients with RRMS, while AZA is more effective than the IFNβ formulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark W (1996) Therapeutic advances: Interferon for multiple sclerosis. J Clin Pharm Ther 21:195–199
Clegg A, Bryant J, Milne R (2000) Disease- modifying drugs for multiple sclerosis: a rapid systematic review. Health Technol Assess 4:9–25
Compston A, Coles A (2002) Multiple sclerosis. Lancet 359:1221–1231
Confavreux C, Saddier P, Grimaud J, Moreau T, Adeleine P, Aimard G (1996) Risk of cancer from azathioprine therapy in multiple sclerosis: a case-control study. Neurology 46:1607–1612
Etemadifar M, Janghorbani M, Shaygannejad V (2006) Comparison of betaferon, avonex and rebif in treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 113:283–287
Fernández O, Fernández V, De Ramón E (2004) Azathioprine and methotrexate in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 223:29–34
Filippini G, Munari L, Incorvaia B, et al. (2003) Interferons in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: a systematic review. Lancet 361:545–552
Frank JA, Richert N, Bash C, et al. (2004) Interferon-beta-1b slows progression of atrophy in RRMS: Threeyear follow-up in NAb– and NAb+ patients. Neurology 62:719–725
Goodin DS, Frohman EM, Gammany Jr GP, et al. (2002) Disease modifying therapies in multiple sclerosis: reports of therapeutics and technology assessment subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the MS Council for Clinical Practice Guideline. Neurology 58:169–178
Goodkin DE, Bailly RC, Teetzen ML, Hertsgaard D, Beatty WW (1991) The efficacy of azathioprine in relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 41:20–25
IFN β Multiple Sclerosis Study Group, Interferon β-1b is effective in relapsing- remitting multiple sclerosis: I (1993) Clinical results of a multicentre, randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial.Neurology 43:655–661
IFN β Multiple Sclerosis Study Group University of British Columbia MS/MRI (1995) Analysis Group. Interferon beta-1b in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: final outcome of the randomized controlled trial.Neurology 45:1277–1285
Jacobs LD, Cookfair DL, Rudick RA, et al. (1996) Intramuscular interferon beta-1a for disease progression in relapsing multiple sclerosis. The Multiple Sclerosis Collaborative Research Group (MSCRG). Ann Neurol 39:285–294
Jacobs L, Rudick R, Simon J (2000) Extended observations on MS patients treated with IM interferon-1a (Avonex™): implications for modern MS trials and therapeutics. J Neuroimmunol 107:167–173
Kinlen LJ (1985) Incidence of cancer in rheumatoid arthritis and other disorders after immunosuppressive treatment. Am J Med 78(Suppl 1A):44–49
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Lhermitte F, Marteau R, Roullet R (1984).Not so benign long-term immunosuppression in multiple sclerosis. Lancet I:276–277
Lublin FD,Whitaker JN, Eideman BH, Miller AE, Arnason BG, Burks JS (1996) Management of patients receiving Interferon β-1b for multiple sclerosis: report of a consensus conference. Neurology 46:12–18
Massacesi L, Parigi A, Barilaro A, et al. (2005) Efficacy of azathioprine on multiple sclerosis new brain lesions evaluated using magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Neurol 62:1843–1847
Mertin J, Kremer M, Knight SC, et al. (1982) Double blind controlled trial of immunosuppressant in the treatment of multiple sclerosis: final report. Lancet II:351–354
Milanese C, La Mantia L, Salmaggi A, Caputo D (2001) Azathioprine and interferon beta-1b treatment in relapsing- remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 70:413–414
Milanese C, La Mantia L, Salmaggi A, Eoli M (1993) A double blind study on azathioprine efficacy in multiple sclerosis: final report. J Neurol 240:295–298
Palace J, Rothwell P (1997) New treatments and azathioprine in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 350:261
Patzold U, Hecker H, Pocklington P (1982) Azathioprine in treatment of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 54:377–394
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, et al. (1983) New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guideline for research protocol. Ann Neurol 13:227–231
PRISMS Study Group and the University of British Columbia MS/MRI Analysis Group (1998) Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study of Interferon beta-1a in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet 352:1498–1504
Randomised double-blind placebocontrolled study of interferon beta-1a in relapsing/remitting multiple sclerosis (1998) PRISMS (Prevention of Relapses and Disability by Interferon beta-1a Subcutaneously in Multiple Sclerosis) Study Group. Lancet 352:1498–1504
Rice G, Ebers GC (1998) Interferons in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Do they prevent the progression of the disease? Arch Neurol 55:1578–1580
Rice G, Incorvais B, Munari L, et al. (2001) A Cochrane review of recombinant interferons trials in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 248(Suppl 2):II/62
Saida T, Tashiro K, Itoyama Y, Sato T, Ohashi Y, Zhao Z (2005) Interferon Beta-1b Multiple Sclerosis Study Group of Japan. Interferon beta-1b is effective in Japanese RRMS patients: a randomized,multicenter study. Neurology 64:621–630
Schultz K, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG (1995) Empirical evidence of bias: dimension of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 273:408–412
Sudlow CL, Counsell CE (2003) Problems with UK government’s risk sharing scheme for assessing drugs for multiple sclerosis. Br Med J 326: 388–392
Wroe SJ (2005) Effects of dose titration on tolerability and efficacy of interferon beta-1b in people with multiple sclerosis. J Int Med Res 33:309–318
Yudkin PL, Ellison GW, Ghezzi A, et al. (1991) Overview of AZA treatment in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 338:1051–1055
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Etemadifar, M., Janghorbani, M. & Shaygannejad, V. Comparison of interferon beta products and azathioprine in the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 254, 1723–1728 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0637-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0637-1