Abstract
Background and purpose
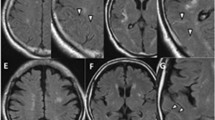
Carotid artery stenosis can be classified by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) as lesion types I–VIII according to a modified histological scheme based on American Heart Association (AHA) guidelines. Lesion types IV–V and VI are regarded as high-risk plaques.We aimed to evaluate the clinical relevance of this classification for identifying unstable plaques.
Methods
Eighty-five patients (29 female) with severe carotid artery stenosis (diagnosed by Doppler and duplex ultrasonography) were imaged using a 1.5 T scanner with bilateral phased-array carotid coils. T1-, T2-, time-offlight (TOF) and proton-density (PD)-weighted studies were obtained. The carotid plaques were classified as lesion types III–VIII according to the MRI-modified AHA criteria.
Results
Thirty-five patients presented with a recently symptomatic stenosis; 50 patients were asymptomatic. Lesion types IV–V (51.4 % vs. 22 %) and VI (20 % vs. 4%; P < 0.0001) were found significantly more often in symptomatic patients compared to those without a history of cerebral ischemia.
Conclusions
The distribution of lesion types differs significantly between symptomatic and asymptomatic carotid artery stenosis. High-risk lesion types IV–V and VI were overrepresented in recently symptomatic patients. MRI according to the modified AHA-criteria may be a suitable tool for detection of unstable carotid lesions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study Group (1989) Study design for randomized prospective trial of carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic atherosclerosis. Stroke 20:844–849
Adame IM, de Koning PJ, Lelieveldt BP, Wasserman BA, Reiber JH, van der Geest RJ (2006) An integrated automated analysis method for quantifying vessel stenosis and plaque burden from carotid MRI images: combined postprocessing of MRA and vessel wall MR. Stroke 37:2162–2164
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Bassiouny HS, Sakaguchi Y, Mikucki SA, McKinsey JF, Piano G, Gewertz BL, Glagov S (1997) Juxtalumenal location of plaque necrosis and neoformation in symptomatic carotid stenosis. J Vasc Surg 26:585–594
Cai J, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, Saam T, Chu B, Takaya N, Polissar NL, Yuan C (2005) In vivo quantitative measurement of intact fibrous cap and lipid-rich necrotic core size in atherosclerotic carotid plaque: comparison of high-resolution, contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Circulation 112:3437–3444
Cai JM, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, Small R, Polissar NL, Yuan C (2002) Classification of human carotid atherosclerotic lesions with in vivo multicontrast magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 106:1368–1373
Carr S, Farb A, Pearce WH, Virmani R, Yao JS (1996) Atherosclerotic plaque rupture in symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. J Vasc Surg 23:755–765; discussion 765–756
Chu B, Hatsukami TS, Polissar NL, Zhao XQ, Kraiss LW, Parker DL, Waterton JC, Raichlen JS, Hamar W, Yuan C (2004) Determination of carotid artery atherosclerotic lesion type and distribution in hypercholesterolemic patients with moderate carotid stenosis using noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 35:2444–2448
Chu B, Kampschulte A, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, Yarnykh VL, O'Brien KD, Polissar NL, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2004) Hemorrhage in the atherosclerotic carotid plaque: a high-resolution MRI study. Stroke 35:1079–1084
Chu B, Zhao XQ, Saam T, Yarnykh VL, Kerwin WS, Flemming KD, Huston J 3rd, Insull W Jr, Morrisett JD, Rand SD, DeMarco KJ, Polissar NL, Balu N, Cai J, Kampschulte A, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2005) Feasibility of in vivo, multicontrast- weighted MR imaging of carotid atherosclerosis for multicenter studies. J Magn Reson Imaging 21:809–817
Clarke SE, Beletsky V, Hammond RR, Hegele RA, Rutt BK (2006) Validation of automatically classified magnetic resonance images for carotid plaque compositional analysis. Stroke 37:93–97
Coombs BD, Rapp JH, Ursell PC, Reilly LM, Saloner D (2001) Structure of plaque at carotid bifurcation: highresolution MRI with histological correlation. Stroke 32:2516–2521
Corti R (2006) Noninvasive imaging of atherosclerotic vessels by MRI for clinical assessment of the effectiveness of therapy. Pharmacol Ther 110:57–70
Denzel C, Balzer K, Muller KM, Lell M, Lang W (2005) Imaging techniques for showing the morphology and surface structure of extracranial internal carotid artery plaques. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 130:1267–1272
Falk E (1992) Why do plaques rupture? Circulation 86:III30–III42
Fayad ZA (2003) MR imaging for the noninvasive assessment of atherothrombotic plaques. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 11:101–113
Fayad ZA, Fuster V (2000) Characterization of atherosclerotic plaques by magnetic resonance imaging. Ann N Y Acad Sci 902:173–186
Gronholdt ML (1999) Ultrasound and lipoproteins as predictors of lipid-rich, rupture-prone plaques in the carotid artery. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2–13
Hatsukami TS, Ross R, Polissar NL, Yuan C (2000) Visualization of fibrous cap thickness and rupture in human atherosclerotic carotid plaque in vivo with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 102:959–964
Honda M, Kitagawa N, Tsutsumi K, Nagata I, Morikawa M, Hayashi T (2006) High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging for detection of carotid plaques. Neurosurgery 58:338–346; discussion 338–346
Kampschulte A, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, Polissar NL, Chu B, Saam T, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2004) Differentiation of intraplaque versus juxtaluminal hemorrhage/thrombus in advanced human carotid atherosclerotic lesions by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 110:3239–3244
Lal BK, Hobson RW 2nd, Hameed M, Pappas PJ, Padberg FT Jr, Jamil Z, Duran WN (2006) Noninvasive identification of the unstable carotid plaque. Ann Vasc Surg 20:167–174
Leiner T, Gerretsen S, Botnar R, Lutgens E, Cappendijk V, Kooi E, van Engelshoven J (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging of atherosclerosis. Eur Radiol 15:1087–1099
Lin K, Zhang ZQ, Detrano R, Lu B, Fan ZM (2006) Carotid vulnerable lesions are related to accelerated recurrence for cerebral infarction magnetic resonance imaging study. Acad Radiol 13:1180–1186
Lusby RJ, Ferrell LD, Ehrenfeld WK, Stoney RJ, Wylie EJ (1982) Carotid plaque hemorrhage. Its role in production of cerebral ischemia. Arch Surg 117:1479–1488
Mathiesen EB, Bonaa KH, Joakimsen O (2001) Echolucent plaques are associated with high risk of ischemic cerebrovascular events in carotid stenosis: the Tromso study. Circulation 103:2171–2175
Mitsumori LM, Hatsukami TS, Ferguson MS, Kerwin WS, Cai J, Yuan C (2003) In vivo accuracy of multisequence MR imaging for identifying unstable fibrous caps in advanced human carotid plaques. J Magn Reson Imaging 17:410–420
Mofidi R, Crotty TB, McCarthy P, Sheehan SJ, Mehigan D, Keaveny TV (2001) Association between plaque instability, angiogenesis and symptomatic carotid occlusive disease. Br J Surg 88:945–950
Moody AR, Murphy RE, Morgan PS, Martel AL, Delay GS, Allder S, Mac- Sweeney ST, Tennant WG, Gladman J, Lowe J, Hunt BJ (2003) Characterization of complicated carotid plaque with magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging in patients with cerebral ischemia. Circulation 107:3047–3052
Murphy RE, Moody AR, Morgan PS, Martel AL, Delay GS, Allder S, MacSweeney ST, Tennant WG, Gladman J, Lowe J, Hunt BJ (2003) Prevalence of complicated carotid atheroma as detected by magnetic resonance direct thrombus imaging in patients with suspected carotid artery stenosis and previous acute cerebral ischemia. Circulation 107:3053–3058
Nordestgaard BG, Gronholdt ML, Sillesen H (2003) Echolucent ruptureprone plaques. Curr Opin Lipidol 14:505–512
Polak JF, Shemanski L, O'Leary DH, Lefkowitz D, Price TR, Savage PJ, Brant WE, Reid C (1998) Hypoechoic plaque at US of the carotid artery: an independent risk factor for incident stroke in adults aged 65 years or older. Cardiovascular Health Study. Radiology 208:649–654
Puppini G, Furlan F, Cirota N, Veraldi G, Piubello Q, Montemezzi S, Gortenuti G (2006) Characterisation of carotid atherosclerotic plaque: comparison between magnetic resonance imaging and histology. Radiol Med (Torino) 111:921–930
Saam T, Cai J, Ma L, Cai YQ, Ferguson MS, Polissar NL, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2006) Comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic atherosclerotic carotid plaque features with in vivo MR imaging. Radiology 240:464–472
Saam T, Ferguson MS, Yarnykh VL, Takaya N, Xu D, Polissar NL, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2005) Quantitative evaluation of carotid plaque composition by in vivo MRI. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:234–239
Saam T, Yuan C, Chu B, Takaya N, Underhill H, Cai J, Tran N, Polissar NL, Neradilek B, Jarvik GP, Isaac C, Garden GA, Maravilla KR, Hashimoto B, Hatsukami TS (2006) Predictors of carotid atherosclerotic plaque progression as measured by noninvasive magnetic resonance imaging. Atherosclerosis 13 (Epub ahead of print)
Serfaty JM, Chaabane L, Tabib A, Chevallier JM, Briguet A, Douek PC (2001) Atherosclerotic plaques: classification and characterization with T2- weighted high-spatial-resolution MR imaging – an in vitro study. Radiology 219:403–410
Shinnar M, Fallon JT, Wehrli S, Levin M, Dalmacy D, Fayad ZA, Badimon JJ, Harrington M, Harrington E, Fuster V (1999) The diagnostic accuracy of ex vivo MRI for human atherosclerotic plaque characterization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2756–2761
Stary HC, Chandler AB, Dinsmore RE, Fuster V, Glagov S, Insull W Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW (1995) A definition of advanced types of atherosclerotic lesions and a histological classification of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Circulation 92:1355–1374
Stary HC, Chandler AB, Glagov S, Guyton JR, Insull W Jr, Rosenfeld ME, Schaffer SA, Schwartz CJ, Wagner WD, Wissler RW (1994) A definition of initial, fatty streak, and intermediate lesions of atherosclerosis. A report from the Committee on Vascular Lesions of the Council on Arteriosclerosis, American Heart Association. Arterioscler Thromb 14:840–856
Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Underhill H, Cai J, Tran N, Polissar NL, Isaac C, Ferguson MS, Garden GA, Cramer SC, Maravilla KR, Hashimoto B, Hatsukami TS (2006) Association between carotid plaque characteristics and subsequent ischemic cerebrovascular events: a prospective assessment with MRI–initial results. Stroke 37:818–823
Toussaint JF, LaMuraglia GM, Southern JF, Fuster V, Kantor HL (1996) Magnetic resonance images lipid, fibrous, calcified, hemorrhagic, and thrombotic components of human atherosclerosis in vivo. Circulation 94:932–938
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, Wrenn SP, Narula J (2005) Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:2054–2061
Yuan C, Kerwin WS, Ferguson MS, Polissar N, Zhang S, Cai J, Hatsukami TS (2002) Contrast-enhanced high resolution MRI for atherosclerotic carotid artery tissue characterization. J Magn Reson Imaging 15:62–67
Yuan C, Kerwin WS, Yarnykh VL, Cai J, Saam T, Chu B, Takaya N, Ferguson MS, Underhill H, Xu D, Liu F, Hatsukami TS (2006) MRI of atherosclerosis in clinical trials. NMR Biomed 19:636–654
Yuan C, Mitsumori LM, Beach KW, Maravilla KR (2001) Carotid atherosclerotic plaque: noninvasive MR characterization and identification of vulnerable lesions. Radiology 221:285–299
Yuan C, Mitsumori LM, Ferguson MS, Polissar NL, Echelard D, Ortiz G, Small R, Davies JW, Kerwin WS, Hatsukami TS (2001) In vivo accuracy of multispectral magnetic resonance imaging for identifying lipid-rich necrotic cores and intraplaque hemorrhage in advanced human carotid plaques. Circulation 104:2051–2056
Yuan C, Zhang SX, Polissar NL, Echelard D, Ortiz G, Davis JW, Ellington E, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS (2002) Identification of fibrous cap rupture with magnetic resonance imaging is highly associated with recent transient ischemic attack or stroke. Circulation 105:181–185
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esposito, L., Sievers, M., Sander, D. et al. Detection of unstable carotid artery stenosis using MRI. J Neurol 254, 1714–1722 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0634-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0634-4