Abstract
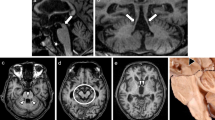
The characteristics of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA) on routine magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are reviewed. In PSP, atrophy of the midbrain tegmentum, truncus of corpus callosum and anterior cingulate cortex was seen on midsagittal plane MRI. These findings probably relate to supranuclear gaze palsy, motor programming dysfunction and emotional dysfunction. In CBD, asymmetric frontoparietal atrophy is usually seen, which could be the basis of focal signs. In MSA, putaminal and pontine involvements are represented by the hyperintense rim and ‘hot-cross bun’ signs on MRI. These would be closely linked via the premotor and motor cortex, which supervise motor execution. MRI findings mirror the clinical signs and symptoms in atypical parkinsonism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai K,Kato N, Ishikawa C,Hirano S, Komatsu K, Hattori T (2005) Features of mid-sagittal MRI in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 20 (Suppl 12):S129–130
Baumgardner TL, Singer HS, Denckla MB, Rubin MA, Abrams MT, Colli MJ, Reiss AL (1996) Corpus callosum morphology in children with Tourette syndrome and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Neurology 47:477–482
Bergeron C, Pollanen MS, Weyer L, Lang AE (1997) Cortical degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. A comparison with cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 56:726–734
Boxer AL, Geschwind MD, Belfor N, Gorno-Tempini ML, Schauer GF, Miller BL, Weiner MW, Rosen HJ (2006) Patterns of brain atrophy that differentiate corticobasal degeneration syndrome from progressive supranuclear palsy. Arch Neurol 63:81–86
Brodal P (1978) The corticopontine projection in the rhesus monkey.Origin and principles of organization. Brain 101:251–283
de Lacoste M, Kirkpatrick J, Ross E (1985) Topography of the human corpus callosum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 44:578–591
Devinsky O, Morrell MJ, Vogt BA (1995) Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain 118:279–306
Doi T, Iwasa K, Makifuchi T, Takamori M (1999) White matter hyperintensities on MRI in a patient with corticobasal degeneration. Acta Neurol Scand 99:199–201
Gilman S, Low PA, Quinn N, Albanese A, Ben-Shlomo Y, Fowler CJ, Kaufmann H, Klockgether T, Lang AE, Lantos PL, Litvan I, Mathias CJ, Oliver E, Robertson D, Schatz I, Wenning GK (1999) Consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Sci 163:94–98
Groschel K, Hauser TK, Luft A, Patronas N, Dichgans J, Litvan I, Schulz JB (2004) Magnetic resonance imaging-based volumetry differentiates progressive supranuclear palsy from corticobasal degeneration. Neuroimage 21:714–724
Grossman M, Crino P, Reivich M, Stern MB, Hurtig HI (1992) Attention and sentence processing deficits in Parkinson’s disease: the role of anterior cingulate cortex. Cereb Cortex 2:513–525
Grossman M, McMillan C, Moore P, Ding L, Glosser G, Work M, Gee J (2004) What’s in a name: voxel-based morphometric analyses of MRI and naming difficulty in Alzheimer’s disease, frontotemporal dementia and corticobasal degeneration. Brain 127:628–649
Haber SN, Fudge JL, McFarland NR (2000) Striatonigrostriatal pathways in primates form an ascending spiral from the shell to the dorsolateral striatum. J Neurosci 20:2369–2382
Hanihara T, Amano N, Takahashi T, Nagatomo H, Yagashita S (1995) Distribution of tangles and threads in the cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuropathol Applied Neurobiol 21:319–326
Jellinger KA, Seppi K, Wenning GK (2005) Grading of neuropathology in multiple system atrophy: proposal for a novel scale. Mov Disord 20 (Suppl 12):S29–36
Josephs KA, Tang-Wai DF, Edland SD, Knopman DS, Dickson DW, Parisi JE, Petersen RC, Jack CR, Jr., Boeve BF (2004) Correlation between antemortem magnetic resonance imaging findings and pathologically confirmed corticobasal degeneration. Arch Neurol 61:1881–1884
Josephs KA, Whitwell JL, Boeve BF, Shiung MM, Gunter JL, Parisi JE, Dickson DW, Jack CR (2006) Rates of cerebral atrophy in autopsy-confirmed progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 59:200–203
Kato N, Arai K, Hattori T (2003) Study of the rostral midbrain atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Sci 210:57–60
Kraft E, Schwarz J, Trenkwalder C,Vogl T, Pfluger T,Oertel WH (1999) The combination of hypointense and hyperintense signal changes on T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging sequences: a specific marker of multiple system atrophy? Arch Neurol 56:225–228
Kraft E, Trenkwalder C, Auer DP (2002) T2*-weighted MRI differentiates multiple system atrophy from Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 59:1265–1267
Lichter DG (2001) Movement disorders and frontal-subcortical circuits. In: Lichter DG, Cummings JL (eds) Frontal-Subcortical Circuits in Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders. The Guilford Press, New York, pp 260–313
Naka H, Imon Y, Ohshita T,Honjo K, Kitamura T, Miyachi T, Katayama S, Mimori Y, Nakamura S (2002) Magnetization transfer measurements of brain structures in patients with multiple system atrophy. Neuroimage 17:1572–1578
Paviour DC, Price SL, Jahanshahi M, Lees AJ, Fox NC (2006) Longitudinal MRI in progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy: rates and regions of atrophy. Brain 129:1040–1049
Quinn NP (2005) How to diagnose multiple system atrophy. Mov Disord 20 (Suppl 12):S5-S10
Righini A, Antonini A, Ferrarini M, de Notaris R, Canesi M, Triulzi F, Pezzoli G (2002) Thin section MR study of the basal ganglia in the differential diagnosis between striatonigral degeneration and Parkinson disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:266–271
Salmon E, Meulemans T, van der Linden M, Degueldre C, Franck G (1996) Anterior cingulate dysfunction in presenile dementia due to progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neurol Belgica 96:247–253
Salmon E, Van der Linden MV, Franck G (1997) Anterior cingulate and motor network metabolic impairment in progressive supranuclear palsy. Neuroimage 5:173–178
Savoiardo M, Grisoli M, Girotti F (2000) Magnetic resonance imaging in CBD, related atypical parkinsonian disorders, and dementias. Adv Neurol 82:197–208
Schrag A, Good CD, Miszkiel K, Morris HR, Mathias CJ, Lees AJ, Quinn NP (2000) Differentiation of atypical parkinsonian syndromes with routine MRI. Neurology 54:697–702
Schrag A, Kingsley D, Phatouros C, Mathias CJ, Lees AJ, Daniel SE, Quinn NP (1998) Clinical usefulness of magnetic resonance imaging in multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65:65–71
Schwarz J, Weis S, Kraft E, Tatsch K, Bandmann O, Mehraein P, Vogl T, Oertel WH (1996) Signal changes on MRI and increases in reactive microgliosis, astrogliosis, and iron in the putamen of two patients with multiple system atrophy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 60:98–101
Soliveri P, Monza D, Paridi D, Radice D, Grisoli M, Testa D, Savoiardo M, Girotti F (1999) Cognitive and magnetic resonance imaging aspects of corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurology 53:502–507
Taki M, Ishii K, Fukuda T,Kojima Y, Mori E (2004) Evaluation of cortical atrophy between progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration by hemispheric surface display of MR images. Am J Neuroradiol 25:1709–1714
Tsuchiya K, Ozawa E, Haga C, Watabiki S, Ikeda M, Sano M, Ooe K, Taki K, Ikeda K (2000) Constant involvement of the Betz cells and pyramidal tract in multiple system atrophy: a clinicopathological study of seven autopsy cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 99:628–636
Ukmar M, Moretti R, Torre P, Antonello RM, Longo R, Bava A (2003) Corticobasal degeneration: structural and functional MRI and single-photon emission computed tomography. Neuroradiology 45:708–712
Vermersch P, Robitaille Y, Bernier L, Wattez A, Gauvreau D, Delacourte A (1994) Biochemical mapping of neurofibrillary degeneration in a case of progressive supranuclear palsy: evidence for general cortical involvement. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87:572–577
von Economo C (1929) The Cytoarchitectonics of the Human Cerebral Cortex. Humphrey Milford and Oxford University Press, London
Voogd J (2004) Cerebellum and Precerebellar Nuclei. In: Paxinos G, Mai JK (eds) The Human Nervous System. Elsevier Academic Press, San Diego, pp 321–392
Wenning GK, Seppi K, Tison F, Jellinger K (2002) A novel grading scale for striatonigral degeneration (multiple system atrophy). J Neural Transm 109:307–320
Winkelmann J, Auer DP, Lechner C, Elbel G, Trenkwalder C (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging findings in corticobasal degeneration. Mov Disord 14:669–673
Yamauchi H, Fukuyama H, Nagahama Y, Katsumi Y, Dong Y, Konishi J, Kimura J (1997) Atrophy of the corpus callosum, cognitive impairment, and cortical hypometabolism in progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 41:606–614
Yekhlef F, Ballan G,Macia F, Delmer O, Sourgen C, Tison F (2003) Routine MRI for the differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease, MSA, PSP, and CBDJ Neural Transm 110:151–169
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, K. MRI of progressive supranuclear palsy, corticobasal degeneration and multiple system atrophy. J Neurol 253 (Suppl 3), iii25–iii29 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-3005-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-3005-7