Abstract
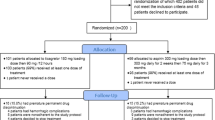
Argatroban, which is a thrombin inhibitor, has an indication as a treatment in the acute phase on atherosclerotic ischemic stroke in Japan. Howeve, in cardioembolic stroke, argatroban is considered to be contraindicated with the side effect of hemorrhage, though there is no clear clinical evidence to show that argatroban increases hemorrhagic compared with heparin. The efficacy of anticoagulant treatment with argatroban on cardioembolic stroke was evaluated retrospectively in this study. We identified 3,113 patients from the Japan Standard Stroke Registry Study who had had a cardioembolic ischemic stroke. We excluded patients with the anti-platelet treatment or the combination therapy of anticoagulation. Our analyses are therefore based on a cohort of 2,529 patients who were treated either with heparin, and argatroban, or with no anti-coagulation treatment. With multivariable regression, hemorrhagic it was shown that hemorrhage was significantly reduced in heparin and argatroban treatments in the patients with mild severity. There was no significant difference in the recurrence of ischemic stroke between the treatments. Both argatroban and heparin showed dramatic improvement compared with the no treatment standard, but only heparin achieved statistical significance for mortality and change in NIHSS score (admission to discharge) in the moderate stroke subgroup [NIHSS 11-2]. Both heparin and argatroban [more so than heparin alone] have a significantly reduced mortality risk. From the present study, it is suggested that argatroban may be useful on cardioembolic stroke, increasing the improvement of recovery of stroke severity without increasing the risk of hemorrhage. Further prospective studies are awaited for evaluating better the efficacy of argatroban on cardioembolic stroke.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry CN, Girardot C, Lecoffre C, Lunven C (1994) Effects of the synthetic thrombin inhibitor argatroban on fibrin- or clot-incorporated thrombin: comparison with heparin and recombinant Hirudin. Thromb Haemost 72:381-86
Brott T, Adams HP, Jr., Olinger CP, Marler JR, Barsan WG, Biller J, Spilker J, Holleran R, Eberle R, Hertzberg V, et al. (1989) Measurements of acute cerebral infarction: a clinical examination scale. Stroke 20:864-70
Goldstein LB, Bertels C, Davis JN (1989) Interrater reliability of the NIH stroke scale. Arch Neurol 46:660-62
Hantgan RR, Jerome WG, Hursting MJ (1998) No effect of clot age or thrombolysis on argatroban's inhibition of thrombin. Blood 92:2064-074
International (1997) The International Stroke Trial (IST): a randomised trial of aspirin, subcutaneous heparin, both, or neither among 19435 patients with acute ischaemic stroke. International Stroke Trial Collaborative Group. Lancet 349:1569-581
Kario K, Kodama K, Koide M, Matsuo T (1995) Thrombin inhibition in the acute phase of ischaemic stroke using argatroban. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 6:423-27
Kathiresan S, Shiomura J, Jang IK (2002) Argatroban. J Thromb Thrombolysis 13:41-7
Kobayashi S, Tazaki Y (1997) Effect of the thrombin inhibitor argatroban in acute cerebral thrombosis. Semin Thromb Hemost 23:531-34
Kondo LM, Wittkowsky AK, Wiggins BS (2001) Argatroban for prevention and treatment of thromboembolism in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Ann Pharmacother 35:440-51
LaMonte MP, Brown PM, Hursting MJ (2004) Stroke in patients with heparininduced thrombocytopenia and the effect of argatroban therapy. Crit Care Med 32:976-80
LaMonte MP, Nash ML, Wang DZ, Woolfenden AR, Schultz J, Hursting MJ, Brown PM (2004) Argatroban anticoagulation in patients with acute ischemic stroke (ARGIS-1): a randomized, placebo-controlled safety study. Stroke 35:1677-682
Lewis BE, Wallis DE, Berkowitz SD, Matthai WH, Fareed J, Walenga JM, Bartholomew J, Sham R, Lerner RG, Zeigler ZR, Rustagi PK, Jang IK, Rifkin SD, Moran J, Hursting MJ, Kelton JG (2001) Argatroban anticoagulant therapy in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Circulation 103:1838-843
Matsuo T, Kario K, Matsuda S, Yamaguchi N, Kakishita E (1995) Effect of Thrombin Inhibition on Patients with Peripheral Arterial Obstructive Disease: A Multicenter Clinical Trial of Argatroban. J Thromb Thrombolysis 2:131-36
Morris DC, Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Lu M, Berens KL, Brown PM, Chopp M (2001) Extension of the therapeutic window for recombinant tissue plasminogen activator with argatroban in a rat model of embolic stroke. Stroke 32:2635-640
Murray CJ, Lopez AD (1997) Mortality by cause for eight regions of the world: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 349:1269-276
NINDS (1990) Special report from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Classification of cerebrovascular diseases III. Stroke 21:637-76
Ohyama H, Hosomi N, Takahashi T, Mizushige K, Kohno M (2001) Thrombin inhibition attenuates neurodegeneration and cerebral edema formation following transient forebrain ischemia. Brain Res 902:264-71
Urabe T, Tanaka R, Noda K, Mizuno Y (2002) Anticoagulant therapy with a selective thrombin inhibitor for acute cerebral infarction: usefulness of coagulation markers for evaluation of efficacy. J Thromb Thrombolysis 13:155-60
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJ, van Gijn J (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19:604-07
Vermeer F, Vahanian A, Fels PW, Besse P, Muller E, Van de Werf F, Fitzgerald D, Darius H, Puel J, Garrigou D, Simoons ML (2000) Argatroban and alteplase in patients with acute myocardial infarction: the ARGAMI Study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 10:233-40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Additional information
JSSRS Group: Division of Stroke Data Bank, The Japan Stroke Association, Osaka 545-0052, Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosomi, N., Naya, T., Kohno, M. et al. Efficacy of anti-coagulant treatment with argatroban on cardioembolic stroke. J Neurol 254, 605–612 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0365-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0365-y