Abstract
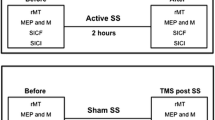
Somatosensory stimulation enhances aspects of motor function in patients with chronic, predominantly subcortical infarcts. We investigated the effects of somatosensory stimulation on motor function in stroke patients with predominantly cortical involvement in the middle cerebral artery territory in a double-blind, pseudorandomized crossover trial. Motor performance was evaluated with the Jebsen-Taylor test before, after 2-hour somatosensory stimulation, and after subsequent motor training (n = 11). In one experimental session, patients were submitted to median nerve stimulation (MNS) and in the other session, to control stimulation (CS). The order of the sessions was counterbalanced across patients. Improvement in performance in the Jebsen-Taylor test after somatosensory stimulation and after motor training was significantly greater in the MNS session than in the CS session. Additionally, patients who received MNS in the second session maintained the beneficial effects of training 30 days later. A single MNS session improves hand motor function in patients with chronic cortico-subcortical strokes and appears to favor consolidation of training effects. Somatosensory stimulation may be an adjuvant tool for stroke rehabilitation in patients with cortical lesions.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calautti C, Baron JC (2003) Functional neuroimaging studies of motor recovery after stroke in adults: a review. Stroke 34:1553–1566
Conforto AB, Kaelin-Lang A, Cohen LG (2002) Increase in hand muscle strength of stroke patients after somatosensory stimulation. Ann Neurol 51:122–125
Dobkin BH (2003) Do electrically stimulated sensory inputs and movements lead to long-term plasticity and rehabilitation gains? Curr Opin Neurol 16:685–691
Fraser C, Power M, Hamdy S, Rothwell J, Hobday D, Hollander I, Tyrell P, Hobson A, Williams S, Thompson D (2002) Driving plasticity in human adult motor cortex is associated with improved motor function after brain injury. Neuron 34:831–840
Hackel ME, Wolfe GA, Bang SM, Canfield JS (1992) Changes in hand function in the aging adult as determined by the Jebsen Test of Hand Function. Phys Ther 72:373–377
Jebsen RH, Taylor N, Trieschmann RB, Trotter MJ, Howard LA (1969) An objective and standardized test of hand function. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 50:311–319
Kaelin-Lang A, Luft AR, Sawaki L, Burstein AH, Sohn YH, Cohen LG (2002) Modulation of human corticomotor excitability by somatosensory input. J Physiol 540:623–633
Luft AR, Waller S, Forrester L, Smith GV, Whitall J, Macko RF, Schulz JB, Hanley DF (2004) Lesion location alters brain activation in chronically impaired stroke survivors. Neuroimage 21:924–935
Reding MJ, Potes E (1988) Rehabilitation outcome following initial unilateral hemispheric stroke. Life table analysis approach. Stroke 19:1354–1358
Ridding MC, Brouwer B, Miles TS, Pitcher JB, Thompson PD (2000) Changes in muscle responses to stimulation of the motor cortex induced by peripheral nerve stimulation in human subjects. Exp Brain Res 131:135–143
Sawaki L, Wu CW, Kaelin-Lang A, Cohen LG (2006) Effects of somatosensory stimulation on use-dependent plasticity in chronic stroke. Stroke 37:246–247
Tiplady B, Jackson SH, Maskrey VM, Swift CG (1998) Validity and sensitivity of visual analogue scales in young and older healthy subjects. Age Ageing 27:63–66
Uy J, Ridding MC, Hillier S, Thompson PD, Miles TS (2003) Does induction of plastic change in motor cortex improve leg function after stroke? Neurology 61:982–984
Wu CW, Seo HJ, Cohen LG (2006) Influence of electric somatosensory stimulation on paretic-hand function in chronic stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 87:351–357
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received in revised form: 2 August 2006
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conforto, A.B., Cohen, L.G., Santos, R.L.d. et al. Effects of somatosensory stimulation on motor function in chronic cortico-subcortical strokes. J Neurol 254, 333–339 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0364-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-006-0364-z