Abstract
This study aimed at an analysis of the release of Braintype and Heart–type Fatty Acid– Binding Proteins (B–FABP and HFABP) in acute ischaemic stroke and their potential value as neurobiochemical markers of brain damage.
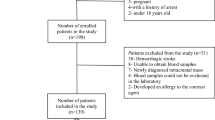
We investigated 42 consecutive patients admitted within 6 hours after ischaemic stroke. Serial venous blood samples were taken hourly between 1 to 6 hours, and at 12, 18, 24, 48, 72, 96, and 120 hours after stroke onset. In all patients lesion topography was assessed and infarct volume was calculated. The neurological deficit was quantified by the National Institutes of Health stroke scale score, and functional outcome was assessed with the modified Rankin Scale 3 months after stroke.
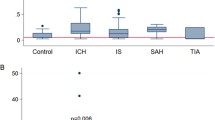
H–FABP and B–FABP concentrations showed peak values already 2 to 3 hours after stroke onset and remained elevated up to last measurements at 120 hours.Unlike BFABP, early H–FABP concentrations were significantly associated with the severity of the neurological deficit and the functional outcome. High H–FABP release was associated with large infarction on CT.
Our study shows for the first time quantitative data of serum BFABP and H–FABP being elevated early in acute ischaemic stroke indicating that especially H–FABP might have the potential to be a rapid marker of brain damage and clinical severity. As both FABPs indicate damage to neuronal and glial tissue but are not specific for cerebral infarction, further investigations are needed to better understand the prolonged release of both in ischaemic stroke which is in contrast to the transient increase after myocardial infarction and can not be explained by their renal extraction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraha HD, Butterworth RJ, Bath PMW, WassifWS, Garthwaite J, Sherwood RA (1997) Serum S–100 protein, relationship to clinical outcome in acute stroke. Ann Clin Biochem 34:366–370
Adams HP, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh III, EE and the TOAST Investigators (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 24:35–41
Bamford J, Sandercock P, Dennis M, Burn J, Warlow C (1991) Classification and natural history of clinically identifiable subtypes of cerebral infarction. Lancet 337:1521–1526
Bass NM, Barker ME, Manning JA, Jones AL, Ockner RJ (1989) Acinar heterogeneity of fatty acid–binding protein in the livers of male, female and clofibrate treated rats. Hepatology 9:12–21
Bertsch T, Casarin W, Kretschmar M, Zimmer W, Walter S, Sommer C, Muehlhauser F, Ragoschke A, Kuehl S, Schmidt R, Pohlmann–Eden B, Nassabi C, Nichterlein T, Fassbender K (2001) Protein S–100B: A serum marker for ischemic and infectious injury of cerebral tissue. Clin Chem Lab Med 39:319–323
Büttner T, Weyers S, Postert T, Sprengelmeyer R, Kuhn W (1997) S–100 Protein: Serum marker of focal brain damage after ischemic territorial MCA infarction. Stroke 28:1961–1965
De Groot MJM, Wodzig KWH, Simoons ML, Glatz JFC, Hermens WT (1999) Measurement of myocardial infarct size from plasma fatty acid–binding protein or myoglobin, using individually estimated clearance rates. Cardiovasc Res 44:315–324
Elting JW, de Jaeger AEJ, Teelken AW, Schaaf MJ, Maurits NM, van der Naalt J, Smit Sibinga CT, Sulter GA, de Keyser J (2000) Comparison of serum S–100 protein levels following stroke and traumatic brain injury. J Neurol Sci 181:104–110
Fassbender K, Schmidt R, Schreiner A, Fatar M, Mühlhauser F, Daffertshofer M, Hennerici M (1997) Leakage of brain–originated proteins in peripheral blood: temporal profile and diagnostic value in early ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci 148:101–105
Feng L, Hatten ME, Heintz N (1994) Brain lipid–binding protein (BLBP): a novel signalling system in the developing mammalian CNS. Neuron 12:895–908
Foerch C, du Mesnil de Rochement R, Singer O, Neumann–Haefelin T, Buchkremer M, Zanella FE, Steinmetz H, Sitzer M (2003) S100B as a surrogate marker for successful clot lysis in hyperacute middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 74:322–325
Glatz JFC, Van der Voort D, Hermens WT (2002) Fatty acid–binding protein as the earliest available plasma marker of acute myocardial injury. J Clin Lig Assay 25:167–177
Glatz JFC, Van der Vusse GJ (1996) Cellular fatty acid–binding proteins. Their function and physiological significance. Prog Lipid Res 35:253–282
Glatz JFC, Van der Vusse GJ, Simoons ML, Kragten JA, Van Dieijen–Visser MP, Hermens WT (1998) Fatty acidbinding protein and the early detection of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta 272:87–92
Herrmann M, Vos P, Wunderlich MT, de Bruijn CHMM, Lamers KJB (2000) Release of glial tissue–specific proteins after acute stroke. Stroke 31:2670–2677
Herrmann M, Ehrenreich H (2003) Brain derived proteins as markers of acute stroke: their relation to pathophysiology, outcome prediction and neuroprotective drug monitoring. Restor Neurol Neurosci 21:177–190
Heuckeroth RO, Birkenmeier EH, Levin MS, Gordon JI (1987) Analysis of the tissue–specific expression, developmental regulation, and linkage relationship of a rodent gene encoding heart fatty acid binding protein. J Biol Chem 262:9709–9717
Jönsson H (2003) S100B and cardiac surgery: Possibilities and limitations. Restor Neurol Neurosci 21:151–157
Kurtz A, Zimmer A, Schnütgen F, Glatz JFC, Hermens WT (1994) The expression pattern of a novel gene encoding brain–fatty acid binding protein correlates neuronal and glial cell development. Development 120:2637–2649
Lyden P, Brott T, Tilley B, Welch KM, Mascha EJ, Levine S, Haley EC, Grotta J, Marler J (1994) Improved reliability of the NIH Stroke Scale using video training. NINDS TPA Stroke Study Group. Stroke 25:2220–2226
Mahony FI, Barthel DW (1965) Functional evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md Med J 14:61–65
Marchi N, Cavaglia M, Fazio V, Bhudia H, Hallene K, Janigro D (2004) Peripheral markers of the blood–brain barrier damage. Clin Chim Acta 342:1–12
Myers–Payne SC, Hubbell T, Pu L, Schnütgen F, Börchers T, Wood WG, Spener F, Schroeder F (1996) Isolation and characterization of two fatty acid binding proteins from mouse brain. J Neurochem 66:1648–1656
Missler U, Wiesmann M, Friedrich C, Kaps M (1997) S–100 protein and neuron– specific enolase concentrations in blood as indicator of stroke volume. Stroke 28:1956–1960
Nakata T, Hashimoto A, Hase M, Tsuchihashi K, Shimamoto K (2003) Human heart–type fatty acid–binding protein as an early diagnostic and prognostic marker in acute coronary syndrome. Cardiology 99:96–104
Oh SH, Lee JG, Na SJ, Park JH, Choi YC, Kim WJ (2003) Prediction of early clinical severity and extent of neuronal damage in anterior–circulation infarction using the initial serum neuronspecific enolase level. Arch Neurol 60:37–41
Pagani F, Bonora R, Bonetti G, Panteghini M (2002) Evaluation of a sandwich enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay for the measurement of serum heart fatty acid–binding protein. Ann Clin Biochem 39:404–405
Pelsers MMAL, Chapelle JP, Knapen M, Hermens WT, Glatz JFC (1999) Influence of age and sex and day–to–day and within–day biological variation on plasma concentrations of fatty acidbinding protein and myoglobin in healthy subjects. Clin Chem 45: 441–443
Pelsers MMAL, Lutgerink JT, Nieuwenhoven FA, Tandon NN, van der Vusse GJ, Arends JW, Hoogenboom HR, Glatz JF (1999) A sensitive immunoassay for rat fatty acid translocase (CD36) using phage antibodies selected on cell transfectants: abundant presence of fatty acid translocase/CD36 in cardiac and red skeletal muscle and up–regulation in diabetes. Biochem J 337:407–414
Pelsers MMAL, Hanhoff T, Van der Voort D, Arts B, Peters M, Ponds R, Honig A, Rudzinski WW, Spener F, de Kruijk JR, Twijnstra A, Hermens WT, Menheere PPCA, Glatz JFC (2004) Brain–type and Heart–type Fatty Acid–Binding Proteins in the Brain; Tissue Distribution and Clinical Utility. Clin Chem 50:1568–1575
Pu L, Igbavboa U, Wood WG, Roths JB, Kier AB, Spener F, Schroeder F (1999) Expression of fatty acid binding proteins is altered in aged mouse brain. Mol Cell Biochem 198:69–78
Reynolds MA, Kirchick HJ, Dahlen JR, Anderberg JM, McPherson PH, Nakamura KK, Laskowitz DT, Valkirs GE, Buechler KF (2003) Early biomarkers of stroke. Clin Chem 49:1733–1739
Reiber H (2003) Proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and blood: Barriers, CSF flow rate and source–related dynamics. Restor Neurol Neurosci 21:79–96
Sambandam N, Lopaschuk GD (2003) AMP–activated protein kinase (AMPK) control of fatty acid and glucose metabolism in the ischemic heart. Prog Lipid Res 42:238–256
van Breda E, Keizer HA, Vork MM, Surtel DA, de Yong YF (1992) Modulation of fatty acid–binding protein content of rat heart and skeletal muscle by endurance training and testosterone treatment. Eur J Physiol 421:274–279
Van Nieuwenhoven FA, Kleine AH, Wodzig KWH, Hermens WT, Kragten HA, Maessen JG, Punt CD, Van Dieijen MP, Van der Vusse GJ, Glatz JFC (1995) Discrimination between myocardial and skeletal muscle injury by assessment of the plasma ration of myoglobin over fatty acid–binding protein. Circulation 92:2848–2854
Van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC, Schouten HJA, van Gijr J (1988) Interobserver agreement for the assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke 19:604–607
Veerkamp JH, Zimmerman AW (2001) Fatty acid–binding proteins of nervous tissue. J Mol Neurosci 16:133–142
Wunderlich MT, Ebert, AD, Kratz T, Goertler M, Jost S, Herrmann M (1999) Early neurobehavioral outcome after stroke is related to release of neurobiochemical markers of brain damage. Stroke 30:1190–1195
Wodzig KWH, Pelsers MMAL, Van der Vusse GJ, Roos W, Glatz JFC (1997) One–step enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for fatty acid–binding protein. Ann Clin Biochem 34:263–268
Zimmermann–Ivol C, Burkhard P, Le Floch–Rohr J, Allard L, Hochstrasser D, Sanchez JC (2004) Fatty acid binding protein as a serum marker for the early diagnosis of stroke: a pilot study. Mol Cell Proteomics 3:66–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wunderlich, M.T., Hanhoff, T., Goertler, M. et al. Release of brain–type and heart–type fatty acid–binding proteins in serum after acute ischaemic stroke. J Neurol 252, 718–724 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0725-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0725-z