Abstract
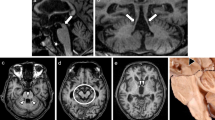
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD) are often clinically confused with each other. Moreover, the discrepancy between clinical and pathological diagnoses of CBD and PSP are still controversial. We report here two atypical cases of PSP and CBD. A 73–yearold woman was admitted with right hand rigidity, limb kinetic apraxia and cortical sensory loss. Brain atrophy, hypoperfusion and hypometabolism predominantly in the left frontoparietal lobes indicated CBD clinically. Pathological studies revealed neuronal loss and spongy change without ballooned neurons (BN) in the cerebral cortex. Modified Gallyas–Braak (G–B) staining revealed neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and tufted astrocytes, indicating pathological diagnosis of PSP. A 75–year–old man admitted with vertical gaze palsy, neck dystonia, parkinsonism and dementia. Atrophy of the frontal lobes and tegmentum of the midbrain and symmetrical frontal hypoperfusion in SPECT indicated PSP. However, neuronal loss and BN in the frontal lobes and clusters of astrocytic plaques indicated CBD pathologically. The G–B staining was useful for differentiating between CBD and PSP, but our atypical cases bring up a new issue about differential diagnosis of CBD and PSP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai T, Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Nonaka T, Hasegawa M, Ishiguro K, Iritani S, Tsuchiya K, Iseki E, Yagishita S, Oda T, Mochizuki A (2004) Identification of amino-terminally cleaved tau fragments that distinguish progressive supranuclear palsy from corticobasal degeneration. Ann Neurol 55:72–79
Arai T, Ikeda K, Akiyama H, Shikamoto Y, Tsuchiya K, Yagishita S, Beach T, Rogers J, Schwab C, McGeer PL (2001) Distinct isoforms of tau aggregated in neurons and glial cells in brains of patients with Pick’s disease, corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 101:167–173
Bergeron C, Pollanen MS, Weyer L, Black SE, Lang AE (1996) Unusual clinical presentations of cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Ann Neurol 40:893–900
Dickson DW, Bergeron C, Chin SS, Duyckaerts C, Horoupian D, Ikeda K, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, Lippa CF, Mirra SS, Tabaton M, Vonsattel JP, Wakabayashi K, Litvan I (2002) Office of Rare Diseases neuropathologic criteria for corticobasal degeneration. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:935–946
Gibb WR, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD (1989) Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 112(Pt 5):1171–1192
Hattori M, Yoshida M, Ojika K, Yuasa H, Mitake S, Hashizume Y (2000) An autopsy case of corticobasal degeneration without prominent cortical pathology – an imitator of progressive supranuclear palsy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 40:372–377
Hauw JJ, Daniel SE, Dickson D, Horoupian DS, Jellinger K, Lantos PL, McKee A, Tabaton M, Litvan I (1994) Preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome (progressive supranuclear palsy). Neurology 44:2015–2019
Hauw JJ, Verny M, Delaere P, Cervera P, He Y, Duyckaerts C (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Basic differences with Alzheimer’s disease and aging. Neurosci Lett 119: 182–186
Hof PR, Delacourte A, Bouras C (1992) Distribution of cortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy: a quantitative analysis of six cases. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84:45–51
Ikebe S, Mori H, Sumino S, Takanashi M, Hamano Y, Shirai T, Ohkuma Y, Mizuno Y (2000) A 77-year-old man with gait and gaze disturbance. No To Shinkei 52:269–279
Inagaki T, Seno HI, Iijima M, Nagai A, Bokura H, Kobayashi S, Wada M, Harada T (1998) A case manifested overlapping neuropathologic features of both progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and corticobasal degeneration (CBD). No To Shinkei 50:263–271
Katsuse O, Iseki E, Arai T, Akiyama H, Togo T, Uchikado H, Kato M, de Silva R, Lees A, Kosaka K (2003) 4-repeat tauopathy sharing pathological and biochemical features of corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 106:251–260
Komori T, Arai N, Oda M, Nakayama H, Mori H, Yagishita S, Takahashi T, Amano N, Murayama S, Murakami S, Shibata N, Kobayashi M, Sasaki S, Iwata M (1998) Astrocytic plaques and tufts of abnormal fibers do not coexist in corticobasal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 96:401–408
Litvan I, Agid Y, Calne D, Campbell G, Dubois B, Duvoisin RC, Goetz CG, Golbe LI, Grafman J, Growdon JH, Hallett M, Jankovic J, Quinn NP, Tolosa E, Zee DS (1996) Clinical research criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele- Richardson-Olszewski syndrome): report of the NINDS-SPSP international workshop. Neurology 47:1–9
Litvan I, Agid Y, Goetz C, Jankovic J, Wenning GK, Brandel JP, Lai EC, Verny M, Ray-Chaudhuri K, McKee A, Jellinger K, Pearce RK, Bartko JJ (1997) Accuracy of the clinical diagnosis of corticobasal degeneration: a clinicopathologic study. Neurology 48: 119–125
Litvan I, Grimes DA, Lang AE, Jankovic J, McKee A, Verny M, Jellinger K, Chaudhuri KR, Pearce RK (1999) Clinical features differentiating patients with postmortem confirmed progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal degeneration. J Neurol 246(Suppl 2):II1–II5
Litvan I, Hauw JJ, Bartko JJ, Lantos PL, Daniel SE, Horoupian DS, McKee A, Dickson D, Bancher C, Tabaton M, Jellinger K, Anderson DW (1996) Validity and reliability of the preliminary NINDS neuropathologic criteria for progressive supranuclear palsy and related disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 55:97–105
Mori H, Nishimura M, Namba Y, Oda M (1994) Corticobasal degeneration: a disease with widespread appearance of abnormal tau and neurofibrillary tangles, and its relation to progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:113–121
Paulus W, Selim M (1990) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia and basal neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 81:89–94
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP Jr (1968) Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 18:20–33
Riley DE, Lang AE, Lewis A, Resch L, Ashby P, Hornykiewicz O, Black S (1990) Cortical-basal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 40:1203–1212
Rinne JO, Lee MS, Thompson PD, Marsden CD (1994) Corticobasal degeneration. A clinical study of 36 cases. Brain 117(Pt 5):1183–1196
Sako H, Nakamura H, Inoue K, Takada K, Tanaka J, Tabuchi Y (1986) Progressive supranuclear palsy – A case with a marked frontal atrophy. Neuropathol 7:7–14
Scully RE, Mark EJ, McNeely WF, McNeely BU (1993) Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 46 – 1993. N Engl J Med 329:1560–1567
Shiozawa M, Fukutani Y, Sasaki K, Isaki K, Hamano T, Hirayama M, Imamura K, Mukai M, Arai N, Cairns NJ (2000) Corticobasal degeneration: an autopsy case clinically diagnosed as progressive supranuclear palsy. Clin Neuropathol 19:192–199
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski J (1964) Progressive Supranuclear Palsy. A Heterogeneous Degeneration Involving the Brain Stem, Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum with Vertical Gaze and Pseudobulbar Palsy, Nuchal Dystonia and Dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Wakabayashi K, Oyanagi K, Makifuchi T, Ikuta F, Homma A, Homma Y, Horikawa Y, Tokiguchi S (1994) Corticobasal degeneration: etiopathological significance of the cytoskeletal alterations. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87:545–553
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizuno, ., Shiga, K., Nakata, . et al. Discrepancy between clinical and pathological diagnoses of CBD and PSP. J Neurol 252, 687–697 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0718-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0718-y