Abstract.
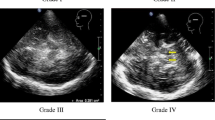
Transcranial ultrasound is a new tool allowing the detection of abnormalities in the echomorphology of the substantia nigra (SN) in patients with Parkinson's disease (PD). Several lines of evidence suggest that the changes in the echo-pattern represent a risk factor as: i) the majority of PD patients exhibit this echo-feature, ii) the presence of such changes in healthy controls is related to a reduced 18F-Dopa-uptake and clinical signs of nigrostriatal dysfunction. The reason for the change of echogenicity is suggested to be an increased iron content in the substantia nigra causing oxidative stress and neuronal cell damage. This hypothesis of changes in SN echomorphology reflecting a risk factor of PD has to be proved in longitudinal studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behnke, S., Berg, D. & Becker, G. Does ultrasound disclose a vulnerability factor for Parkinson's disease?. J Neurol 250 (Suppl 1), i24–i27 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-1104-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-1104-0