Abstract
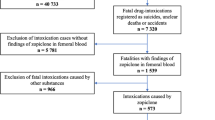
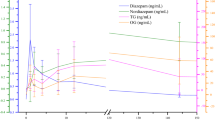
Today, new psychoactive substances (NPS) producers increasingly appear to be targeting new synthetic opioids (NSOs), and the recent emergence of NSOs is causing considerable concern in North America and in Europe. For toxicologists, NSO detection in a forensic context presents three additional difficulties to the general NPS analytical detection challenge: (i) high frequency of new products, (ii) low concentrations (in μg/L range and under) in biological samples related to their high opioid potency, and (iii) extensive metabolism. In this context, the present work aims to highlight the relevance of NSO metabolite detection in potential intoxication cases. Illustration is given with U-47700, an emerging NSO, (i) that was identified in a powder recently collected in France and in a fatality case, (ii) whose metabolites were in vitro produced using human liver microsomes and their mass spectra (MS) added in our MS/MS and HRMS libraries, and (iii) for which metabolism data were compared to those of the literature: U-47700 was identified in the powder and at 3040 μg/L in peripheral blood in the fatality case. In addition, high amounts of several U-47700 metabolites, especially N-desmethyl-U-47700, were observed in urine. Even if metabolite formation may largely depend on the enzymatic activity as well as on the length of the survival time, confrontation of these results to data found in the literature strongly suggests that this metabolite is regularly a better blood and (mainly) urine biomarker of U-47700 intake than U-47700 itself. Indeed, in this fatality and in other previous reports, N-desmethyl-U-47700 produced the main observed chromatographic signal (i) systematically in vitro and (ii) commonly in vivo, especially in urines. N,N-Didesmethyl-U-47700 is also sometimes a better biomarker of U-47700 intake than U-47700 itself. Accordingly, we suggest adding N-desmethyl-U-47700 (and N,N-didesmethyl-U-47700) in mass spectrum databases used for toxicological screening in order to reduce the risk of false-negative results in intoxication cases involving U-47700.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
EMCDDA (2017) European Drug Report 2017: Trends and Developments. Publications Office of the European Union, Luxembourg
Prekupec MP, Mansky PA, Baumann MH (2017) Misuse of novel synthetic opioids: a deadly new trend. J Addict Med 11:256–265. https://doi.org/10.1097/ADM.0000000000000324
Fabregat-Safont D, Carbón X, Ventura M, Fornís I, Guillamón E, Sancho JV, Hernández F, Ibáñez M (2017) Updating the list of known opioids through identification and characterization of the new opioid derivative 3,4-dichloro-N-(2-(diethylamino)cyclohexyl)-N-methylbenzamide (U-49900). Sci Rep 7(1):6338. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06778-9
Mohr AL, Friscia M, Papsun D, Kacinko SL, Buzby D, Logan BK (2016) Analysis of novel synthetic opioids U-47700, U-50488 and furanyl fentanyl by LC-MS/MS in postmortem casework. J Anal Toxicol 40(9):709–717. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkw086
Rambaran KA, Fleming SW, An J, Burkhart S, Furmaga J, Kleinschmidt KC, Spiekerman AM, Alzghari SK (2017) U-47700: a clinical review of the literature. J Emerg Med 53(4):509–519. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.05.034
Rohrig TP, Miller SA, Baird T (2017) U-47700: a not so new opioid. J Anal Toxicol 11:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkx081
Cheney BV, Szmuszkovicz J, Lahti RA, Zichi DA (1985) Factors affecting binding of trans-N-[2-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]benzamides at the primary morphine receptor. J Med Chem 28:1853–1864
Baumann MH, Majumdar S, Le Rouzic V, Hunkele A, Uprety R, Huang XP, Xu J, Roth BL, Pan YX, Pasternak GW (2017) Pharmacological characterization of novel synthetic opioids (NSO) found in the recreational drug marketplace. Neuropharmacology 134:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.08.016
Nikolaou P, Katselou M, Papoutsis I, Spiliopoulou C, Athanaselis S (2017) U-47700. An old opioid becomes a recent danger. Forensic Toxicol 35(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-016-0347-4
Coopman V, Cordonnier J (2017) ‘Spice-like’ herbal incense laced with the synthetic opioid U-47700. Toxicol Anal Clin 30:75–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2017.07.004
U-47700 Critical Review Report Agenda Item 4.1 Expert Committee on Drug Dependence Thirty-eighth Meeting Geneva, 14–18 November 2016 Available from http://www.who.int/medicines/access/controlled-substances/4.1_U-47700_CritReview.pdf
DEA Headquarters News. (2016) DEA schedules deadly synthetic drug U-47700. Drug Enforcement Administration. Washington D.C. https:// www.dea.gov/divisions/hq/2016/hq111016.shtml (accessed November 17, 2017)
Jones MJ, Hernandez BS, Janis GC, Stellpflug SJ (2017) A case of U-47700 overdose with laboratory confirmation and metabolite identification. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 55(1):55–59. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650.2016.1209767
Ruan X, Chiravuri S, Kaye AD (2016) Comparing fatal cases involving U-47700. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 12(3):369–371. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-016-9795-8
Drug Enforcement Administration, Department of Justice (2016) Schedules of Controlled Substances: Temporary Placement of U-47700 Into Schedule I. Final Order Fed Regist 81(219):79389–79393
Elliott SP, Brandt SD, Smith C (2016) The first reported fatality associated with the synthetic opioid 3,4-dichloro-N-[2-(dimethylamino) cyclohexyl]-N-methylbenzamide (U47700) and implications for forensic analysis. Drug Test Anal 8(8):875–879. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.1984
Coopman V, Blanckaert P, Van Parys G, Van Calenbergh S, Cordonnier J (2016) A case of acute intoxication due to combined use of fentanyl and 3,4-dichloro-N-[2 (dimethylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-methylbenzamide (U-47700). Forensic Sci Int 266:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.05.001
Dziadosz M, Klintschar M, Teske J (2017) Postmortem concentration distribution in fatal cases involving the synthetic opioid U-47700. Int J Legal Med 131(6):1555–1556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-017-1593-7
Kriikku P. Novel psychoactive substances in postmortem toxicology, http://emcdda.europa.eu/system/files/attachments/3233/Kriikku_NPS%20in%20postmortem%20investigations.pdf_en (accessed december 6 2017)
Bui TV, Batisse A, Marillier M, Bourgogne E, Djezzar S, Megarbane B (2017) L’arrivée des opioïdes de synthèse en France, un signal d’addictovigilance à surveiller : illustration par un cas clinique. Toxac 29:S60–S61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2017.03.087
UNODC (2017) World Drug Report 2017 (ISBN: 978–92–1-148291-1, eISBN: 978–92–1-060623-3, United Nations publication, Sales No. E.17.XI.6)
SFTA guidelines for the achievement of toxicological analyzes for deaths involving NPS (2018) Recommandations de la SFTA pour la réalisation des analyses toxicologiques dans les cas de décès impliquant des NPS. Toxicol Anal Clin 30:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2017.07.002
Kronstrand R, Brinkhagen L, Birath-Karlsson C, Roman M, Josefsson M (2014) LC-QTOF-MS as a superior strategy to immunoassay for the comprehensive analysis of synthetic cannabinoids in urine. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:3599–3609
Watanabe S, Vikingsson S, Roman M, Green H, Kronstrand R, Wohlfarth A (2107) In vitro and in vivo metabolite identification studies for the new synthetic opioids acetylfentanyl, acrylfentanyl, furanylfentanyl, and 4-fluoro-isobutyrylfentanyl. AAPS J 19(4):1102–1122. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-017-0070-z
Allibe N, Richeval C, Phanithavong M, Faure A, Allorge D, Paysant F, Stanke-Labesque F, Eysseric-Guerin H, Gaulier JM (2018) Fatality involving ocfentanil documented by identification of metabolites. Drug Test Anal 10(6):995–1000. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2326
Richeval C, Gicquel T, Hugbart C, Le Dare B, Allorge D, Morel I, Gaulier JM (2017) In vitro characterization of NPS metabolites produced by human liver microsomes and the HepaRG cell line using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS) analysis: application to furanyl fentanyl. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 18(10):806–814. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389201018666171122124401
Fleming SW, Cooley JC, Johnson L, Frazee CC, Domanski K, Kleinschmidt K, Garg U (2017) Analysis of U-47700, a novel synthetic opioid, in human urine by LC-MS-MS and LC-QToF. J Anal Toxicol 41(3):173–180. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkw131
Seither J, Reidy L (2017) Confirmation of Carfentanil, U-47700 and other synthetic opioids in a human performance case by LC-MS-MS. J Anal Toxicol 41(6):493–497. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkx049
Krotulski AJ, Mohr ALA, Papsun DM, Logan BK (2018) Metabolism of novel opioid agonists U-47700 and U-49900 using human liver microsomes with confirmation in authentic urine specimens from drug users. Drug Test Anal 10(1):127–136
Gaillard YP, Cuquel AC, Boucher A, Romeuf L, Bevalot F, Prevosto JM, Menard JM (2013) A fatality following ingestion of the designer drug meta-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) in an asthmatic—HPLC-MS/MS detection in biofluids and hair. J Forensic Sci 58(1):263–269. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1556-4029.2012.02254.x
Mazoyer C, Carlier J, Boucher A, Péoc'h M, Lemeur C, Gaillard Y (2013) Fatal case of a 27-year-old male after taking iboga in withdrawal treatment: GC-MS/MS determination of ibogaine and ibogamine in iboga roots and postmortem biological material. J Forensic Sci 58(6):1666–1672. https://doi.org/10.1111/1556-4029.12250
Carlier J, Guitton J, Romeuf L, Bévalot F, Boyer B, Fanton L, Gaillard Y (2015) Screening approach by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the blood quantification of thirty-four toxic principles of plant origin. Application to forensic toxicology. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 975:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.10.028
Peters FT, Drummer OH, Musshoff F (2007) Validation of new methods. Forensic Sci Int 165(2–3):216–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.forsciint.2006.05.021
Wille SMR, Peters FT, Di Fazio V, Samyn N (2011) Practical aspects concerning validation and quality control for forensic and clinical bioanalytical quantitative methods. Accred Qual Assur 16:279–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00769-011-0775-0
Feasel MG, Wohlfarth A, Nilles JM, Pang S, Kristovich RL, Huestis MA (2016) Metabolism of Carfentanil, an ultra-potent opioid, in human liver microsomes and human hepatocytes by high-resolution mass spectrometry. AAPS J 18:1489–1499. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-016-9963-5
Meyer MR, Dinger J, Schwaninger AE, Wissenbach DK, Zapp J, Fritschi G, Maurer HH (2012) Qualitative studies on the metabolism and the toxicological detection of the fentanyl-derived designer drugs 3-methylfentanyl and isofentanyl in rats using liquid chromatography-linear ion trap-mass spectrometry (LC-MS(n)). Anal Bioanal Chem 402:1249–1255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5528-8
Steuer AE, Williner E, Staeheli SN, Kraemer T (2017) Studies on the metabolism of the fentanyl-derived designer drug butyrfentanyl in human in vitro liver preparations and authentic human samples using liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). Drug Test Anal 9(7):1085–1092
Launiainen T, Ojanperä I (2014) Drug concentrations in post-mortem femoral blood compared with therapeutic concentrations in plasma. Drug Test Anal 6(4):308–316. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.1507
Seeger E. Pykrolidino ketones. Patent US; 1967/3314970 A
Uchiyama N, Shimokawa Y, Kawamura M, Kikura-Hanajiri R, Hakamatsuka T (2014) Chemical analysis of a benzofuran derivative, 2-(2-ethylaminopropyl)benzofuran (2-EAPB), eight synthetic cannabinoids, five cathinone derivatives, and five other designer drugs newly detected in illegal products. Forensic Toxicol 32(2):266–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11419-014-0238-5
Paul M, Bleicher S, Guber S, Ippisch J, Polettini A, Schultis W (2015) Identification of phase I and II metabolites of the new designer drug α-pyrrolidinohexiophenone (α-PHP) in human urine by liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS). J Mass Spectrom 50(11):1305–1317. https://doi.org/10.1002/jms.3642 Erratum in: J Mass Spectrom 2016 51(4):322
Manier SK, Richter LHJ, Schäper J, Maurer HH, Meyer MR (2018) Different in vitro and in vivo tools for elucidating the human metabolism of alpha-cathinone-derived drugs of abuse. Drug Test Anal 10:1119–1130. https://doi.org/10.1002/dta.2355
Fujita Y, Mita T, Usui K, Kamijo Y, Kikuchi S, Onodera M, Fujino Y, Inoue Y (2017) Toxicokinetics of the synthetic cathinone α-pyrrolidinohexanophenone. J Anal Toxicol 28:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/jat/bkx080
Nachon-Phanithavong M, Richeval C, Gaulier JM, Humbert L, Tournebize J, Kieffer P, Allorge D (2017) Intoxication aiguë et consommation chronique de cathinones chez un polyconsommateur. Toxac 29(2s):22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxac.2017.03.019
Marusich JA, Antonazzo KR, Wiley JL, Blough BE, Partilla JS, Baumann MH (2014) Pharmacology of novel synthetic stimulants structurally related to the “bath salts” constituent 3,4-methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV). Neuropharmacology 87:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.02.016
Short SA, Schultz J, Lawler E, Wells K (2016) Postmortem cases involving fentanyl derivatives and U-47700. Toxtalk 40(4):11–13
McIntyre IM, Gary RD, Joseph S, Stabbley R (2017) A fatality related to the synthetic opioid U-47700: postmortem concentration distribution. J Anal Toxicol 41(2):158–160
Kapil RP, Friedman K, Cipriano A, Michels G, Shet M, Mondal SA, Harris SC (2015) Effects of paroxetine, a CYP2D6 inhibitor, on the pharmacokinetic properties of hydrocodone after coadministration with a single-entity, once-daily, extended-release hydrocodone tablet. Clin Ther 37(10):2286–2296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.08.007
Feng XQ, Zhu LL, Zhou Q (2017) Opioid analgesics-related pharmacokinetic drug interactions: from the perspectives of evidence based on randomized controlled trials and clinical risk management. J Pain Res 10:1225–1239. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S138698
Schulz M, Iwersen-Bergmann S, Andresen H, Schmoldt A (2012) Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of nearly 1,000 drugs and other xenobiotics. Crit Care 16(4):R136. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc11441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richeval, C., Gaulier, JM., Romeuf, L. et al. Case report: relevance of metabolite identification to detect new synthetic opioid intoxications illustrated by U-47700. Int J Legal Med 133, 133–142 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1969-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00414-018-1969-3