Abstract.
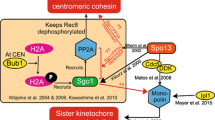
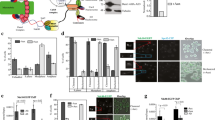
Faithful segregation of sister chromatids during cell division requires properly regulated cohesion between the sister centromeres. The sister chromatids are attached along their lengths, but particularly tightly in the centromeric regions. Therefore specific cohesion proteins may be needed at the centromere. Here we show that Drosophila MEI-S332 protein localizes to mitotic metaphase centromeres. Both overexpression and mutation of MEI-S332 increase the number of apoptotic cells. In mei-S332 mutants the ratio of metaphase to anaphase figures is lower than wild type, but it is higher if MEI-S332 is overexpressed. In chromosomal squashes centromeric attachments appear weaker in mei-S332 mutants than wild type and tighter when MEI-S332 is overexpressed. These results are consistent with MEI-S332 contributing to centromeric sister-chromatid cohesion in a dose-dependent manner. MEI-S332 is the first member identified of a predicted class of centromeric proteins that maintain centromeric cohesion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 December 1998; in revised form: 4 August 1999 / Accepted: 13 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
LeBlanc, H., Tang, TL., Wu, J. et al. The mitotic centromeric protein MEI-S332 and its role in sister-chromatid cohesion. Chromosoma 108, 401–411 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050392
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004120050392