Abstract
Mouse telomeres have been suggested to resemble common fragile sites (CFS), showing disrupted TTAGGG fluorescent in situ hybridization signals after aphidicolin treatment. This “fragile” telomere phenotype is induced by deletion of TRF1, a shelterin protein that binds telomeric DNA and promotes efficient replication of the telomeric ds[TTAGGG]n tracts. Here we show that the chromosome-internal TTAGGG repeats present at human chromosome 2q14 form an aphidicolin-induced CFS. TRF1 binds to and stabilizes CFS 2q14 but does not affect other CFS, establishing 2q14 as the first CFS controlled by a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. The data show that telomeric DNA is inherently fragile regardless of its genomic position and imply that CFS can be caused by a specific DNA sequence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez L, Evans JW, Wilks R, Lucas JN, Brown JM, Giaccia AJ (1993) Chromosomal radiosensitivity at intrachromosomal telomeric sites. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 8:8–14
Ashley T, Ward DC (1993) A "hot spot" of recombination coincides with an interstitial telomeric sequence in the Armenian hamster. Cytogenet Cell Genet 62:169–171
Bartkova J, Rezaei N, Liontos M, Karakaidos P, Kletsas D, Issaeva N, Vassiliou LV, Kolettas E, Niforou K, Zoumpourlis VC, Takaoka M, Nakagawa H, Tort F, Fugger K, Johansson F, Sehested M, Andersen CL, Dyrskjot L, Orntoft T, Lukas J, Kittas C, Helleday T, Halazonetis TD, Bartek J, Gorgoulis VG (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is part of the tumorigenesis barrier imposed by DNA damage checkpoints. Nature 444:633–637
Bertoni L, Attolini C, Tessera L, Mucciolo E, Giulotto E (1994) Telomeric and nontelomeric (TTAGGG)n sequences in gene amplification and chromosome stability. Genomics 24:53–62
Bester AC, Schwartz M, Schmidt M, Garrigue A, Hacein-Bey-Abina S, Cavazzana-Calvo M, Ben-Porat N, Von Kalle C, Fischer A, Kerem B (2006) Fragile sites are preferential targets for integrations of MLV vectors in gene therapy. Gene Ther 13:1057–1059
Bester AC, Roniger M, Oren YS, Im MM, Sarni D, Chaoat M, Bensimon A, Zamir G, Shewach DS, Kerem B (2011) Nucleotide deficiency promotes genomic instability in early stages of cancer development. Cell 145:435–446
Bianchi A, Smith S, Chong L, Elias P, de Lange T (1997) TRF1 is a dimer and bends telomeric DNA. Embo J 16:1785–1794
Bianchi A, Stansel RM, Fairall L, Griffith JD, Rhodes D, de Lange T (1999) TRF1 binds a bipartite telomeric site with extreme spatial flexibility. Embo J 18:5735–5744
Bignell GR, Greenman CD, Davies H, Butler AP, Edkins S, Andrews JM, Buck G, Chen L, Beare D, Latimer C, Widaa S, Hinton J, Fahey C, Fu B, Swamy S, Dalgliesh GL, Teh BT, Deloukas P, Yang F, Campbell PJ, Futreal PA, Stratton MR (2010) Signatures of mutation and selection in the cancer genome. Nature 463:893–898
Brueckner LM, Sagulenko E, Hess EM, Zheglo D, Blumrich A, Schwab M, Savelyeva L (2012) Genomic rearrangements at the FRA2H common fragile site frequently involve non-homologous recombination events across LTR and L1(LINE) repeats. Hum Genet. doi:10.1007/s00439-012-1165-3
Chu WK, Hickson ID (2009) RecQ helicases: multifunctional genome caretakers. Nat Rev Cancer 9:644–654
Ciullo M, Debily MA, Rozier L, Autiero M, Billault A, Mayau V, El Marhomy S, Guardiola J, Bernheim A, Coullin P, Piatier-Tonneau D, Debatisse M (2002) Initiation of the breakage-fusion-bridge mechanism through common fragile site activation in human breast cancer cells: the model of PIP gene duplication from a break at FRA7I. Hum Mol Genet 11:2887–2894
Coquelle A, Pipiras E, Toledo F, Buttin G, Debatisse M (1997) Expression of fragile sites triggers intrachromosomal mammalian gene amplification and sets boundaries to early amplicons. Cell 89:215–225
Cortez D, Guntuku S, Qin J, Elledge SJ (2001) ATR and ATRIP: partners in checkpoint signaling. Science 294:1713–1716
Day JP, Limoli CL, Morgan WF (1998) Recombination involving interstitial telomere repeat-like sequences promotes chromosomal instability in Chinese hamster cells. Carcinogenesis 19:259–65
de Lange T (2009) How telomeres solve the end-protection problem. Science 326:948–952
Dereli-Oz A, Versini G, Halazonetis TD (2011) Studies of genomic copy number changes in human cancers reveal signatures of DNA replication stress. Mol Oncol 5:308–314
Di Micco R, Fumagalli M, Cicalese A, Piccinin S, Gasparini P, Luise C, Schurra C, Garre' M, Nuciforo PG, Bensimon A, Maestro R, Pelicci PG, d'Adda di Fagagna F (2006) Oncogene-induced senescence is a DNA damage response triggered by DNA hyper-replication. Nature 444:638–642
Durkin SG, Glover TW (2007) Chromosome fragile sites. Annu Rev Genet 41:169–192
Feichtinger W, Schmid M (1989) Increased frequencies of sister chromatid exchanges at common fragile sites (1)(q42) and (19)(q13). Hum Genet 83:145–147
Fernandez JL, Gosalvez J, Goyanes V (1995) High frequency of mutagen-induced chromatid exchanges at interstitial telomere-like DNA sequence blocks of Chinese hamster cells. Chromosome Res 3:281–284
Fundia A, Gorla N, Larripa I (1995) Non-random distribution of spontaneous chromosome aberrations in two Bloom syndrome patients. Hereditas 122:239–243
Glover TW, Stein CK (1987) Induction of sister chromatid exchanges at common fragile sites. Am J Hum Genet 41:882–890
Glover TW, Stein CK (1988) Chromosome breakage and recombination at fragile sites. Am J Hum Genet 43:265–273
Gorgoulis VG, Vassiliou LV, Karakaidos P, Zacharatos P, Kotsinas A, Liloglou T, Venere M, Ditullio RAJ, Kastrinakis NG, Levy B, Kletsas D, Yoneta A, Herlyn M, Kittas C, Halazonetis TD (2005) Activation of the DNA damage checkpoint and genomic instability in human precancerous lesions. Nature 434:907–913
Hastie ND, Allshire RC (1989) Human telomeres: fusion and interstitial sites. Trends Genet 5:326–331
Hellman A, Zlotorynski E, Scherer SW, Cheung J, Vincent JB, Smith DI, Trakhtenbrot L, Kerem B (2002) A role for common fragile site induction in amplification of human oncogenes. Cancer Cell 1:89–97
Helmrich A, Ballarino M, Tora L (2011) Collisions between replication and transcription complexes cause common fragile site instability at the longest human genes. Mol Cell 44:966–977
IJdo JW, Baldini A, Ward DC, Reeders ST, Wells RA (1991) Origin of human chromosome 2: an ancestral telomere–telomere fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:9051–9055
Kilburn AE, Shea MJ, Sargent RG, Wilson JH (2001) Insertion of a telomere repeat sequence into a mammalian gene causes chromosome instability. Mol Cell Biol 21:126–35
Krutilina RI, Oei S, Buchlow G, Yau PM, Zalensky AO, Zalenskaya IA, Bradbury EM, Tomilin NV (2001) A negative regulator of telomere-length protein trf1 is associated with interstitial (TTAGGG)n blocks in immortal Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 280:471–45
Le Tallec B, Dutrillaux B, Lachages AM, Millot GA, Brison O, Debatisse M (2011) Molecular profiling of common fragile sites in human fibroblasts. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18:1421–1423
Letessier A, Millot GA, Koundrioukoff S, Lachages AM, Vogt N, Hansen RS, Malfoy B, Brison O, Debatisse M (2011) Cell-type-specific replication initiation programs set fragility of the FRA3B fragile site. Nature 470:120–123
Loayza D, de Lange T (2003) POT1 as a terminal transducer of TRF1 telomere length control. Nature 424:1013–1018
Martinez P, Thanasoula M, Munoz P, Liao C, Tejera A, McNees C, Flores JM, Fernandez-Capetillo O, Tarsounas M, Blasco MA (2009) Increased telomere fragility and fusions resulting from TRF1 deficiency lead to degenerative pathologies and increased cancer in mice. Genes Dev 23:2060–2075
Matzner I, Savelyeva L, Schwab M (2003) Preferential integration of a transfected marker gene into spontaneously expressed fragile sites of a breast cancer cell line. Cancer Lett 189:207–219
Miller CT, Lin L, Casper AM, Lim J, Thomas DG, Orringer MB, Chang AC, Chambers AF, Giordano TJ, Glover TW, Beer DG (2006) Genomic amplification of MET with boundaries within fragile site FRA7G and upregulation of MET pathways in esophageal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 25:409–418
Mishmar D, Rahat A, Scherer SW, Nyakatura G, Hinzmann B, Kohwi Y, Mandel-Gutfroind Y, Lee JR, Drescher B, Sas DE, Margalit H, Platzer M, Weiss A, Tsui LC, Rosenthal A, Kerem B (1998) Molecular characterization of a common fragile site (FRA7H) on human chromosome 7 by the cloning of a simian virus 40 integration site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:8141–8146
Mrasek K, Schoder C, Teichmann AC, Behr K, Franze B, Wilhelm K, Blaurock N, Claussen U, Liehr T, Weise A (2010) Global screening and extended nomenclature for 230 aphidicolin-inducible fragile sites, including 61 yet unreported ones. Int J Oncol 36:929–940
Ozeri-Galai E, Lebofsky R, Rahat A, Bester AC, Bensimon A, Kerem B (2011) Failure of origin activation in response to fork stalling leads to chromosomal instability at fragile sites. Mol Cell 43:122–131
Palm W, de Lange T (2008) How shelterin protects mammalian telomeres. Annu Rev Genet 42:301–334
Pelliccia F, Bosco N, Curatolo A, Rocchi A (2008) Replication timing of two human common fragile sites: FRA1H and FRA2G. Cytogenet Genome Res 121:196–200
Pelliccia F, Bosco N, Rocchi A (2010) Breakages at common fragile sites set boundaries of amplified regions in two leukemia cell lines K562—molecular characterization of FRA2H and localization of a new CFS FRA2S. Cancer Lett 299:37–44
Ragland RL, Glynn MW, Arlt MF, Glover TW (2008) Stably transfected common fragile site sequences exhibit instability at ectopic sites. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 47:860–872
Rassool FV, McKeithan TW, Neilly ME, van Melle E, Rr E, Le Beau MM (1991) Preferential integration of marker DNA into the chromosomal fragile site at 3p14: an approach to cloning fragile sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 88:6657–6661
Reshmi SC, Huang X, Schoppy DW, Black RC, Saunders WS, Smith DI, Gollin SM (2007) Relationship between FRA11F and 11q13 gene amplification in oral cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 46:143–154
Salvati E, Scarsella M, Porru M, Rizzo A, Iachettini S, Tentori L, Graziani G, D'Incalci M, Stevens MF, Orlandi A, Passeri D, Gilson E, Zupi G, Leonetti C, Biroccio A (2010) PARP1 is activated at telomeres upon G4 stabilization: possible target for telomere-based therapy. Oncogene 29:6280–6293
Schwartz M, Zlotorynski E, Kerem B (2006) The molecular basis of common and rare fragile sites. Cancer Lett 232:13–26
Sfeir A, Kosiyatrakul ST, Hockemeyer D, MacRae SL, Karlseder J, Schildkraut CL, de Lange T (2009) Mammalian telomeres resemble fragile sites and require TRF1 for efficient replication. Cell 138:90–103
Simonet T, Zaragosi LE, Philippe C, Lebrigand K, Schouteden C, Augereau A, Bauwens S, Ye J, Santagostino M, Giulotto E, Magdinier F, Horard B, Barbry P, Waldmann R, Gilson E (2011) The human TTAGGG repeat factors 1 and 2 bind to a subset of interstitial telomeric sequences and satellite repeats. Cell Res 21:1028–1038
Slijepcevic P, Xiao Y, Dominguez I, Natarajan AT (1996) Spontaneous and radiation-induced chromosomal breakage at interstitial telomeric sites. Chromosoma 104:596–604
Smogorzewska A, van Steensel B, Bianchi A, Oelmann S, Schaefer MR, Schnapp G, de Lange T (2000) Control of human telomere length by TRF1 and TRF2. Mol Cell Biol 20:1659–1668
Sutherland GR, Mattei JF (1987) Report of the committee on cytogenetic markers. Cytogenet Cell Genet 46:316–324
Sutherland GR, Baker E, Richards RI (1998) Fragile sites still breaking. Trends Genet 14:501–506
Takai KK, Hooper S, Blackwood S, Gandhi R, de Lange T (2010) In vivo stoichiometry of shelterin components. J Biol Chem 285:1457–1467
Thorland EC, Myers SL, Gostout BS, Smith DI (2003) Common fragile sites are preferential targets for HPV16 integrations in cervical tumors. Oncogene 22:1225–1237
Tsantoulis PK, Kotsinas A, Sfikakis PP, Evangelou K, Sideridou M, Levy B, Mo L, Kittas C, Wu XR, Papavassiliou AG, Gorgoulis VG (2008) Oncogene-induced replication stress preferentially targets common fragile sites in preneoplastic lesions. A genome-wide study. Oncogene 27:3256–3264
Vannier JB, Pavicic-Kaltenbrunner V, Petalcorin MI, Ding H, Boulton SJ (2012) RTEL1 dismantles T loops and counteracts telomeric G4-DNA to maintain telomere integrity. Cell 149:795–806
Wilke CM, Hall BK, Hoge A, Paradee W, Smith DI, Glover TW (1996) FRA3B extends over a broad region and contains a spontaneous HPV16 integration site: direct evidence for the coincidence of viral integration sites and fragile sites. Hum Mol Genet 5:187–195
Yang D, Xiong Y, Kim H, He Q, Li Y, Chen R, Songyang Z (2011) Human telomeric proteins occupy selective interstitial sites. Cell Res 21:1013–1027
Zimonjic DB, Durkin ME, Keck-Waggoner CL, Park SW, Thorgeirsson SS, Popescu NC (2003) SMAD5 gene expression, rearrangements, copy number, and amplification at fragile site FRA5C in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasia 5:390–396
Zlotorynski E, Rahat A, Skaug J, Ben-Porat N, Ozeri E, Hershberg R, Levi A, Scherer SW, Margalit H, Kerem B (2003) Molecular basis for expression of common and rare fragile sites. Mol Cell Biol 23:7143–7151
Acknowledgments
We thank Agnel Sfeir for the help in the early stages of this work and members of the de Lange lab for comments on this manuscript. We are grateful to Eugene Rudensky for the help with qPCR. This work was supported by a grant from the NIH (AG16642) to TdL. TdL is an American Cancer Society Research Professor. NB is supported by “The Alessandro & Catherine di Montezemolo” American-Italian Cancer Foundation Post-Doctoral Research Fellowship.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jan Karlseder
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Table 3
Frequency of CFS 2q14 after treatment with shBLM and shTRF1 (Fig. 4e). (DOCX 32 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Frequency of NFRA, FRA3B, FRA7H and FRA16D after treatment with shBLM and shTRF1 (Fig. 4f). (DOCX 64 kb)
Fig. S1
The human chromosome 2q14 region. a. DNA sequence from 2q14.1 containing the telomere fusion of two ancestral ape chromosomes. Highlighted are the recognition sites for the TRF1 Myb/SANT DNA binding domain (TAGGGTT or AACCCTA in the other strand). b. Sequence from the genomic locus encoding the Rap1 (TERF1, TRF2 interacting factor 1) gene on chromosome 16, which does not contain TRF1 binding sites. The underlined sequences in both panels indicate the positions of the qPCR primers given in the methods section. (JPEG 951 kb)
Fig. S2
Mapping the breakages on chromosome arm 2q. a, b. Example of a metaphase obtained from BJ/hTERT/SV40 after aphidicolin treatment. The two chromosomes 2 are highlighted, one of which is detailed in Fig. 1 (bottom box). The other chromosome 2, enlarged in panel b, shows two breakages centromeric to the CFS 2q14, which could be FRA2A and FRA2B. (JPEG 159 kb)
Fig. S3
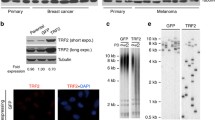
Monitoring the effect of TRF1 and TRF2 shRNAs. a. Quantification of the effect of shRNA treatment on TRF1 levels at telomeres determined by IF-FISH. b. Quantification of TIF formation upon inhibition of TRF1 with shRNAs. (c,d) Quantification of the frequency of fragile telomeres induced by repression of TRF1 (c) or TRF2 (d) with shRNAs. For all panels the bars represent mean values of three independent experiments with SD. At least 50 nuclei or 30 metaphases were analyzed per IF or FISH experiment. Brackets with asterisks indicate p values below 0.05 (student’s t-test). (JPEG 141 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bosco, N., de Lange, T. A TRF1-controlled common fragile site containing interstitial telomeric sequences. Chromosoma 121, 465–474 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-012-0377-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-012-0377-6