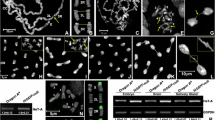
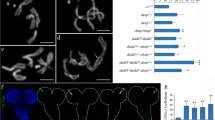
Abstract
We report in this paper that the pentoxyresorufin-O-dealkylase (PROD) protein, encoded by the gene proliferation disrupter (prod), is associated with the telomeric chromatin in Drosophila melanogaster. It binds to a region just upstream of the promoter of the telomere-specific retrotransposon HeT-A, which is located in the long 3′untranslated region of the element near its oligo(A) tail. Reduction of PROD in prod heterozygote flies results in elevated levels of HeT-A RNA in the ovaries, suggesting that PROD functions as a repressor of HeT-A transcriptional activity at the telomeres.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abad JP, de Pablos B, Osoegawa K, de Jong PJ, Martin-Gallardo A, Villasante A (2004a) Genomic analysis of Drosophila melanogaster telomeres: full-length copies of HeT-A and TART elements at the telomeres. Mol Biol Evol 21:1613–1619
Abad JP, de Pablos B, Osoegawa K, de Jong PJ, Martin-Gallardo A, Villasante A (2004b) TAHRE, a novel telomeric retrotransposon from Drosophila melanogaster, reveals the origin of Drosophila telomeres. Mol Biol Evol 21:1620–1624
Andreyeva EN, Belyaeva ES, Semeshin V, Pokholkova GV, Zhimulev IF (2005) Three distinct chromatin domains in telomere ends of polytene chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster Tel mutants. J Cell Sci 118:5465–5477
Bi X, Wei S-CD, Rong YS (2004) Telomere protection without telomerase: the role of ATM and Mre11 in Drosophila telomere maintenance. Curr Biol 14:1348–1353
Biessmann H, Mason JM (1988) Progressive loss of DNA sequences from terminal chromosome deficiencies in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 7:1081–1086
Biessmann H, Carter SB, Mason JM (1990) Chromosome ends in Drosophila without telomeric DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1758–1761
Biessmann H, Champion LE, O’Hair M, Ikenaga K, Kasravi B, Mason JM (1992a) Frequent transpositions of Drosophila melanogaster HeT-A transposable elements to receding chromosome ends. EMBO J 11:4459–4469
Biessmann H, Valgeirsdottir K, Lofsky A, Chin C, Ginther B, Levis RW, Pardue ML (1992b) HeT-A, a transposable element specifically involved in healing broken chromosome ends in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 12:3910–3918
Biessmann H, Kasravi B, Jakes K, Bui T, Ikenaga K, Mason JM (1993) The genomic organization of HeT-A retroposons in Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 102:297–305
Biessmann H, Kasravi B, Bui T, Fujiwara G, Champion LE, Mason JM (1994) Comparison of two active HeT-A retroposons of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma 103:90–98
Biessmann H, Walter MF, Mason JM (1997) Drosophila telomere elongation. Ciba Found Symp 211:53–67
Biessmann H, Prasad S, Semeshin V, Andreyeva EN, Nguyen Q, Walter MF, Mason JM (2005a) Two distinct domains at Drosophila melanogaster telomeres. Genetics 171:1767–1777
Biessmann H, Prasad S, Walter MF, Mason JM (2005b) Euchromatic and heterochromatic domains at Drosophila telomeres. Biochem Cell Biol 83:477–485
Biggin MD (1999) Ultraviolet cross-linking assay to measure sequence-specific DNA binding in vivo. Methods Enzymol 304:496–515
Boivin A, Gally C, Netter S, Anxolabehere D, Ronsseray S (2003) Telomeric associated sequences of Drosophila recruit polycomb-group proteins in vivo and can induce pairing-sensitive repression. Genetics 164:195–208
Cenci G, Siriaco G, Raffa GD, Kellum R, Gatti M (2003) The Drosophila HOAP protein is required for telomere capping. Nat Cell Biol 5:82–84
Cenci G, Ciapponi L, Gatti M (2005) The mechanism of telomere protection: a comparison between Drosophila and humans. Chromosoma 114:135–145
Chan SW, Blackburn EH (2002) New ways not to make ends meet: telomerase, DNA damage proteins and heterochromatin. Oncogene 21:553–563
Ciapponi L, Cenci G, Ducau J, Flores C, Johnson-Schlitz DM, Engels WR, Gatti M (2004) The Drosophila Mre11/Rad50 complex is required to prevent both telomeric fusion and chromosome breakage. Curr Biol 14:1360–1366
Ciapponi L, Cenci G, Gatti M (2006) The Drosophila Nbs protein functions in multiple pathways for the maintenance of genome stability. Genetics 173:1447–1454
Cryderman DE, Morris EJ, Biessmann H, Elgin SCR, Wallrath LL (1999) Silencing at Drosophila telomeres: nuclear organization and chromatin structure play critical roles. EMBO J 18:3724–3735
Csink AK, Henikoff S (1998) Something from nothing: the evolution and utility of satellite repeats. Trends Genet 14:200–204
Danilevskaya ON, Arkhipova IR, Traverse KL, Pardue ML (1997) Promoting in tandem: the promoter for telomere transposon HeT-A and implications for the evolution of retroviral LTRs. Cell 88:647–655
Danilevskaya ON, Traverse KL, Hogan NC, Debaryshe PG, Pardue ML (1999) The two Drosophila telomeric transposable elements have very different patterns of transcription. Mol Cell Biol 19:873–881
Delattre M, Spierer A, Tonka CH, Spierer P (2000) The genomic silencing of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster: interaction between the heterochromatin-associated proteins Su(Var)3–7 and HP1. J Cell Sci 113:4253–4261
Deng H, Zhang W, Bao X, Martin JN, Girton J, Johansen J, Johansen KM (2005) The JIL-1 kinase regulates the structure of Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma 114:173–182
Eggert H, Gortchakov A, Saumweber H (2004) Identification of the Drosophila interband-specific protein Z4 as a DNA-binding zinc-finger protein determining chromosomal structure. J Cell Sci 117:4253–4264
Eissenberg JC, James TC, Foster-Hartnett DM, Hartnett T, Ngan V, Elgin SC (1990) Mutation in a heterochromatin-specific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:9923–9927
Eissenberg JC, Morris GD, Reuter G, Hartnett T (1992) The heterochromatin-associated protein HP-1 is an essential protein in Drosophila with dosage-dependent effects on position-effect variegation. Genetics 131:345–352
Fanti L, Giovinazzo G, Berloco M, Pimpinelli S (1998) The heterochromatin protein 1 prevents telomere fusions in Drosophila. Mol Cell 2:527–538
Golubovsky MD, Konev AY, Walter MF, Biessmann H, Mason JM (2001) Terminal retrotransposons activate a subtelomeric white transgene at the 2L telomere in Drosophila. Genetics 158:1111–1123
Kahn T, Savitsky M, Georgiev P (2000) Attachment of HeT-A sequences to chromosomal termini in Drosophila melanogaster may occur by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol 20:7634–7642
Karpen GH, Spradling AC (1992) Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by Single-P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics 132:737–753
Levis RW (1989) Viable deletions of a telomere from a Drosophila chromosome. Cell 58:791–801
Levis RW, Ganesan R, Houtchens K, Tolar LA, Sheen FM (1993) Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell 75:1083–1093
Lohe AR, Brutlag DL (1986) Multiplicity of satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:697–700
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Marin L, Lehmann M, Nouaud D, Izaabel H, Anxolabehere D, Ronsseray S (2000) P element repression in Drosophila melanogaster by a naturally occurring defective telomeric P copy. Genetics 155:1841–1854
Mason JM, Biessmann H (1995) The unusual telomeres of Drosophila. Trends Genet 11:58–62
Mason JM, Strobel E, Green MM (1984) mu-2: mutator gene in Drosophila that potentiates the induction of terminal deficiencies. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:6090–6094
Mason JM, Haoudi A, Konev AY, Kurenova E, Walter MF, Biessmann H (2000) Control of telomere elongation and telomeric silencing in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetica 109:61–70
Mason JM, Konev AY, Biessmann H (2003a) Telomeric position effect in Drosophila melanogaster reflects a telomere length control mechanism. Genetica 117:319–325
Mason JM, Konev AY, Golubovsky MD, Biessmann H (2003b) Cis- and trans-acting influences on telomeric position effect in Drosophila melanogaster detected with a subterminal transgene. Genetics 163:917–930
Mason JM, Ransom J, Konev AY (2004) A deficiency screen for dominant suppressors of telomeric silencing in Drosophila. Genetics 168:1353–1370
Melnikova L, Georgiev P (2002) Enhancer of terminal gene conversion, a new mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that induces telomere elongation by gene conversion. Genetics 162:1301–1312
Melnikova L, Biessmann H, Georgiev P (2005) The Ku protein complex is involved in length regulation of Drosophila telomeres. Genetics 170:221–235
Oikemus SR, McGinnis N, Queiroz-Machado J, Tukachinsky H, Takada S, Sunkel CE, Brodsky MH (2004) Drosophila atm/telomere fusion is required for telomeric localization of HP1 and telomeric position effect. Genes Dev 18:1850–1861
Oikemus SR, Queiroz-Machado J, Lai K, McGinnis N, Sunkel CE, Brodsky MH (2006) Epigenetic telomere protection by Drosophila DNA damage response pathways. PLoS Genet 2:693–706
Orlando V, Strutt H, Paro R (1997) Analysis of chromatin structure by in vivo formaldehyde cross-linking. Methods 11:205–214 (a companion to Methods Enzymol)
Pardue ML, DeBaryshe PG (2003) Retrotransposons provide an evolutionarily robust non-telomerase mechanism to maintain telomeres. Annu Rev Genet 37:485–511
Perrini B, Piacentini L, Fanti L, Altieri F, Chichiarelli S, Berloco M, Turano C, Ferraro A, Pimpinelli S (2004) HP1 controls telomere capping, telomere elongation, and telomere silencing by two different mechanisms in Drosophila. Mol Cell 15:467–476
Platero JS, Csink AK, Quintanilla A, Henikoff S (1998) Changes in chromosomal localization of heterochromatin-binding proteins during the cell cycle in Drosophila. J Cell Biol 140:1297–1306
Raff JW, Kellum R, Alberts B (1994) The Drosophila GAGA transcription factor is associated with specific regions of heterochromatin throughout the cell cycle. EMBO J 13:5977–5983
Raffa GD, Cenci G, Goldberg ML, Gatti M (2005) The putative Drosophila transcription factor woc is required to prevent telomere fusions. Mol Cell 20:821–831
Savitsky M, Kravchuk O, Melnikova L, Georgiev P (2002) Heterochromatin protein 1 is involved in control of telomere elongation in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol 22:3204–3218
Savitsky M, Kwon D, Georgiev P, Kalmykova A, Gvozdev V (2006) Telomere elongation is under the control of the RNAi-based mechanism in the Drosophila germline. Genes Dev 20:345–354
Shareef MM, King C, Damaj M, Badagu R, Huang DW, Kellum R (2001) Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1 (HPI)/origin recognition complex (ORC) protein is associated with HP1 and ORC and functions in heterochromatin-induced silencing. Mol Biol Cell 12:1671–1685
Silva E, Tiong S, Pedersen M, Homola E, Royou E, Fasulo B, Siriaco G, Campbell SD (2004) ATM is required for telomere maintenance and chromosome stability during Drosophila development. Curr Biol 14:1341–1347
Siriaco GM, Cenci G, Haoudi A, Champion LE, Zhou C, Gatti M, Mason JM (2002) Telomere elongation (Tel), a new mutation in Drosophila melanogaster that produces long telomeres. Genetics 160:235–245
Song Y-H, Mirey G, Betson M, Haber DA, Settleman J (2004) The Drosophila ATM ortholog, dATM, mediates the response to ionizing radiation and spontaneous DNA damage during development. Curr Biol 14:1354–1359
Stuart JR, Haley KJ, Swedzinski D, Lockner S, Kocian PE, Merriman PJ, Simmons MJ (2002) Telomeric P elements associated with cytotype regulation of the P transposon family in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 162:1641–1654
Török T, Harvie PD, Buratovich M, Bryant PJ (1997) The product of proliferation disrupter is concentrated at centromeres and required for mitotic chromosome condensation and cell proliferation in Drosophila. Genes Dev 11:213–225
Török T, Gorjanacz M, Bryant PJ, Kiss I (2000) Prod is a novel DNA-binding protein that binds to the 1.686 g/cm(3) 10 bp satellite repeat of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res 28:3551–3557
Vega LR, Mateyak MK, Zakian VA (2003) Getting to the end: telomerase access in yeast and humans. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:948–959
Walter MF, Biessmann H (2004) Expression of telomere retrotransposons, HeT-A and TART, in Drosophila melanogaster is correlated with cell proliferation. Dev Genes Evol 214:211–219
Walter MF, Jang C, Kasravi B, Donath J, Mechler BM, Mason JM, Biessmann H (1995) DNA organization and polymorphism of a wild-type Drosophila telomere region. Chromosoma 104:229–241
Wang Y, Zhang W, Jin Y, Johansen J, Johansen KM (2001) The JIL-1 tandem kinase mediates Histone H3 phosphorylation and is required for maintenance of chromatin structure in Drosophila. Cell 105:433–443
Wei C, Price M (2003) Protecting the terminus: t-loops and telomere end-binding proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:2283–2294
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Hungarian National Science Foundation OTKA no. T 037422 to Tibor Török and partially by the U.S. Public Health Service grant GM-56729 to H.B. C.B. was a participant in the AGEP Summer Research Program at UCI. We thank Jim Mason and Marika Walter for suggestions and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Lehner
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Török, T., Benitez, C., Takács, S. et al. The protein encoded by the gene proliferation disrupter (prod) is associated with the telomeric retrotransposon array in Drosophila melanogaster . Chromosoma 116, 185–195 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0090-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0090-4