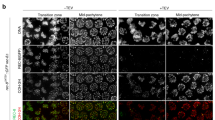
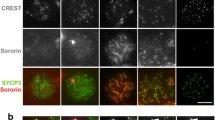
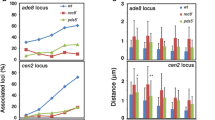
Abstract
Recent progress in elucidating the function of synaptonemal complex (SC) proteins and of cohesins in meiocytes made possible, in particular, through the analysis of mice deficient in SC or cohesin proteins has significantly enriched our understanding of how meiotic chromosome architecture is determined. Cohesins and the SC proteins act together in generating the characteristic axis-loop structure of meiotic chromosomes, their pairing into bivalents, their ability to recombine, and to be properly segregated. This minireview attempts to summarize the current knowledge with a focus on higher eukaryotic systems and to ask questions that ought to be addressed in the future.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LK, Royer SM, Page SL, McKim KS, Lai A, Lilly MA, Hawley RS (2005) Juxtaposition of C(2)M and the transverse filament protein C(3)G within the central region of Drosophila synaptonemal complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:4482–4487
Bannister LA, Reinholdt LG, Munroe RJ, Schimenti JC (2004) Positional cloning and characterization of mouse mei8, a disrupted allele of the meiotic cohesin Rec8. Genesis 40:184–194
Chuma S, Nakatsuji N (2001) Autonomous transition into meiosis of mouse fetal germ cells in vitro and its inhibition by gp130-mediated signaling. Dev Biol 229:468–479
de Vries FA, de Boer E, van den Bosch M, Baarends WM, Ooms M, Yuan L, Liu JG, van Zeeland AA, Heyting C, Pastink A (2005) Mouse Sycp1 functions in synaptonemal complex assembly, meiotic recombination, and XY body formation. Genes Dev 19:1376–1389
Eijpe M, Heyting C, Gross B, Jessberger R (2000) Association of mammalian SMC1 and SMC3 proteins with meiotic chromosomes and synaptonemal complexes. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 4):673–682
Eijpe M, Offenberg H, Jessberger R, Revenkova E, Heyting C (2003) Meiotic cohesin REC8 marks the axial elements of rat synaptonemal complexes before cohesins SMC1beta and SMC3. J Cell Biol 160:657–670
Firooznia A, Revenkova E, Jessberger R (2005) From the XXVII North American testis workshop: the function of SMC and other cohesin proteins in meiosis. J Androl 26:1–10
Hagstrom KA, Meyer BJ (2003) Condensin and cohesin: more than chromosome compactor and glue. Nat Rev Genet 4:520–534
Heidmann D, Horn S, Heidmann S, Schleiffer A, Nasmyth K, Lehner CF (2004) The Drosophila meiotic kleisin C(2)M functions before the meiotic divisions. Chromosoma 113:177–187
Hirano T (2005) SMC proteins and chromosome mechanics: from bacteria to humans. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:507–514
Hodges CA, Revenkova E, Jessberger R, Hassold TJ, Hunt PA (2005) SMC1beta-deficient female mice provide evidence that cohesins are a missing link in age-related nondisjunction. Nat Genet 37:1351–1355
Jessberger R (2002) The many functions of SMC proteins in chromosome dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:767–778
Kim JS, Krasieva TB, LaMorte V, Taylor AM, Yokomori K (2002) Specific recruitment of human cohesin to laser-induced DNA damage. J Biol Chem 277:45149–45153
Klein F, Mahr P, Galova M, Buonomo SB, Michaelis C, Nairz K, Nasmyth K (1999) A central role for cohesins in sister chromatid cohesion, formation of axial elements, and recombination during yeast meiosis. Cell 98:91–103
Kolas NK, Yuan L, Hoog C, Heng HH, Marcon E, Moens PB (2004) Male mouse meiotic chromosome cores deficient in structural proteins SYCP3 and SYCP2 align by homology but fail to synapse and have possible impaired specificity of chromatin loop attachment. Cytogenet Genome Res 105:182–188
Kouznetsova A, Novak I, Jessberger R, Hoog C (2005) SYCP2 and SYCP3 are required for cohesin core integrity at diplotene but not for centromere cohesion at the first meiotic division. J Cell Sci 118:2271–2278
Liebe B, Alsheimer M, Hoog C, Benavente R, Scherthan H (2004) Telomere attachment, meiotic chromosome condensation, pairing, and bouquet stage duration are modified in spermatocytes lacking axial elements. Mol Biol Cell 15:827–837
Manheim EA, McKim KS (2003) The synaptonemal complex component C(2)M regulates meiotic crossing over in Drosophila. Curr Biol 13:276–285
Parra MT, Viera A, Gomez R, Page J, Benavente R, Santos JL, Rufas JS, Suja JA (2004) Involvement of the cohesin Rad21 and SCP3 in monopolar attachment of sister kinetochores during mouse meiosis I. J Cell Sci 117:1221–1234
Pasierbek P, Jantsch M, Melcher M, Schleiffer A, Schweizer D, Loidl J (2001) A Caenorhabditis elegans cohesion protein with functions in meiotic chromosome pairing and disjunction. Genes Dev 15:1349–1360
Pelttari J, Hoja MR, Yuan L, Liu JG, Brundell E, Moens P, Santucci-Darmanin S, Jessberger R, Barbero JL, Heyting C, Hoog C (2001) A meiotic chromosomal core consisting of cohesin complex proteins recruits DNA recombination proteins and promotes synapsis in the absence of an axial element in mammalian meiotic cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:5667–5677
Prieto I, Suja JA, Pezzi N, Kremer L, Martinez AC, Rufas JS, Barbero JL (2001) Mammalian STAG3 is a cohesin specific to sister chromatid arms in meiosis I. Nat Cell Biol 3:761–766
Prieto I, Pezzi N, Buesa JM, Kremer L, Barthelemy I, Carreiro C, Roncal F, Martinez A, Gomez L, Fernandez R, Martinez AC, Barbero JL (2002) STAG2 and Rad21 mammalian mitotic cohesins are implicated in meiosis. EMBO Rep 3:543–550
Revenkova E, Jessberger R (2005) Keeping sister chromatids together: cohesins in meiosis. Reproduction 130:783–790
Revenkova E, Eijpe M, Heyting C, Gross B, Jessberger R (2001) Novel meiosis-specific isoform of mammalian SMC1. Mol Cell Biol 21:6984–6998
Revenkova E, Eijpe M, Heyting C, Hodges CA, Hunt PA, Liebe B, Scherthan H, Jessberger R (2004) Cohesin SMC1 beta is required for meiotic chromosome dynamics, sister chromatid cohesion and DNA recombination. Nat Cell Biol 6:555–562
Strom L, Sjogren C (2005) DNA damage-induced cohesion. Cell Cycle 4:536–539
Strom L, Lindroos HB, Shirahige K, Sjogren C (2004) Postreplicative recruitment of cohesin to double-strand breaks is required for DNA repair. Mol Cell 16:1003–1015
Trelles-Sticken E, Adelfalk C, Loidl J, Scherthan H (2005) Meiotic telomere clustering requires actin for its formation and cohesin for its resolution. J Cell Biol 170:213–223
Unal E, Arbel-Eden A, Sattler U, Shroff R, Lichten M, Haber JE, Koshland D (2004) DNA damage response pathway uses histone modification to assemble a double-strand break-specific cohesin domain. Mol Cell 16:991–1002
Watanabe Y, Nurse P (1999) Cohesin Rec8 is required for reductional chromosome segregation at meiosis. Nature 400:461–464
Xu H, Beasley M, Verschoor S, Inselman A, Handel MA, McKay MJ (2004) A new role for the mitotic RAD21/SCC1 cohesin in meiotic chromosome cohesion and segregation in the mouse. EMBO Rep 5:378–384
Xu H, Beasley MD, Warren WD, van der Horst GT, McKay MJ (2005) Absence of mouse REC8 cohesin promotes synapsis of sister chromatids in meiosis. Dev Cell 8:949–961
Yuan L, Liu JG, Hoja MR, Wilbertz J, Nordqvist K, Hoog C (2002) Female germ cell aneuploidy and embryo death in mice lacking the meiosis-specific protein SCP3. Science 296:1115–1118
Acknowledgements
Work in the authors’ laboratory is supported by grants from the NIH and from the DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Benavente
The synaptonemal complex—50 years
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Revenkova, E., Jessberger, R. Shaping meiotic prophase chromosomes: cohesins and synaptonemal complex proteins. Chromosoma 115, 235–240 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0060-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-006-0060-x