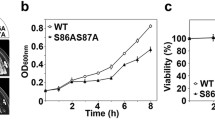
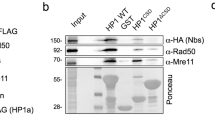
Abstract
Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) is a conserved component of the highly compact chromatin found at centromeres and telomeres. A conserved feature of the protein is multiple phosphorylation. Hyper-phosphorylation of HP1 accompanies the assembly of cytologically distinct heterochromatin during early embryogenesis. Hypo-phosphorylated HP1 is associated with the DNA-binding activities of the origin recognition complex (ORC) and an HMG-like HP1/ORC-Associated Protein (HOAP). Perturbations in HP1 localization in pericentric and telomeric heterochromatin in mutants for Drosophila ORC2 and HOAP, respectively, indicate roles for these HP1 phosphoisoforms in heterochromatin assembly also. To elucidate the roles of hypo- and hyper-phosphophorylated HP1 in heterochromatin assembly, we have mutated consensus Protein Kinase-A phosphorylation sites in the HP1 hinge domain and examined the mutant proteins for distinct in vitro and in vivo activities. Mutations designed to mimic hyper-phosphorylation render the protein incapable of binding HOAP and the DmORC1 subunit but confer enhanced homo-dimerization and lysine 9-methylated histone H3-binding to the protein. Mutations rendering the protein unphosphorylatable, by contrast, do not affect homo-dimerization or binding to lysine 9-di-methylated histone H3, HOAP, or DmORC1 but do confer novel DmORC2-binding activity to the protein. This mutant protein is ectopically localized throughout the chromosomes when overexpressed in vivo in the presence of a full dose of DmORC2. This ectopic targeting is accompanied by ectopic targeting of lysine 9 tri-methylated histone H3. The distinct activities of these mutant proteins could reflect distinct roles for HP1 phosphoisoforms in heterochromatin structure and function.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allshire RC, Nimmo ER, Ekwall K, Javerzat JP, Cranston G (1995) Mutations derepressing silent centromeric domains in fission yeast disrupt chromosome segregation. Genes Dev 9:218–233
Badugu R, Shareef MM, Kellum R (2003) Novel Drosophila HOAP repeat motif in HP1/HOAP interactions and chromocenter associations. J Biol Chem 278:34491–33498
Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T (2001) Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410:120–124
Bernard P, Maure J-F, Partridge JF, Genier S, Javerzat J-P, Allshire RC (2001) Requirement of heterochromatin for cohesion at centromeres. Science 294:2539–2542
Bernat RL, Delannoy MR, Rothfield N, Earnshaw WC (1991) Disruption of centromere assembly during interphase inhibits kinetochore morphogenesis and function in mitosis. Cell 66:1229–1238
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem 72:248–254
Brasher SV, Smith BO, Rasmus RH., Nietlispach D, Thiru A, Nielsen PR, Broadhurst RW, Ball LJ, Murzina NV, Laue ED (2000) The structure of mouse HP1 suggests a unique mode of single peptide recognition by the shadow chromo domain dimer. EMBO J 19:1587–1597
Chesnokov I, Remus D, Botchan M (2001) Functional analysis of mutant and wild-type Drosophila origin recognition complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:11997–12002
Cowell IG, Aucott R, Mahadevaiah SK, Burgoyne PS, Huskisson N, Bongiorni S, Prantera G, Fanti L, Pimpinelli S, Wu R, Gilbert DM, Shi W, Fundele R, Morrison H, Jeppesen P, Singh PB (2002) Heterochromatin, HP1, and methylation at lysine 9 of histone H3 in animals. Chromosoma 111:22–36
Dernburg AF, Sedat JW, Hawley RS (1996) Direct evidence of a role for heterochromatin in meiotic chromosome segregation. Cell 86:135–146
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SCR (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:204–210
Eissenberg JC, Guo YW, Hartnett T (1994) Increased phosphorylation of HP1, a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila, is correlated with heterochromatin assembly. J Biol Chem 269:21315–21321
Fanti L, Giovinazzo G, Berloco M, Pimpinelli S (1998) The heterochromatin protein 1 prevents telomere fusions in Drosophila. Mol Cell 2:527–538
Hall IM, Shankaranarayana GD, Noma K-i, Ayoub N, Cohen A, Grewal SIS (2002) Establishment and maintenance of a heterochromatin domain. Science 297:2232–2237
Hearn MG, Hedrick A, Grigliatti TA, Wakimoto BT (1991) The effect of modifiers of position-effect variegation on the variegation of heterochromatic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 128:785–797
Heitz E (1928) Das Heterochromatin der Moose. Jahrb Wissensch Bot 69:762–818
Huang DW, Fanti L, Pak DTS, Botchan MR, Pimpinelli S, Kellum R (1998) Distinct cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of Drosophila heterochromatin protein 1: their phosphorylation levels and associations with origin recognition complex proteins. J Cell Biol 142:307–318
Jacobs SA, Taverna SD, Zhang Y, Briggs SD, Li J, Eissenberg JC, Allis CD, Khorasanizadeh S (2001) Specificity of the HP1 chromo domain for the methylated N-terminus of histone H3. EMBO J 20:5232–5241
James TC, Elgin SCR (1986) Identification of a nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila melanogaster and its gene. Mol Cell Biol 6:3862–3872
Kellum R (2003) HP1 complexes and heterochromatin assembly. In: Workman, JL (ed) Protein complexes that modify chromatin. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 54–71
Kellum R, Alberts BM (1995) Heterochromatin protein 1 is required for correct chromosome segregation in Drosophila embryos. J Cell Sci 108:1419–1431
Klemm RD, Austin RJ, Bell SP (1997) Coordinate binding of ATP and origin DNA regulates the ATPase activity of the origin recognition complex. Cell 88:493–502
Koike N, Maita H, Taira T, Ariga H, Iguchi-Ariga SMM (2000) Identification of heterochromatin protein (HP1) as a phosphorylation target by Pim-1 kinase and the effect of phosphorylation on the transcriptional repression function of HP1. FEBS Lett 467:17–21
Lachner M, O’Carroll D, Rea S, Mechtler K, Jenuwein T (2001) Methylation of histone H3 lysine 9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410:116–120
Lechner MS, Begg GE, Speicher DW, Rauscher FJ III (2000) Molecular determinants for targeting heterochromatin protein 1-mediated gene silencing: direct chromoshadow domain-KAP-1 corepressor interaction is essential. Mol Cell Biol 20:6449–6465
Li Y, Kirschmann DA, Wallrath LL (2002) Does HP1 always follow code? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:16462–16469
Li Y, Danzer JR, Alvarez P, Belmont AS, Wallrath LL (2003) Effects of tethering HP1 to euchromatic regions of the Drosophila genome. Development 130:1817–1824
Lu BY, Ma J, Eissenberg JC (1998) Developmental regulation of heterochromatin-mediated gene silencing in Drosophila. Development 125:2223–2234
Maison C, Bailly D, Peters AHFM, Quivy J-P, Roche D, Taddei A, Lachner M, Jenuwein T, Almouzni G (2002) Higher-order structure in pericentric heterochromatin involves a distinct pattern of histone modification and an RNA component. Nat Genet 30:329–334
Minc E, Allory Y, Worman HJ, Courvalin J-C, Buendia B (1999) Localization and phosphorylation of HP1 proteins during the cell cycle in mammalian cells. Chromosoma 108:220–234
Moazed D (2001) Common themes in mechanisms of gene silencing. Mol Cell 8:489–498
Nielsen AL, Oulad-Abdelghani M, Ortiz JA, Remboutsika E, Chambon P, Losson R (2001a) Heterochromatin formation in mammalian cells: interaction between histones and HP1 proteins. Mol Cell 7:729–739
Nielsen SJ, Schneider R, Bauer UM, Bannister AJ, Morrison, O’Carroll D, Firestein R, Cleary M, Jenuwein T, Herrera RE, Kouzarides T (2001b) Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 412:561–565
Nonaka N, Kitajima T, Yokobayashi S, Xiao G, Yamamoto M, Grewal SIS, Watanabe Y (2001) Recruitment of cohesin to heterochromatic regions by Swi6/HP1 in fission yeast. Nat Cell Biol 4:89–93
Pak DTS, Pflumm M, Chesnokov I, Huang DW, Kellum R, Marr J, Romanowski P, Botchan M (1997) Association of the origin recognition complex with heterochromatin and HP1 in higher eukaryotes. Cell 91:311–323
Partridge JF, Scott KSC, Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T, Allshire RC (2002) cis-acting DNA from fission yeast centromeres mediates histone H3 methylation and recruitment of silencing factors and cohesin to an ectopic site. Curr Biol 12:1652–1660
Perrini B, Piacentini L, Fanti L, Altieri F, Chichiarelli S, Berloco M, Pimpinelli S (2004) HP1 controls telomere capping, telomere elongation, and telomere silencing by two different mechanisms in Drosophila. Mol Cell 15:467–476
Piacentini L, Fanti L, Berloco M, Perrini B, Pimpinelli S (2003) Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) is associated with induced gene expression in Drosophila euchromatin. J Cell Biol 161:707–714
Prasanth SG, Prasanth KV, Siddigui K, Spector DL, Stillman B (2004) Human Orc2 localizes to centrosomes, centromeres and heterochromatin during chromosome inheritance. EMBO J 23:2651–2663
Rubin GM, Spradling AC (1982) Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science 218:348–353
Schotta G, Ebert A, Krauss V, Fisher A, Hoffman J, Rea S, Jenuwein T, Dorn R, Reuter G (2002) Central role of Drosophila SU(VAR)3-9 in histone H3-K9 methylation and heterochromatic gene silencing. EMBO J 21:1121–1131
Schultz D, Ayyanathan K, Negorev D, Maul GG, Rauscher FJ III (2002) SETDB1: a novel KAP-1-associated histone H3, lysine 9-specific methyltransferase that contributes to HP1-mediated silencing of euchromatic genes by KRAB zinc-finger proteins. Genes Dev 16:919–932
Shareef MM, King C, Damaj M, Badugu RK, Huang DW, Kellum R (2001) Drosophila Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1)/Origin Recognition Complex (ORC) Protein is associated with HP1 and ORC and functions in heterochromatin-induced silencing. Mol Biol Cell 12:1671–1685
Simon JA, Lis JT (1987) A germline transformation analysis reveals flexibility in the organization of heat shock consensus elements. Nucleic Acids Res 15:2971–2988
Sinclair DAR, Mottus RC, Grigliatti TA (1983) Genes which suppress position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster are clustered. Mol Gen Genet 191:326–333
Smothers JF, Henikoff S (2000) The HP1 chromo shadow domain binds a consensus peptide pentamer. Curr Biol 10:27–30
Smothers JF, Henikoff S (2001) The hinge and chromo shadow domain impart distinct targeting of HP1-like proteins. Mol Cell Biol 21:2555–2569
Wallrath LL, Elgin SCR (1995) Position effect variegation in Drosophila is associated with an altered chromatin structure. Genes Dev 9:1263–1277
Weiler KS, Wakimoto BT (1995) Heterochromatin and gene expression in Drosophila. Annu Rev Genet 29:577–605
Wustmann G, Szidonya J, Taubert H, Reuter G (1989) The genetics of position-effect variegation modifying loci in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet 217:520–527
Zhao T, Eissenberg JC (1999) Phosphorylation of heterochromatin protein 1 by casein kinase II is required for efficient heterochromatin binding in Drosophila. J Biol Chem 274:15095–15100
Zhao T, Heyduk T, Eissenberg JC (2001) Phosphorylation site mutations in heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) reduce or eliminate silencing activity. J Biol Chem 276:9512–9518
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Eissenberg for providing the In(3L)BL1 reporter (Lu et al. 1998). This work was supported by NIH grant GM059765.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Pimpinelli
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Badugu, R., Yoo, Y., Singh, P.B. et al. Mutations in the heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1) hinge domain affect HP1 protein interactions and chromosomal distribution. Chromosoma 113, 370–384 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0324-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0324-2