Abstract
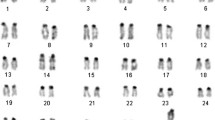
We mapped chromosomal homologies in two species of Chiropotes (Pitheciini, Saki Monkeys) and one species of Aotus (Aotinae, Owl Monkey) by multi-directional chromosome painting. Human chromosome probes were hybridized to Chiropotes utahicki, C. israelita and Aotus nancymae metaphases. Wooly Monkey chromosome paints were also hybridized to Owl Monkey metaphases. We established Owl Monkey chromosome paint probes by flow sorting and reciprocally hybridized them to human chromosomes. The karyotypes of the Bearded Saki Monkeys studied here are close to the hypothesized ancestral platyrrhine karytoype, while that of the Owl Monkey appears to be highly derived. The A. nancymae karyotype is highly shuffled and only three human syntenic groups were found conserved coexisting with 17 derived human homologous associations. A minimum of 14 fissions and 13 fusions would be required to derive the A. nancymae karyotype from that of the ancestral New World primate karyotype. An inversion between homologs to segments of human 10 and 16 suggests a link between Callicebus and Chiropotes, while the syntenic association of 10/11 found in Aotus and Callicebus suggests a link between these two genera. Future molecular cytogenetic work will be needed to determine whether these rearrangements represent synapomorphic chromosomal traits.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barros RM, Nagamachi CY, Pieczarka JC, Rodrigues LR, Neusser M, de Oliveira EH, Wienberg J, Muniz JA, Rissino JD, Muller S (2003) Chromosomal studies in Callicebus donacophilus pallescens, with classic and molecular cytogenetic approaches: multicolour FISH using human and Saguinus oedipus painting probes. Chromosome Res 11:327–334
De Boer LEM (1974) Cytotaxonomy of the Platyrrhini (primates). Genen Phaenen 17:1–155
Bonvicino CR, Boubli JP, Otazu IB, Almeida FC, Nascimento FF, Coura JR, Seuánez HN (2003) Morphologic, karyotypic, and molecular evidence of a new form of Chiropotes (Primates, Pitheciinae). Am J Primatol 61:123–133
Brumback RA, Staton RD, Benjamin SA, Lang CM (1971) The chromosomes of Aotus trivirgatus Humboldt 1812. Folia Primatol (Basel) 15:264–273
Consigliere S, Stanyon R, Koehler U, Arnold N, Wienberg J (1998) In situ hybridization (FISH) maps chromosomal homologies between Alouatta belzebul (Platyrrhini, Cebidae) and other primates and reveals extensive interchromosomal rearrangements between howler monkey genomes. Am J Primatol 46:119–133
Ford S (1986) Systematics of the New World monkeys. In: Swindler D, Erwin J (eds) Comparative primate biology. AR Liss, New York, pp 73–135
Groves CP (2001) Primate taxonomy. Smithsonian Institution, Washington
Hershkovitz P (1983) Two new species of night monkeys, genus Aotus (Cebidae, Platyrrhini): a preliminary report on Aotus taxonomy. Am J Primatol 4:209–243
Hershkovitz P (1985) A preliminary taxonomic review of the South American bearded saki monkeys, genus Chiropotes (Cebidae, Platyrrhini) with the description of a new subspecies. Fieldiana Zool n.s. 27:iii
Hershkovitz P (1987a) Uacaries, New World monkeys of the genus Cacajao. A preliminary taxonomic review with the description of a new subspecies. Am J Primat 12:1–53
Hershkovitz P (1987b) The taxonomy of South American sakis, genus Pithecia: a preliminary report and critical review with the description of a new species and subspecies. Am J Primat 12:387–468
Horovitz I, Zardoya R, Meyer A (1998) Platyrrhine systematics: a simultaneous analysis of molecular and morphological data. Am J Phys Anthropol 106:261–281
Hugot JP (1998) Phylogeny of neotropical monkeys: the interplay of morphological, molecular, and parasitological data. Mol Phylogenet Evol 9:408–413
Kay RF (1990) The phyletic relationships of extant and fossil Pitheciinae (Platyrrhini, Anthropoidea). J Hum Evol 4:448–456
Ma NS (1981) Chromosome evolution in the owl monkey. Am J Phys Anthropol 54:293–303
Ma NS, Jones TC, Miller AC, Morgan LM, Adams EA (1976) Chromosome polymorphism and banding patterns in the owl monkey (Aotus). Lab Anim Sci 26:1022–1036
Ma NS, Rossan RN, Kelley ST, Harper JS, Bedard MT, Jones TC (1978) Banding patterns of the chromosomes of two new karyotypes of the owl monkey, Aotus, captured in Panama. J Med Primatol 7:146–155
Ma NS, Aquino R, Collins WE (1985) Two new karyotypes in the Peruvian owl monkey (Aotus trivirgatus). Am J Primatol 1985:333–341
Muller S, Stanyon R, Finelli P, Archidiacono N, Wienberg J (2000) Molecular cytogenetic dissection of human chromosomes 3 and 21 evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:206–211
Muller S, Neusser M, O’Brien PC, Wienberg J (2001) Molecular cytogenetic characterization of the EBV-producing cell line B95-8 (Saguinus oedipus, Platyrrhini) by chromosome sorting and painting. Chromosome Res 9:689–693
Murphy WJ, Fronicke L, O’Brien SJ, Stanyon R (2003) The origin of human chromosome 1 and its homologs in placental mammals. Genome Res 13:1880–1888
Neusser M, Stanyon R, Bigoni F, Wienberg J, Muller S (2001) Molecular cytotaxonomy of New World monkeys (Platyrrhini)—comparative analysis of five species by multi-color chromosome painting gives evidence for a classification of Callimico goeldii within the family of Callitrichidae. Cytogenet Cell Genet 94:206–215
de Oliveira EH, Neusser M, Figueiredo WB, Nagamachi C, Pieczarka JC, Sbalqueiro IJ, Wienberg J, Muller S (2002) The phylogeny of howler monkeys (Alouatta, Platyrrhini): reconstruction by multicolor cross-species chromosome painting. Chromosome Res 10:669–683
Porter CA, Czelusniak J, Schneider H, Schneider MP, Sampaio I, Goodman M (1999) Sequences from the 5′ flanking region of the epsilon-globin gene support the relationship of Callicebus with the pitheciines. Am J Primatol 48:69–75
Rosenberger AL (1992) Evolution of feeding niches in New World monkeys. Am J Phys Anthropol 88:525–562
Rosenberger AL (2002) Platyrrhine paleontology and systematics: the paradigm shifts. In: Hartwig WC (ed) The primate fossil record. Cambridge University Press, New York, pp 151–159
Rosenberger AL, Norconk MA, Garber PA (1996) New perspectives on the pithecines. In: (ed) Adaptive radiations of neotropical primates. Plenum, New York, pp 329–333
Scammell JG, Reynolds PD, Elkhalifa MY, Tucker JA, Moore CM (1997) An EBV-transformed owl monkey B-lymphocyte cell line. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim 33:88–91
Schneider H, Canavez FC, Sampaio I, Moreira MA, Tagliaro CH, Seuánez HN (2001) Can molecular data place each neotropical monkey in its own branch? Chromosoma 109:515–523
Seuánez HN, Alves G, Lima MMC, de Souza Barros R, Barroso CML, Muniz JAPC (1992) Chromosome studies in Chiropotes satanas utahicki Hershkovitz 1985 (Cebidae, Platyrrhini): a comparison with Chiropotes satanas chiropotes. Am J Primatol 28:213–222
Singer SS, Schmitz J, Schwiegk C, Zischler H (2003) Molecular cladistic markers in New World monkey phylogeny (Platyrrhini, Primates). Mol Phylogenet Evol 26:490–501
Spix JB von (1823) Simiarum et vespertiliarum Brasiliensium: Smithsonian Institution Libraries Digital Edition 2000, http://www.sil.si.edu/DigitalCollections/NHRareBooks/Spix/spix.htm
Stanyon R, Consigliere S, Muller S, Morescalchi A, Neusser M, Wienberg J (2000) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) maps chromosomal homologies between the dusky titi and squirrel monkey. Am J Primatol 50:95–107
Stanyon R, Consigliere S, Bigoni F, Ferguson Smith M, O’Brien PCM, Wienberg J (2001) Reciprocal chromosome painting between a New World primate, the woolly monkey, and humans. Chromosome Res 9:97–106
Stanyon R, Bonvicino CR, Svartman M, Seuánez HN (2003) Chromosome painting in Callicebus lugens, the species with the lowest diploid number (2n=16) known in primates. Chromosoma 112:201–206
Steiper ME, Ruvolo M (2003) New World monkey phylogeny based on X-linked G6PD DNA sequences. Mol Phylogenet Evol 27:121–130
Telenius H, Pelmear AH, Tunnacliffe A, Carter NP, Behmel A, Ferguson-Smith MA, Nordenskjold M, Pfragner R, Ponder BA (1992) Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 4:257–263
Torres OM, Enciso S, Ruiz F, Silva E, Yunis I (1998) Chromosome diversity of the genus Aotus from Colombia. Am J Primatol 44:255–275
Viegas Pequignot E, Koiffmann CP, Dutrillaux B (1985) Chromosomal phylogeny of Lagothrix, Brachyteles, and Cacajao. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39:99–104
Wienberg J, Stanyon R (1997) Comparative painting of mammalian chromosomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7:784–791
Acknowledgements
We would like to dedicate this work to Prof. Brunetto Chiarelli, the father of primate cytogenetics, on the occasion of his becoming Professor Emeritus at the University of Florence. The research of H.N.S. and C.R.B. was supported by INCA, FAF and Pronex-CNPq (Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by E. Nigg
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanyon, R., Bigoni, F., Slaby, T. et al. Multi-directional chromosome painting maps homologies between species belonging to three genera of New World monkeys and humans. Chromosoma 113, 305–315 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0320-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00412-004-0320-6