Abstract
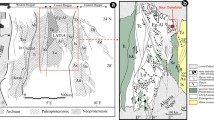
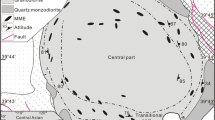
The lower Austroalpine orthogneiss-micachist complex of the Sopron-Fertörákos area of W. Hungary contains Mg-chlorite-muscovite-quartzphyllites (leuco- phyllite) and Mg-chlorite-bearing kyanite quartzites whose chemical compositions differ greatly from their surrounding rocks. Formation of leucophyllites took place in shear zones and was associated with depletion in alkalies and iron and enrichment of magnesium and H2O. Mg-zonation of relict igneous muscovites of leucophyllites and changes in the whole rock chemical compositions suggest Mg-metasomatism. Material gains and losses have been assessed using the composition-volume relationship approach. Proceeding from metagranite through transition rocks to leucophyllites, MgO, H2O, FeO, and alkalies show continuously increasing dispersion in isocon plots with Mg-enrichment even in sheared gneiss not in contact with leucophyllite. The metasomatic processes that formed the Mg-rich rocks may be similar to those responsible for the formation of high pressure whiteschists in the Central and Western Alps. The geochemical characteristics of the Dora Maira whiteschists (Italy) and their country gneisses are very similar to those of the Sopron leucophyllites, supporting the theory that Mg-metasomatism produced the whiteschist chemistry. On the basis of oxygen isotope compositions of relict igneous muscovites, the precursor granitic rock had a δ18O value around 13‰ proving its crustal anatectic origin. The leucophyllites have whole rock oxygen isotope compositions around 8.5‰ which is in conflict with the theory of an Mg-rich sedimentary protolith. Rather, the low δ18O values reflect fluid/rock interaction with a low δ18O fluid. Quartz-mineral oxygen isotope fractionations yield a metamorphic temperature of 560 ± 30 °C which agrees with earlier estimates from mineral stabilities. Silicon contents of phengites correspond to a metamorphic pressure of ∼13 GPa at this temperature indicating eclogite facies metamorphism. The fluids in equilibrium with leucophyllites had oxygen isotope compositions around 7.9‰, similar to those calculated for the ultrahigh pressure Dora Maira whiteschists (7.6‰), further supporting the genetic link between the leucophyllites and whiteschists. Hydrogen isotope compositions of mixed white mica + chlorite samples from leucophyllites range from −40 to −35‰, correlating with chlorite contents. The calculated endmember chlorite and white mica have δD values of −30 and −40‰, respectively. The similar δD values of the white micas in leucophyllites, gneisses and metagranites suggest an overall equilibration with respect to H isotopes. The calculated δD value of the fluid is approximately 0‰, suggesting a seawater origin. This conclusion was also reached for the Dora Maira whiteschists. A possible fluid source that satisfies both metasomatic and isotopic data is dehydration of hydrothermally altered oceanic crust. The mafic–ultramafic complex of the Alpine Penninic unit underlying the Austroalpine nappes is a likely candidate. The subduction and subsequent dehydration of the ophiolite series would supply the Mg-rich fluids whose migration brought about the metasomatic alteration of the overlying gneiss-micaschist complexes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 25 June 1996 / Accepted: 24 February 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demény, A., Sharp, Z. & Pfeifer, HR. Mg-metasomatism and formation conditions of Mg-chlorite-muscovite-quartzphyllites (leucophyllites) of the Eastern Alps (W. Hungary) and their relations to Alpine whiteschists. Contrib Mineral Petrol 128, 247–260 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050306
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004100050306