Abstract
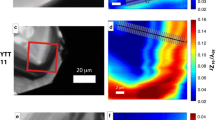
To better understand the origin of oscillatory zoning in zircons, distributions of REEs (represented by Ce, Sm, Dy and Lu), Y, Ti, Li and P in the igneous zircons (QH) from a felsic syenite in the Qinghu alkaline complex and metamorphic zircons (DMP06-14) from a banded granulite xenolith from Hannuoba basalts have been investigated with NanoSIMS. The NanoSIMS analyses reveal well correlation between the trace element distributions and the cathodoluminescence dark–bright zonings of zircons. The QH zircons with oscillatory zonings display large trace element variations within single grains by a factor up to 13.5, with Y and P ranging from 574 and 227 ppm in the bright zones to 7754 and 2464 ppm in the dark zones, respectively. By contrast, the DMP06-14 zircons without oscillatory zonings show much smaller trace element variations by a factor of 1.4, with Y ranging from 477 to 636 ppm and P from 331 to 467 ppm. Such large trace element variations in oscillatory zonings cannot be produced by compositional fluctuation in the magma chambers. The correlations between P and Y, REEs (Ce, Sm, Dy and Lu) (R 2 > 0.97) indicate xenotime substitution in zircons. The oscillatory distribution of P in zircon could be formed by the fluctuation of P in the melt adjacent to the mineral-melt boundary, either because P diffuses slower than Zr in the melt or due to surfacial interaction of melt with crystals. Such a zoned distribution of P in turn controls the substitution types of phosphates in zircon, developing oscillatory distributions of Y and REEs. Our results indicate that apparent partition coefficients of Y and REEs between zircon and melt are controlled by P contents, which may result in the large discrepancy in zircon partitioning data.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amelin Y, Lee D-C, Halliday AN, Pidgeon RT (1999) Nature of the Earth’s earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature 399:252–255. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v399/n6733/suppinfo/399252a0_S1.html
Burnham AD, Berry AJ (2012) An experimental study of trace element partitioning between zircon and melt as a function of oxygen fugacity. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 95:196–212. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.07.034
Cherniak D, Watson E (2010) Li diffusion in zircon. Contrib Mineral Petrol 160:383–390. doi:10.1007/s00410-009-0483-5
Davis DW, Krogh TE, Williams IS (2003) Historical development of zircon geochronology. Rev Mineral Geochem 53:145–181. doi:10.2113/0530145
Ferry JM, Watson EB (2007) New thermodynamic models and revised calibrations for the Ti-in-zircon and Zr-in-rutile thermometers. Contrib Mineral Petrol 154:429–437. doi:10.1007/s00410-007-0201-0
Finch RJ, Hanchar JM (2003) Structure and chemistry of zircon and zircon-group. Miner Rev Mineral Geochem 53:1–25. doi:10.2113/0530001
Finch RJ, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO, Burns PC (2001) Rare-earth elements in synthetic zircon: part 2. A single-crystal X-ray study of xenotime substitution. Am Mineral 86:681–689
Fowler A, Prokoph A, Stern R, Dupuis C (2002) Organization of oscillatory zoning in zircon: analysis, scaling, geochemistry, and model of a zircon from Kipawa, Quebec, Canada. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:311–328
Fu B et al (2008) Ti-in-zircon thermometry: applications and limitations. Contrib Miner Petrol 156:197–215. doi:10.1007/s00410-008-0281-5
Gardner J, Carey S, Rutherford M, Sigurdsson H (1995) Petrologic diversity in Mount St. Helens dacites during the last 4000 years: implications for magma mixing. Contrib Miner Petrol 119:224–238. doi:10.1007/bf00307283
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, van Achterbergh E, O’Reilly SY, Shee SR (2000) The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:133–147
Halden NM, Hawthorne FC (1993) The fractal geometry of oscillatory zoning in crystals; application to zircon. Am Mineral 78:1113–1116
Hanchar JM, van Westrenen W (2007) Rare earth element behavior in zircon-melt systems. Elements 3:37–42. doi:10.2113/gselements.3.1.37
Hanchar JM, Finch RJ, Hoskin PWO, Watson EB, Cherniak DJ, Mariano AN (2001) Rare earth elements in synthetic zircon: part 1. Synthesis, and rare earth element and phosphorus doping. Am Mineral 86:667–680
Harrison TM, Schmitt AK (2007) High sensitivity mapping of Ti distributions in Hadean zircons. Earth Planet Sci Lett 261:9–19
Harrison TM, Watson EB (1983) Kinetics of zircon dissolution and zirconium diffusion in granitic melts of variable water content. Contrib Miner Petrol 84:66–72. doi:10.1007/bf01132331
Harrison TM, Watson EB (1984) The behavior of apatite during crustal anatexis: equilibrium and kinetic considerations. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1467–1477
Hiess J, Nutman AP, Bennett VC, Holden P (2008) Ti-in-zircon thermometry applied to contrasting Archean metamorphic and igneous systems. Chem Geol 247:323–338
Hofmann A, Valley J, Watson E, Cavosie A, Eiler J (2009) Sub-micron scale distributions of trace elements in zircon. Contrib Miner Petrol 158:317–335. doi:10.1007/s00410-009-0385-6
Hofmann A, Baker M, Eiler J (2014) Sub-micron-scale trace-element distributions in natural zircons of known provenance: implications for Ti-in-zircon thermometry. Contrib Miner Petrol 168:1–21. doi:10.1007/s00410-014-1057-8
Hoskin PWO (2000) Patterns of chaos: fractal statistics and the oscillatory chemistry of zircon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64:1905–1923
Hoskin PWO (2005) Trace-element composition of hydrothermal zircon and the alteration of Hadean zircon from the Jack Hills, Australia. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69:637–648
Hoskin PWO, Ireland TR (2000) Rare earth element chemistry of zircon and its use as a provenance indicator. Geology 28:627–630. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<627:reecoz>2.0.co;2
Hoskin PWO, Schaltegger U (2003) The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Rev Mineral Geochem 53:27–62. doi:10.2113/0530027
Hoskin P, Arslan M, Aslan Z, Bolnmu JMJ (1998) Clinopyroxene phenocryst formation in an alkaline magma: interpretations from oscillatory zoning. Mineral Mag 62:653–654
Huang F et al (2009) Chemical and isotopic fractionation of wet andesite in a temperature gradient: experiments and models suggesting a new mechanism of magma differentiation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:729–749. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2008.11.012
Huang F, Chakraborty P, Lundstrom CC, Holmden C, Glessner JJG, Kieffer SW, Lesher CE (2010) Isotope fractionation in silicate melts by thermal diffusion. Nature 464:396–400. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v464/n7287/suppinfo/nature08840_S1.html
Kemp AIS et al (2007) Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon. Science 315:980–983
L’Heureux I, Fowler AD (1996) Dynamical model of oscillatory zoning in plagioclase with nonlinear partition relation. Geophys Res Lett 23:17–20. doi:10.1029/95gl03327
Li XH, Liu Y, Li QL, Guo CH, Chamberlain KR (2009) Precise determination of Phanerozoic zircon Pb/Pb age by multicollector SIMS without external standardization. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 10:Q04010. doi:10.1029/2009GC002400
Li WY, Teng FZ, Ke S, Rudnick RL, Gao S, Wu FY, Chappell BW (2010) Heterogeneous magnesium isotopic composition of the upper continental crust. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 74:6867–6884
Liu SJ, Li JH, Santosh M (2010) First application of the revised Ti-in-zircon geothermometer to Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature granulites of Tuguiwula, Inner Mongolia, North China Craton. Contrib Mineral Petrol 159:225–235. doi:10.1007/s00410-009-0425-2
Loomis T (1982) Numerical simulations of crystallization processes of plagioclase in complex melts: the origin of major and oscillatory zoning in plagioclase. Contrib Miner Petrol 81:219–229. doi:10.1007/bf00371299
Luo Y, Ayers JC (2009) Experimental measurements of zircon/melt trace-element partition coefficients. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 73:3656–3679. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2009.03.027
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Mojzsis SJ, Harrison TM, Pidgeon RT (2001) Oxygen-isotope evidence from ancient zircons for liquid water at the Earth’s surface 4300[thinsp]Myr ago. Nature 409:178–181. http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v409/n6817/suppinfo/409178A0_S1.html
Nardi LVS, Formoso MLL, Müller IF, Fontana E, Jarvis K, Lamarão C (2013) Zircon/rock partition coefficients of REEs, Y, Th, U, Nb, and Ta in granitic rocks: uses for provenance and mineral exploration purposes. Chem Geol 335:1–7. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2012.10.043
Nasdala L et al (2008) Zircon M257—homogeneous natural reference material for the ion microprobe U-Pb Analysis of zircon. Geostand Geoanal Res 32:247–265
Page FZ et al (2007) Zircons from kimberlite: new insights from oxygen isotopes, trace elements, and Ti in zircon thermometry. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 71:3887–3903
Pearce N, Perkins W, Westgate J, Gorton M, Jackson S, Neal C, Chenery S (1997) A compilation of new and published major and trace element data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 glass reference materials. Geostand Geoanal Res 21:115–144
Poitrasson F, Freydier R (2005) Heavy iron isotope composition of granites determined by high resolution MC-ICP-MS. Chem Geol 222:132–147
Richter FM, Watson EB, Mendybaev RA, Teng F-Z, Janney PE (2008) Magnesium isotope fractionation in silicate melts by chemical and thermal diffusion. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 72:206–220
Rustad J (2015) Interaction of rhyolite melts with monazite, xenotime, and zircon surfaces. Contrib Miner Petrol 169:1–8. doi:10.1007/s00410-015-1142-7
Sano Y, Terada K, Fukuoka T (2002) High mass resolution ion microprobe analysis of rare earth elements in silicate glass, apatite and zircon: lack of matrix dependency. Chem Geol 184:217–230
Singer BS, Dungan MA, Layne GD (1995) Textures and Sr, Ba, Mg, Fe, K, and Ti compositional profiles in volcanic plagioclase: clues to the dynamics of calc-alkaline magma chambers. Am Mineral 80:776–798
Speer J (1980) Zircon. In: Ribbe PH (ed) Orthosilicates. Reviews in mineralogy, vol 5. Mineralogical Society of America, Washington, DC, pp 67–112
Thomas JB, Bodnar RJ, Shimizu N, Sinha AK (2002) Determination of zircon/melt trace element partition coefficients from SIMS analysis of melt inclusions in zircon. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 66:2887–2901. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)00881-5
Trail D, Mojzsis SJ, Harrison TM, Schmitt AK, Watson EB, Young ED (2007) Constraints on Hadean zircon protoliths from oxygen isotopes, Ti-thermometry, and rare earth elements. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 8:Q06014. doi:10.1029/2006gc001449
Ushikubo T, Kita NT, Cavosie AJ, Wilde SA, Rudnick RL, Valley JW (2008) Lithium in Jack Hills zircons: evidence for extensive weathering of Earth’s earliest crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 272:666–676
Vavra G (1990) On the kinematics of zircon growth and its petrogenetic significance: a cathodoluminescence study. Contrib Miner Petrol 106:90–99. doi:10.1007/BF00306410
Wang Y, Merino E (1992) Dynamic model of oscillatory zoning of trace elements in calcite: double layer, inhibition, and self-organization. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:587–596
Wang S-J, Li S-G, An S-C, Hou Z-H (2012) A granulite record of multistage metamorphism and REE behavior in the Dabie orogen: constraints from zircon and rock-forming minerals. Lithos 136–139:109–125. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.11.001
Watson EB (1979) Zircon saturation in felsic liquids: experimental results and applications to trace element geochemistry. Contrib Miner Petrol 70:407–419. doi:10.1007/bf00371047
Watson EB (1980) Some experimentally determined zircon/liquid partition coefficients for the rare earth elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:895–897
Watson EB (1996) Dissolution, growth and survival of zircons during crustal fusion: kinetic principals, geological models and implications for isotopic inheritance. Earth Environ Sci Trans R Soc Edinb 87:43–56. doi:10.1017/S0263593300006465
Watson EB, Harrison TM (1983) Zircon saturation revisited: temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth Planet Sci Lett 64:295–304
Watson EB, Harrison TM (2005) Zircon thermometer reveals minimum melting conditions on earliest. Earth Sci 308:841–844. doi:10.1126/science.1110873
Watson E, Wark D, Thomas J (2006) Crystallization thermometers for zircon and rutile. Contrib Miner Petrol 151:413–433. doi:10.1007/s00410-006-0068-5
Wiedenbeck M et al (1995) Three natural zircon standards for U-Th-Pb, Lu-Hf, trace element and REE analyses. Geostand Newslett 19:1–23. doi:10.1111/j.1751-908X.1995.tb00147.x
Wilde SA, Valley JW, Peck WH, Graham CM (2001) Evidence from detrital zircons for the existence of continental crust and oceans on the Earth 4.4 Gyr ago. Nature 409:175–178
Yang J-H, Wu F-Y, Wilde S, Xie L-W, Yang Y-H, Liu X-M (2007) Tracing magma mixing in granite genesis: in situ U-Pb dating and Hf-isotope analysis of zircons. Contrib Miner Petrol 153:177–190. doi:10.1007/s00410-006-0139-7
Yuan H, Gao S, Liu X, Li H, Günther D, Wu F (2004) Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostand Geoanal Res 28:353–370. doi:10.1111/j.1751-908X.2004.tb00755.x
Zhang Y (2008) Geochemical kinetics. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 409–411
Zhang H-F, Yang Y-H, Santosh M, Zhao X-M, Ying J-F, Xiao Y (2012) Evolution of the Archean and Paleoproterozoic lower crust beneath the Trans-North China Orogen and the Western Block of the North China Craton. Gondwana Res 22:73–85
Acknowledgments
We thank Xianhua Li, Hongfu Zhang, Qiuli Li, Yu Liu, Guoqiang Tang for providing zircon samples, Lu Feng, Xuchao Zhao, Yuchen Xu for assistances in the laboratory and Yun Liu for discussion. Constructive comments from Qinzhu Yin, Fang Huang, Yan Luo, Shuijiong Wang, Liwei Deng and two anonymous reviewers are greatly appreciated. This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grants 41322022, 41230209, 41521062, 41173012, 41430105) and by CNSA (Grant No. TY3Q20110029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Timothy L. Grove.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, W., Lin, Y., Hao, J. et al. Phosphorus-controlled trace element distribution in zircon revealed by NanoSIMS. Contrib Mineral Petrol 171, 28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-016-1242-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-016-1242-z