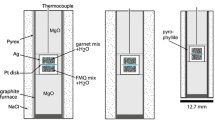
Abstract
We performed high strain (up to 47 %) axial compression experiments on natural quartz single crystals with added rutile powder (TiO2) and ~0.2 wt% H2O to investigate the effects of deformation on the titanium-in-quartz (TitaniQ) geothermobarometer. One of the objectives was to study the relationships between different deformation mechanisms and incorporation of Ti into recrystallized quartz grains. Experiments were performed in a Griggs-type solid-medium deformation apparatus at confining pressures of 1.0–1.5 GPa and temperatures of 800–1,000 °C, at constant strain rates of 1 × 10−6 or 1 × 10−7 s−1. Mobility of Ti in the fluid phase and saturation of rutile at grain boundaries during the deformation experiments are indicated by precipitation of secondary rutile in cracks and along the grain boundaries of newly recrystallized quartz grains. Microstructural analysis by light and scanning electron microscopy (the latter including electron backscatter diffraction mapping of grain misorientations) shows that the strongly deformed quartz single crystals contain a wide variety of deformation microstructures and shows evidence for subgrain rotation (SGR) and grain boundary migration recrystallization (GBMR). In addition, substantial grain growth occurred in annealing experiments after deformation. The GBMR and grain growth are evidence of moving grain boundaries, a microstructure favored by high temperatures. Electron microprobe analysis shows no significant increase in Ti content in recrystallized quartz grains formed by SGR or by GBMR, nor in grains grown by annealing. This result indicates that neither SGR nor moving grain boundaries during GBMR and grain growth are adequate processes to facilitate re-equilibration of the Ti content in experimentally deformed quartz crystals at the investigated conditions. More generally, our results suggest that exchange of Ti in quartz at low H2O contents (which may be realistic for natural deformation conditions) is still not fully understood. Thus, the application of the TitaniQ geothermobarometer to deformed metamorphic rocks at low fluid contents may not be as straightforward as previously thought and requires further research.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi T, Hokada T, Osanai Y, Toyoshima T, Baba S, Nakano N (2010) Titanium behavior in quartz during retrograde hydration: occurrence of rutile exsolution and implications for metamorphic processes in the Sør Rondane Mountains, East Antarctica. Polar Sci 3:222–234. doi:10.1016/j.polar.2009.08.005
Adams BL, Wright SI, Kunze K (1993) Orientation imaging: the emergence of a new microscopy. Metall Trans A 24:819–831
Baeta RD, Ashbee KH (1969a) Slip system in quartz: I experiments. Am Mineral 54:1551–1573
Baeta RD, Ashbee KH (1969b) Slip system in quartz: II interpretation. Am Mineral 54:1574–1582
Barker AK, Coogan LA, Gillis KM, Hayman NW, Weis D (2010) Direct observation of a fossil high-temperature, fault-hosted, hydrothermal upflow zone in crust formed at the East Pacific Rise. Geology 38:379–382. doi:10.1130/G30542.1
Bastin GF, Van Loo FJJ, Vosters PJC, Vrolijk JWGA (1984) An iterative procedure for the correction of secondary fluorescence effects in electron-probe microanalysis near phase boundaries. Spectrochim Acta B 39:1517–1522. doi:10.1016/0584-8547(84)80174-3
Blacic JD, Christie JM (1984) Plasticity and hydrolytic weakening of quartz single crystals. J Geophys Res 89:4223–4239
Campbell ME, Hanson JB, Minarik WG, Stix J (2009) Thermal history of the bandelier magmatic system: evidence for magmatic injection and recharge at 1.61 Ma as revealed by cathodoluminescence and titanium geothermometry. J Geol 117:469–485. doi:10.1086/604744
Cherniak DJ, Watson BE, Wark DA (2007) Ti diffusion in quartz. Chem Geol 236:65–74. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.09.001
Derby B (1991) The dependence of grain size on stress during dynamic recrystallization. Acta Metall 39:955–962
Donovan JJ, Lowers HA, Rusk BG (2011) Improved electron probe microanalysis of trace elements in quartz. Am Mineral 96:274–282. doi:10.2138/am2011.3631
Drury MR, Urai JL (1990) Deformation-related recrystallization processes. Tectonophysics 172:235–253
Evans B, Hay RS, Shimizu N (1986) Diffusion-induced grain-boundary migration in calcite. Geology 14:60–63. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<60
Flem B, Larsen RB, Grimstvedt A, Mansfeld J (2002) In situ analysis of trace elements in quartz by using laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Chem Geol 182:237–247. doi:10.1016/S0009-2541(01)00292-3
Fournelle J (2007) Problems in trace elements EMPA: modeling secondary fluorescence with PENEPMA. EOS transactions American Geophysical Union 88:52. Abstract V51A-0329
Frondel C (1962) Silica Minerals. In: Dana JD, Dana ES (eds) The system of mineralogy. Wiley, New York
Fynn GW, Powell WJA (1979) The cutting and polishing of electro-optical minerals. Adams Higer, London, p 216
Girard G, Stix J (2010) Rapid extraction of discrete magma batches from a large differentiating magma chamber: the Central Plateau Member rhyolites, Yellowstone Caldera, Wyoming. Contrib Miner Petrol 160:441–465. doi:10.1007/s00410-009-0487-1
Gottstein G, Mecking H (1985) Recrystallization. In: Wenk HR (ed) Preferred orientation in deformed metals and rocks: an introduction to modern texture analysis. Academic Press, Orlando, pp 183–218
Griggs D, Blacic JD (1964) The strength of quartz in the ductile regime. Transactions American Geophysical Union 45:102–103
Griggs D (1967) Hydrolytic weakening of quartz and other silicates. Geophys J Roy Astron Soc 14:19–31
Grujic D, Stipp M, Wooden JL (2011) Thermometry of quartz mylonites: importance of dynamic recrystallization on Ti-in-quartz reequilibration. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 12:1–19. doi:10.1029/2010GC003368
Guillope M, Poirier JP (1979) Dynamic recrystallization during creep of single-crystalline halite: an experimental study. J Geophys Res 84:5557–5567
Härtel M, Herweg M (2013) Titanium-in-quartz thermometry on synkinematic quartz veins in a retrograde crustal-scale normal fault zone. Tectonophysics 608:468–481
Hay RS, Evans B (1987a) Chemically induced migration in low and high angle calcite grain boundaries. Acta Metall 35:2049–2062
Hay RS, Evans B (1987b) Chemically induced grain boundary migration in calcite: temperature dependence, phenomenology, and possible applications to geologic systems. Contrib Miner Petrol 97:127–141
Hayden LA, Watson BE (2007) Rutile saturation in hydrous siliceous melts and its bearing on Ti-thermometry of quartz and zircon. Earth Planet Sci Lett 258:561–568. doi:10.1016/j.epsl.2007.04.020
Hermann J, O’Neill HSC, Berry AJ (2005) Titanium solubility in olivine in the system TiO2–MgO–SiO2: no evidence for an ultra-deep origin of Ti-bearing olivine. Contrib Miner Petrol 148:746–760. doi:10.1007/s00410-004-0637-4
Hirth G, Tullis J (1992) Dislocation creep regimes in quartz aggregates. J Struct Geol 14:145–159. doi:10.1016/0191-8141(92)90053-Y
Hirth G, Teyssier C, Dunlap J (2001) An evaluation of quartzite flow laws based on comparisons between experimentally and naturally deformed rocks. Int J Earth Sci 90:77–87. doi:10.1007/s005310000152
Huang R, Audétat A (2011) A critical look at the titanium-in-quartz (TitaniQ) thermobarometer. Mineralogical Magazine Goldschmidt Abstract p 1065
Huang R, Audétat A (2012) The titanium-in-quartz (TitaniQ) thermobarometer: a critical examination and re-calibration. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 84:75–89. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2012.01.009
Jacamon F, Larsen RB (2009) Trace element evolution of quartz in the charnockitic Kleivan granite, SW-Norway: the Ge/Ti ratio of quartz as an index of igneous differentiation. Lithos 107:281–291. doi:10.1016/j.lithos.2008.10.016
Jessell MW (1987) Grain-boundary migration microstructures in a naturally deformed quartzite. J Struct Geol 9:1007
Kawasaki T, Osanai Y (2008) Empirical thermometer of TiO2 in quartz for ultrahigh-temperature granulites of East Antarctica. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 308:419–430. doi:10.1144/SP308.21
Kohn MJ, Northrup CJ (2009) Taking mylonites’ temperatures. Geology 37:47–50. doi:10.1130/G25081A.1
Larsen RB, Henderson I, Ihlen PM, Jacamon F (2004) Distribution and petrogenetic behaviour of trace elements in granitic pegmatite quartz from South Norway. Contrib Miner Petrol 147:615–628. doi:10.1007/s00410-004-0580-4
Martin JJ, Armington AF (1983) Effect of growth rate on quartz defects. J Cryst Growth 62:203–206
Menegon L, Nasipuri P, Stünitz H, Behrens H, Ravna E (2011) Dry and strong quartz during deformation of the lower crust in the presence of melt. J Geophys Res 116:1–23. doi:10.1029/2011JB008371
Ostapenko GT, Tarashchan AN, Mitsyuk BM (2007) Rutile-quartz geothermobarometer. Geochem Int 45:506–508. doi:10.1134/S0016702907050084
Pec M, Stünitz H, Heilbronner R (2011) Semi-brittle deformation of granitoid gouges in shear experiments at elevated pressures and temperatures. J Struct Geol 1–22. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2011.09.001
Pennacchioni G, Menegon L, Leiss B, Nestola F, Bromiley G (2010) Development of crystallographic preferred orientation and microstructure during plastic deformation of natural coarse-grained quartz veins. J Geophys Res. doi:10.1029/2010JB007674
Perkins D (2002) Mineralogy, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall Publishers, New Jersey
Poirier J (1985) Creep of crystals. Cambridge University Press, New York
Prior DJ, Boyle AP, Brenker F, Cheadle MC, Austin D, Lopez G, Peruzzo L, Potts GJ, Reddy S, Spiess R, Timms NE, Trimby PW, Wheeler J, Zetterström L (1999) The application of electron backscatter diffraction and orientation contrast imaging in the SEM to textural problems in rocks. Am Mineral 84:1741–1759
Rankama K, Sahama TG (1950) Geochemistry. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Rossi M, Rolland Y, Vidal O, Cox SF (2005) Geochemical variations and element transfer during shear-zone development and related episyenites at middle crust depths: insights from the Mont Blanc granite (French—Italian Alps). Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 245:373–396. doi:10.1144/GSL.SP.2005.245.01.18
Rusk BG (2006) Intensity of quartz cathodoluminescence and trace-element content in quartz from the porphyry copper deposit at Butte, Montana. Am Mineral 91:1300–1312. doi:10.2138/am 2006.1984
Rusk BG, Lowers HA, Reed MH (2008) Trace elements in hydrothermal quartz: relationships to cathodoluminescent textures and insights into vein formation. Geology 36:547. doi:10.1130/G24580A.1
Sato K, Santosh M (2007) Titanium in quartz as a record of ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism: the granulites of Karur, southern India. Mineral Mag 71:143–154. doi:10.1180/minmag.2007.071.2.143
Sinha AK, Hewitt DA, Rimstidt JD (1986) Fluid interaction and element mobility in the development of ultramylonites. Geology 14:883–886. doi:10.1130/0091-7613(1986)14<883
Smith V, Shane P, Nairn I (2010) Insights into silicic melt generation using plagioclase, quartz and melt inclusions from the caldera-forming Rotoiti eruption, Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand. Contrib Miner Petrol 160:951–971. doi:10.1007/s00410-010-0516-0
Spear FS, Wark DA (2009) Cathodoluminescence imaging and titanium thermometry in metamorphic quartz. J Metamorph Geol 27:187–205. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2009.00813.x
Stipp M, Tullis J (2003) The recrystallized grain size piezometer for quartz. Geophys Res Lett 30:1–5. doi:10.1029/2003GL018444
Stipp M, Stünitz H, Heilbronner R, Schmid SM (2002a) Dynamic recrystallization of quartz: correlation between natural and experimental deformation conditions. In: de Meer S, Drury MR, Bresser JHP, Pennock GM (eds) Deformation mechanisms, rheology and tectonics: current status and future perspectives. Special Publication, Geological Society, London 200:171–190
Stipp M, Stünitz H, Heilbronner R, Schmid SM (2002b) The eastern Tonale fault zone: a “natural laboratory” for crystal plastic deformation of quartz over a temperature range from 250 to 700 °C. J Struct Geol 24:1861–1884
Stipp M, Tullis J, Behrens H (2006) Effect of water on the dislocation creep microstructure and flow stress of quartz and implications for the recrystallized grain size piezometer. J Geophys Res 111:B04201. doi:10.1029/2005JB003852
Stipp M, Tullis J, Scherwath M, Behrmann JH (2010) A new perspective on paleopiezometry: dynamically recrystallized grain size distributions indicate mechanism changes. Geology 38:759–762. doi:10.1130/G31162.1
Storm LC, Spear FS (2009) Application of the titanium-in-quartz thermometer to pelitic migmatites from the Adirondack Highlands, New York. J Metamorph Geol 27:479–494. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2009.00829.x
Stünitz H (1998) Syndeformational recrystallization: dynamic or compositionally induced? Contrib Miner Petrol 131:219–236
Stünitz H, Fitz Gerald JD, Tullis J (2003) Dislocation generation, slip systems, and dynamic recrystallization in experimentally deformed plagioclase single crystals. Tectonophysics 372:215–233. doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(03)00241-5
Tarantola A, Diamond LW, Stünitz H (2010) Modification of fluid inclusions in quartz by deviatoric stress I: experimentally induced changes in inclusion shapes and microstructures. Contrib Miner Petrol 160:825–843. doi:10.1007/s00410-010-0509-z
Tarantola A, Diamond LW, Stünitz H, Thust A, Pec M (2012) Modification of fluid inclusions in quartz by deviatoric stress. III: influence of principal stresses on inclusion density and orientation. Contrib Miner Petrol. doi:10.1007/s00410-012-0749-1
Thomas JB, Watson BE (2012) Application of the Ti-in-quartz thermobarometer to rutile-free systems. Reply to: a comment on: “TitaniQ under pressure: the effect of pressure and temperature on the solubility of Ti in quartz” by Thomas et al. Contrib Miner Petrol. doi:10.1007/s00410-012-0761-5
Thomas JB, Watson BE, Spear FS, Shemella PT, Nayak SK, Lanzirotti A (2010) TitaniQ under pressure: the effect of pressure and temperature on the solubility of Ti in quartz. Contrib Miner Petrol 160:743–759. doi:10.1007/s00410-010-0505-3
Thust A, Tarantola A, Stünitz H, Heilbronner R, Behrens H, Fitz Gerald JD (2012) Water redistribution in experimentally deformed natural quartz single crystals. PhD Thesis at university of Basel, Switzerland
Tullis TE, Tullis J (1986) Experimental rock deformation techniques. In: Hobbs BE, Heard HC (eds) Mineral and rock deformation: laboratory studies. Geophys Monogr Ser 36:297–324. AGU, Washington. doi:10.1029/GM036p0297
Urai JL, Means WD, Lister GS (1986) Dynamic recrystallization of minerals. In: Hobbs E, Heard HC (eds) Mineral and rock deformation: laboratory studies. Geophys Monogr Ser 36:161–199 AGU, Washington. doi:10.1029/GM036p0161
Vazquez JA, Kyriazis SF, Reid MR, Sehler RC, Ramos FC (2009) Thermochemical evolution of young rhyolites at Yellowstone: evidence for a cooling but periodically replenished postcaldera magma reservoir. J Volcanol Geoth Res 188:186–196. doi:10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2008.11.030
Vernooij MGC, Kunze K, Den Brok B (2006a) “Brittle” shear zones in experimentally deformed quartz single crystals. J Struct Geol 28:1292–1306. doi:10.1016/j.jsg.2006.03.018
Vernooij MGC, Den Brok B, Kunze K (2006b) Development of crystallographic preferred orientations by nucleation and growth of new grains in experimentally deformed quartz single crystals. Tectonophysics 427:35–53. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2006.06.008
Wark DA, Watson BE (2006) TitaniQ: a titanium-in-quartz geothermometer. Contrib Miner Petrol 152:743–754. doi:10.1007/s00410-006-0132-1
Wark DA, Hildreth W, Spear FS, Cherniak DJ, Watson BE (2007) Pre-eruption recharge of the Bishop magma system. Geology 35:235. doi:10.1130/G23316A.1
Watson BE (2004) A conceptual model for near-surface kinetic controls on the trace-element and stable isotope composition of abiogenic calcite crystals. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1473–1488. doi:10.1016/j.gca.2003.10.003
Watson BE, Liang Y (1995) A simple model for sector zoning in slowly grown crystals: implications for growth rate and lattice diffusion, with emphasis on accessory minerals in crustal rocks. Am Mineral 80:1179–1187
Wheeler J, Prior DJ, Jiang Z, Spiess R, Trimby PW (2001) The petrological significance of misorientations between grains. Contrib Miner Petrol 141:109–124. doi:10.1007/s004100000225
White S (1976) The effects of strain on the microstructures, fabrics, and deformation mechanisms in quartzites. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 283:69–86
Wilson CJN, Seward TM, Allan ASR, Charlier BLA, Bello L (2012) A comment on: “TitaniQ under pressure: the effect of pressure and temperature on the solubility of Ti in quartz”, by Jay B. Thomas, E. Bruce Watson, Frank S. Spear, Philip T. Shemella, Saroj K. Nayak and Antonio Lanzirotti. Contrib Miner Petrol. doi:10.1007/s00410-012-0757-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Hoefs.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Negrini, M., Stunitz, H., Berger, A. et al. The effect of deformation on the TitaniQ geothermobarometer: an experimental study. Contrib Mineral Petrol 167, 982 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-0982-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-014-0982-x