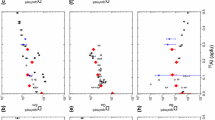
Abstract
We present the variation in trace element partition coefficients measured at the interface between rapidly cooled clinopyroxene crystals and co-existing melts. Results indicate that, as the cooling rate is increased, clinopyroxene crystals are progressively depleted in Si, Ca and Mg counterbalanced by enrichments in Al (mainly tetrahedral Aliv), Na and Ti. Partition coefficients (Ds) for rare earth elements (REE), high field strength elements (HFSE) and transition elements (TE) increase with increasing cooling rate, in response to clinopyroxene compositional variations. The entry of REE into the M2 site is facilitated by a coupled substitution where either Na substitutes for Ca on the M2 site or Aliv substitutes for Si in the tetrahedral site. The latter substitution reflects an increased ease of locally balancing the excess charge at M2 as the number of surrounding Aliv atoms increases. Due to the lower concentration of Ca in rapidly cooled clinopyroxenes, divalent large ion lithophile elements (LILE) on M2 decrease at the expense of monovalent cations. Conversely, higher concentrations of HFSE and TE on the M1 site are facilitated as the average charge on this site increases with the replacement of divalent-charged cations by Alvi. Although crystallization kinetics modify clinopyroxene composition, deviations from equilibrium partitioning are insufficient to change the tendency of a trace element to be compatible or incompatible. Consequently, there are regular relationships between ionic radius, valence of the trace element and D. At both equilibrium and cooling rate conditions, Ds for isovalent cations define parabola-like curves when plotted against ionic radius, consistent with the lattice strain model, demonstrating that the partitioning of trace elements is driven by charge balance mechanisms; cation substitution reactions can be treated in terms of the energetics of the various charge-imbalanced configurations.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker DR (2008) The fidelity of melt inclusions as records of melt composition. Contrib Mineral Petrol 157:377–395
Beattie P (1993) The generation of uranium series disequilibria by partial melting of spinel peridotite: constraints from partitioning studies. Earth Planet Sci Lett 117:379–391
Bennett S, Blundy J, Elliott J (2004) The effect of sodium and titanium on crystal-melt partitioning of trace elements. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:2335–2347
Blundy JD, Wood BJ (1994) Prediction of crystal-melt partition coefficients from elastic moduli. Nature 372:452–454
Blundy JD, Wood B (2003) Partitioning of trace elements between crystals and melts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 210:383–397
Blundy JD, Falloon TJ, Wood BJ, Dalton JA (1995) Sodium partitioning between clinopyroxene and silicate melts. J Geophys Res 100:15501–15516
Blundy JD, Robinson JAC, Wood BJ (1998) Heavy REE are compatible in clinopyroxene on the spinel lherzolite solidus. Earth Planet Sci Lett 160:493–504
Brice JC (1975) Some thermodynamic aspects of the growth of strained crystals. J Cryst Growth 28:249–253
Burkhard DJM (2002) Kinetics of crystallization: example of microcrystallization in basalt lava. Contrib Mineral Petrol 142:724–737
Cashman KV, Kauahikaua JP, Thornber C (1999) Cooling and crystallization of lava in open channels, and the transition of pahoehoe lava to a’a. Bull Volcanol 61:306–323
Chistyakova S, Latypov R (2009) On the development of internal chemical zonation in small mafic dykes. Geol Mag 147:1–12
Coish RA, Taylor LA (1979) The effect of cooling rate on texture and pyroxene chemistry in DSDP Leg 34 basalt: a microprobe study. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42:389–398
Conte AM, Perinelli C, Trigila R (2006) Cooling kinetics experiments on different Stromboli lavas: effects on crystal morphologies and phases compositions. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 155:179–200
Del Gaudio P, Mollo S, Ventura G, Iezzi G, Taddeucci J, Cavallo A (2010) Cooling rate induced differentiation in anhydrous and hydrous basalts at 500 MPa: implications for the storage and transport of magmas in dikes. Chem Geol 270:164–178
Dingwell DB (2006) Transport properties of magmas: diffusion and rheology. Elements 2:281–286
Dowty E (1976) Crystal structure and crystal growth: I. The influence of internal structure on morphology. Am Mineral 61:448–459
Dowty E (1980) Crystal growth and nucleation theory and the numerical simulation of igneous crystallization. In: Hargraves RB (ed) The physics of magmatic processes. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 419–485
Ferlito C, Viccaro M, Nicotra E, Cristofolini R (2011) Regimes of magma recharge on the eruptive behaviour during the period 2001–2005 at Mt. Etna volcano. Bull Volcanol 74:533–543
Forsythe LM, Nielsen RL, Fisk MR (1994) High-field strength element partitioning between pyroxene and basaltic to dacitic magmas. Chem Geol 117:107–125
Francis D, Minarik W (2008) Aluminum-dependent trace element partitioning in clinopyroxene. Contrib Mineral Petrol 156:439–451
Gaetani GA, Grove TL (1995) Partitioning of rare earth elements between clinopyroxene and silicate melt: crystal-chemical controls. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:1951–1962
Gallahan WE, Nielsen RL (1992) The partitioning of Sc, Y, and the rare-earth elements between High-Ca pyroxene and natural Mafic to intermediate lavas at 1-atmosphere. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:2387–2404
Gamble RP, Taylor LA (1980) Crystal/liquid partitioning in augite: effects of cooling rate. Earth Planet Sci Lett 47:21–33
Green T, Blundy J, Adam J, Yaxley G (2000) SIMS determination of trace element partition coefficients between garnet, clinopyroxene and hydrous basaltic liquids at 2–7.5 GPa and 1080–1200 °C. Lithos 53:165–187
Grove TL, Bence AE (1977) Experimental study of pyroxene-liquid interaction in quartz-normative basalt 15597. In: Proceedings of Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 8th, pp 1549–1579
Grove TL, Bence AE (1979) Crystallization kinetics in a multiply saturated basalt magma: an experimental study of Luna 24 ferrobasalt. In: Proceedings of the 10th lunar science conference, pp 439–478
Grove TL, Raudsepp M (1978) Effects of kinetics on the crystallization of quartznormative basalt 15597: an experimental study. In: Proceedings of Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 9th, pp 585–599
Hammer JE (2006) Influence of fO2 and cooling rate on the kinetics and energetics of Fe-rich basalt crystallization. Earth Planet Sci Lett 248:618–637
Hammer JE (2008) Experimental studies of the kinetics and energetics of magma crystallization. In: Putirka KD, Tepley FJ (eds) Minerals, inclusions and volcanic processes. Reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 69. Mineralogical Society of America, Chantilly, VA, pp 9–59
Hart SR, Dunn T (1993) Experimental cpx-melt partitioning of 24 trace elements. Contrib Mineral Petrol 113:1–8
Heap MJ, Mollo S, Vinciguerra S, Lavallée Y, Hess K-U, Dingwell DB, Baud P, Iezzi G (2013) Thermal weakening of the carbonate basement under Mt. Etna volcano (Italy): implications for volcano instability. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 250:42–60
Hill E, Wood BJ, Blundy JD (2000) The effect of Ca-Tschermaks component on trace element partitioning between clinopyroxene and silicate melt. Lithos 53:203–215
Hollister LS (1970) Origin, mechanism, and consequences of compositional sector-zoning in staurolite. Am Mineral 55:742–766
Hollister LS, Gancarz AJ (1971) Compositional sector-zoning in clinopyroxene from the Narce area, ltaly. Am Mineral 56:959–979
Hoover SR, Cashman KV, Manga M (2001) The yield strength of subliquidus basalts: experimental results. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 107:1–18
Iezzi G, Mollo S, Ventura G, Cavallo A, Romano C (2008) Experimental solidification of anhydrous latitic and trachytic melts at different cooling rates: the role of nucleation kinetics. Chem Geol 253:91–101
Iezzi G, Mollo S, Torresi G, Ventura G, Cavallo A, Scarlato P (2011) Experimental solidification of an andesitic melt by cooling. Chem Geol 283:261–273
Kennedy AK, Lofgren GE, Wasserburg GJ (1993) An experimental-study of trace-element partitioning between olivine, ortho-pyroxene and melt in chondrules—equilibrium values and kinetic effects. Earth Planet Sci Lett 115:177–195
Kirkpatrick RJ (1981) Kinetics of crystallization of igneous rocks. In Kinetics of geochemical processes. Rev Mineral Geochem 8:321–395
Kirkpatrick RJ (1983) Theory of nucleation in silicate melts. Am Mineral 68:66–77
Kress VC, Carmichael ISE (1991) The compressibility of silicate liquids containing Fe2O3 and the effect of composition, temperature, oxygen fugacity and pressure on their redox states. Contrib Mineral Petrol 108:82–92
Lanzafame G, Mollo S, Iezzi G, Ferlito C, Ventura G (2013) Unraveling the solidification path of a pahoehoe “cicirara” lava from Mount Etna volcano. Bull Volcanol. doi:10.1007/s00445-013-0703-8
LaTourette TZ, Burnett DS (1992) Experimental determination of U and Th partitioning between clinopyroxene and natural and synthetic basaltic liquid. Earth Planet Sci Lett 110:227–244
Leung IS (1974) Sector-zoned titanaugites: morphology, crystal chemistry, and growth. Am Mineral 59:127–138
Lindsley DH (1980) Phase equilibria of Ca-Mg-Fe pyroxenes at pressures greater than 1 atm. Rev Mineral 7:289–307
Lindstrom DJ (1976) Experimental study of the partitioning of the transition metals between clinopyroxene and coexisting silicate liquids. PhD Thesis, University of Oregon, OR, USA
Lofgren G (1980) Experimental studies on the dynamic crystallization of silicate melts. In: Hargraves RB (ed) The physics of magmatic processes. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 487–551
Lofgren GE, Huss GR, Wasserburg GJ (2006) An experimental study of trace element partitioning between Ti–Al–clinopyroxene and melt: equilibrium and kinetic effects including sector zoning. Am Mineral 91:1596–1606
Lundstrom CC, Shaw HF, Ryerson FJ, Phinney DL, Gill JB, Williams Q (1994) Compositional controls on the partitioning of U, Th, Ba, Pb, Sr and Zr between clinopyroxene and haplobasaltic melts: implications for uranium series disequilibria in basalts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 128:407–423
Lundstrom CC, Shaw HF, Ryerson FJ, Williams Q, Gill J (1998) Crystal chemical control of clinopyroxene-melt partitioning in the Di–Ab–An system: implications for elemental fractionations in the depleted mantle. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:2849–2862
Marks M, Halama R, Wenzel T, Markl G (2004) Trace element variations in clinopyroxene and amphibole from alkaline to peralkaline syenites and granites: implications for mineral-melt trace-element partitioning. Chem Geol 211:185–215
Matsui Y, Onuma N, Nagasawa H, Higuchi H, Banno S (1977) Crystal structure control in trace element partition between crystal and magma. Tectonics 100:315–324
McKay G, Le L, Wagstaff J, Crozaz G (1994) Experimental partitioning of rare earth element and strontium: constraints on the petrogenesis and redox conditions during crystallisation of Antarctic angrite Lewis Cliff 86010. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 58:2911–2919
Métrich N, Rutherford MJ (1998) Low pressure crystallization paths of H2O-saturated basaltic-hawaiitic melts from Mt Etna: implications for open-system degassing of basaltic volcanoes. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 62:1195–1205
Mevel C, Velde D (1976) Clinopyroxenes in Mesozoic pillow lavas from the French Alps: influence of cooling rate on compositional trends. Earth Planet Sci Lett 32:158–164
Mollo S, Del Gaudio P, Ventura G, Iezzi G, Scarlato P (2010a) Dependence of clinopyroxene composition on cooling rate in basaltic magmas: implications for thermobarometry. Lithos 118:302–312
Mollo S, Gaeta M, Freda C, Di Rocco T, Misiti V, Scarlato P (2010b) Carbonate assimilation in magmas: a reappraisal based on experimental petrology. Lithos 114:503–514
Mollo S, Lanzafame G, Masotta M, Iezzi G, Ferlito C, Scarlato P (2011a) Cooling history of a dike as revealed by mineral chemistry: a case study from Mt. Etna volcano. Chem Geol 288:39–52
Mollo S, Putirka K, Iezzi G, Del Gaudio P, Scarlato P (2011b) Plagioclase-melt (dis)equilibrium due to cooling dynamics: implications for thermometry, barometry and hygrometry. Lithos 125:221–235
Mollo S, Vinciguerra S, Iezzi G, Iarocci A, Scarlato P, Heap MJ, Dingwell DB (2011c) Volcanic edifice weakening via devolatilization reactions. Geophys J Int 186:1073–1077
Mollo S, Misiti V, Scarlato P, Soligo M (2012a) The role of cooling rate in the origin of high temperature phases at the chilled margin of magmatic intrusions. Chem Geol 322–323:28–46
Mollo S, Iezzi G, Ventura G, Cavallo A, Scarlato P (2012b) Heterogeneous nucleation mechanisms and formation of metastable phase assemblages induced by different crystalline seeds in a rapidly cooled andesitic melt. J Non-Cryst Solids 358:1624–1628
Mollo S, Putirka K, Misiti V, Soligo M, Scarlato P (2013a) A new test for equilibrium based on clinopyroxene-melt pairs: clues on the solidification temperatures of Etnean alkaline melts at post-eruptive conditions. Chem Geol 352:92–100. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.05.026
Mollo S, Putirka K, Iezzi G, Scarlato P (2013b) The control of cooling rate on titanomagnetite composition: implications for a geospeedometry model applicable to alkaline rocks from Mt. Etna volcano. Contrib Mineral Petrol 165:457–475
Mollo S, Scarlato P, Lanzafame G, Ferlito C (2013c) Deciphering lava flow post-eruption differentiation processes by means of geochemical and isotopic variations: a case study from Mt. Etna volcano. Lithos 162–163:115–127
Nagasawa H (1966) Trace element partition coefficient in ionic crystals. Science 152:767–769
Nakamura Y (1973) Origin of sector-zoning of igneous clinopyroxenes. Am Mineral 58:986–990
Naney MT, Swanson SE (1980) The effect of Fe and Mg on crystallization in granitic systems. Am Mineral 65:639–653
Onuma N, Higuchi H, Wakita H, Nagasawa H (1968) Trace element partitioning between two pyroxenes and the host lava. Earth Planet Sci Lett 5:47–51
Pinilla C, Davis SA, Scott TB, Allan NL, Blundy JD (2012) Interfacial storage of noble gases and other trace elements in magmatic systems. Earth Planet Sci Lett 319–320:287–294
Press WH, Teukolsky SA, Vetterling WT, Flannery BP (1992) Numerical recipes in C, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, London
Putirka K (1999) Clinopyroxene + liquid equilibria to 100 kbar and 2450 K. Contrib Mineral Petrol 135:151–163
Putirka KD (2008) Thermometers and barometers for volcanic systems. In: Putirka KD, Tepley F (eds) Minerals, inclusions, and volcanic processes: reviews in mineralogy and geochemistry, vol 69, American Mineralogical Society, Washington, DC, pp 61–120
Putirka K, Johnson M, Kinzler R, Longhi J, Walker D (1996) Thermobarometry of mafic igneous rocks based on clinopyroxene-liquid equilibria, 0–30 kbar. Contrib Mineral Petr 123:92–108
Ray GL, Shimizu N, Hart SR (1983) An ion microprobe study of the partitioning of trace elements between clinopyroxene and liquid in the system diopside–albite–anorthite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 47:2131–2140
Schosnig M, Hoffer E (1998) Compositional dependence of REE partitioning between diopside and melt at 1 atmosphere. Contrib Mineral Petrol 133:205–216
Shannon RD (1976) Revised effective ionic radii in oxides and fluorides. Acta Crystallogr A 32:751–757
Shearer CK, Papike JJ, Simon SB, Shimizu N (1989) An ion microprobe study of the intra-crystalline behavior of REE and selected trace elements in pyroxene from mare basalts with different cooling and crystallization histories. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:1041–1054
Shimizu N (1981) Trace element incorporation into growing augite phenocryst. Nature 289:575–577
Skulski T, Minarik W, Watson EB (1994) High pressure experimental trace-element partitioning between clinopyroxene and basaltic melts. Chem Geol 117:127–147
Smith D, Lindsley DH (1971) Stable and metastable augite crystallization trends in a single basalt flow. Am Mineral 56:225–233
Smith VG, Tiller WA, Rutter JW (1955) A mathematical analysis of solute redistribution during solidification. Can J Phys 33:723–745
Sunagawa I (1992) In situ investigation of nucleation, growth, and dissolution of silicate crystals at high temperatures. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 20:113–142
Tanguy JC, Condomines M, Kieffer G (1997) Evolution of the Mount Etna magma: constraints on the present feeding system and eruptive mechanism. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 75:221–250
Tiller WA, Jackson KA, Rutter JW, Chalmers B (1953) The redistribution of solute atoms during the solidification of metals. Acta Metall 1:428–437
Tormey DR, Grove TL, Bryan WB (1987) Experimental petrology of normal MORB near the Kane fracture zone: 22–25°N, mid-Atlantic ridge. Contrib Mineral Petrol 96:121–139
Tuff J, Gibson S (2007) Trace-element partitioning between garnet, clinopyroxene and Fe-rich picritic melts at 3 to 7 GPa. Contrib Mineral Petrol 153:369–387
Ujike O (1982) Microprobe mineralogy of plagioclase, clinopyroxene and amphibole as records of cooling rate in the Shirotori-Hiketa dike swarm, northeastern Shikoku, Japan. Lithos 15:281–293
Vetere F, Iezzi G, Behrens H, Cavallo A, Misiti V, Dietrich M, Knipping J, Ventura G, Mollo S (2013) Intrinsic solidification behaviour of basaltic to rhyolitic melts: a cooling rate experimental study. Chem Geol. doi:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2013.06.007
Watson EB (1996) Surface enrichment and trace-element uptake during crystal growth. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:5013–5020
Watson EB, Liang Y (1995) A simple model for sector zoning in slowly-grown crystals: implications for growth rate and lattice diffusion, with emphasis on accessory minerals in crustal rocks. Am Mineral 80:1170–1187
Watson EB, Muller T (2009) Non-equilibrium isotopic and elemental fractionation during diffusion-controlled crystal growth under static and dynamic conditions. Chem Geol 267:111–124
Wood BJ, Blundy JD (1997) A predictive model for rare earth element partitioning between clinopyroxene and anhydrous silicate melt. Contrib Mineral Petrol 129:166–181
Wood BJ, Blundy JD (2001) The effect of cation charge on crystal-melt partitioning of trace elements. Earth Planet Sci Letts 188:59–72
Wood B, Trigila R (2001) Experimental determination of aluminium clinopyroxene-melt partition coefficients for potassic liquids, with application to the evolution of the Roman province potassic magmas. Chem Geol 172:213–222
Wood BJ, Blundy JD, Robinson JAC (1999) The role of clinopyroxene in generating U-series disequilibrium during mantle melting. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:1613–1620
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to the reviewers, J. E. Hammer and G. A. Gaetani, for their helpful suggestions. T. L. Grove is warmly acknowledged for the editorial handling. A. Cavallo is thanked for assistance during electron microprobe analysis. The research activities of the HP-HT laboratory of the INGV were supported by the European Observing System Infrastructure Project (EPOS). S. Mollo was supported by the ERC Starting grant 259256 GLASS project. This study was funded by the “Fondi Ateneo of the University G. d’Annunzio” and the PRIN project “Experimental determination of the glass-forming ability (GFA), nucleation and crystallization of natural silicate melts” awarded to G. Iezzi. J. Blundy acknowledges support from a Wolfson Research Merit Award from the Royal Society and ERC Advanced Grant “CRITMAG.”
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. L. Grove.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mollo, S., Blundy, J.D., Iezzi, G. et al. The partitioning of trace elements between clinopyroxene and trachybasaltic melt during rapid cooling and crystal growth. Contrib Mineral Petrol 166, 1633–1654 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-013-0946-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-013-0946-6