Abstract
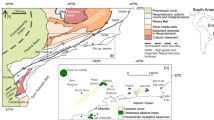
Upper mantle xenoliths from the southern Rio Grande rift axis (Potrillo and Elephant Butte) and flank (Adam’s Diggings) have been investigated to determine chemical depletion and enrichment processes. The variation of modal, whole rock, and mineral compositions reflect melt extraction. Fractional melting is the likely process. Fractional melting calculations show that most spinel peridotites from rift axis locations have undergone <5% melting versus 7–14% melting for xenoliths from the rift shoulder, although the total range of fractional melting overlaps at all three locations. In the rift axis, deformed (equigranular and porphyroclastic texture) spinel peridotites are generally characterized by significantly less fractional melting (2–5%) than undeformed (protogranular) xenoliths (up to 16%). This difference may reflect undeformed xenoliths being derived from greater depths and higher temperatures than deformed rocks. Spinel peridotites from the axis and shoulder of the Rio Grande rift have undergone mantle metasomatism subsequent to melt extraction. Under the rift shoulder spinel peridotites have undergone both cryptic and patent (modal) metasomatism, possibly during separate events, whereas the upper mantle under the rift axis has undergone only cryptic metasomatism by alkali basaltic magma.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam J, Green TH (1994) The effects of pressure and temperature on the partitioning of Ti, Sr, and REE between amphibole, clinopyroxene and basanitic melts. Chem Geol 117:219–233
Aldrich MJJr, Chapin CE, Laughlin AW (1986) Stress history and tectonic development of the Rio Grande rift, New Mexico. J Geophys Res 91:6199–6211
Bachman GO, Mehnert HH (1978) New K-Ar dates and the late Pliocene to Holocene geomorphic history of the central Rio Grande region, New Mexico. Geol Soc Am Bull 89:283–292
Baldridge WS (1979) Mafic and ultramafic inclusion suites from the Rio Grande rift (New Mexico) and their bearing on the composition and thermal state of the lithosphere. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 6:319–351
Baldridge WS, Damon PE, Shafiqullah M, Bridwell RJ (1980) Evolution of the central Rio Grande rift, New Mexico: new potassium–argon ages. Earth Plant Sci Lett 51:309–321
Baldridge WS, Olsen KH, Callender JF (1984) Rio Grande rift: problems and perspectives. N M Geol Soc Guidebook 35:1–12
Baldridge WS, Perry FV, Vaniman DT, Nealey LD, Leavy BD, Laughlin AW, Kyle P, Bartow Y, Steinitz G, Gladney ES (1991) Middle to late Cenozoic magmatism of the southeastern Colorado Plateau and central Rio Grande rift (New Mexico and Arizona, USA): a model for continental rifting. Tectonophysics 197:327–354
Baldridge WS, Keller GR, Haak V, Wendlandt E, Jiracek GR, Olsen KH (1995) The Rio Grande rift, In: Olsen KH (ed) Continental rifts: evolution, structure, tectonic. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 233–275
Beccaluva L, Bonadiman C, Coltorti M, Salvini L, Siena F (2001) Depletion event, nature of metasomatizing agent and timing of enrichment processes in lithospheric mantle xenoliths from the Veneto volcanic province. J Petrol 42:173–187
Bonatti E, Ottonello G, Hamlyn PR (1986) Peridotites from Island of Zabargad (St John) Red Sea: petrology and geochemistry. J Geophys Res 91:599–631
Brown GC, Mussett AE (1981) The inaccessible Earth. Allen & Unwin, London, pp 235
Bussod GYA, Williams DR (1991) Thermal and kinematic model of the southern Rio Grande rift: inferences from crustal and mantle xenoliths from Kilbourne Hole, New Mexico. Tectonophysics 197:373–389
Carlson, RW, Nowell, GM (2001) Olivine-poor sources for mantle-derived magmas: Os and Hf isotopic evidence from potassic magmas of the Colorado Plateau. Geochem Geophys Geosys 2. Paper number 2000GC000128
Coltorti M, Bonadiman C, Hinton RW, Siena F, Upton BGJ (1999) Carbonatite metasomatism of the oceanic upper mantle: evidence from clinopyroxenes and glasses in ultramafic xenoliths of Grande Comore, Indian Ocean. J Petrol 40:133–165
Dawson JB (1984) Contrasting types of upper mantle metasomatism? In: Kornprobst J (ed) Kimberlites II. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 289–294
Fedorowich JS, Richards JP, Jain JC, Kerrich R, Fan J (1993) A rapid method for REE and trace-element analysis using laser sampling ICP-MS on direct fusion whole-rock glasses. Chem Geol 106:229–249
Frey FA, Green DH (1974) The mineralogy, geochemistry and origin of lherzolite inclusions in Victorian basanites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 49:2469–2491
Frey FA, Prinz M (1978) Ultramafic inclusions from San Carlos, Arizona: petrologic and geochemical data bearing on their petrogenesis. Earth Planet Sci Lett 38:129–176
Gamble JA, McGibbon F, Kyle PR, Menzies MA, Kirsch I (1988) Metasomatised xenoliths from Foster Crater, Antarctica: implications for lithospheric structure and processes beneath the Transantarctic Mountain Front. J Petrol Spec Lithosphere Issue, pp 109–138
Griffin WL, O’Reilly SY, Ryan CG, Gaul O, Ionov D (1998) Secular variation in the composition of subcontinental lithospheric mantle. In: Braun J et al (ed) Structure and evolution of the Australian continent. American Geophysical Union, Geodynamics Series 26:1–25
Halliday A, Lee D-C, Tommasini S, Davies GR, Paslick CR, Fitton JG, James DE (1995) Incompatible trace elements in OIB and MORB and source enrichment in the sub-oceanic mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 133:379–395
Hamilton DL, Bedson P, Esson J (1989) The behavior of trace element in the evolution of carbonatites. In: Bell K (ed) Carbonatites-Genesis and evolution, Unwin Hyman, London, pp 405–427
Hofmann AW (1988) Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 90:297–314
Johnson KE, Davis AM, Bryndzia LT (1996) Contrasting styles of hydrous metasomatism in the upper mantle: an ion microprobe investigation. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 60:1367–1385
Kelemen P, Shimizu N, Dunn T (1993) Relative depletion of niobium in some magmas and the continental crust: partitioning of K, Nb, La and Ce during melt/rock reaction in the upper mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 120:111–134
Kil Y (2002) Mantle evolution associated with the Rio Grande rift: Geochemistry and geothermobarometry of upper mantle xenoliths. PhD dissertation, Colorado School of Mines, Golden, pp 160
Kil Y, Wendlandt RF (2004) Pressure and temperature evolution of upper mantle under the Rio Grande rift. Contrib Mineral Petrol 148:265–280
Kyser TK, Rison W (1982) Systematics of rare gas isotopes in basic lavas and ultramafic xenoliths. J Geophys Res 87:5611–5630
Leeman WP (1982), Tectonic and magmatic significance of strontium isotopic variations in Cenozoic volcanic rocks from the western Unites States. Geol Soc Am Bull 93:487–503
Lichte FE (1995) Determination of elemental content of rocks by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 67:2479–2485
Maalöe S, Aoki K (1977) The major element composition of upper mantle estimated from the composition of lherzolites. Contrib Mineral Petrol 63:161–173
Mattery DP, Menzies M, Pillinger CT (1985) Carbon isotopes in lithosphere peridotites and pyroxenites. Terra Cognita 5:147
McKenzie D (1985) The extraction of magma from the crust and mantle. Earth Planet Sci Lett 74:81–91
McKenzie D, O’Nions RK (1991) Partial melt distributions from inversion of rare earth element concentrations. J Petrol 32:1021–1091
McMillan NJ, Dickin AP, Haag D (2000) Evolution of magma source regions in the Rio Grande rift, southern New Mexico. Geol Soc Am Bull 112:1582–1593
Menzies M, Kempton P, Dungan M (1985) Interaction of continental lithosphere and asthenospheric melts below the Geronimo volcanic field, Arizona, USA. J Petrol 26:663–693
Menzies MA, Hawkesworth CJ (1987) Mantle metasomatism. Academic, London, pp 472
Menzies MA, Arculus RJ, Best MG, Bergman SC, Ehrenberg SN, Irving AJ, Roden MF, Schulze DJ (1987) A record of subduction processes and within-plate volcanism in lithospheric xenoliths of the southwestern USA. In: Nixon PH (ed) Mantle xenoliths, Wiley, New York, pp 59–74
Nagasawa H, Schreiber HD, Morris RV (1980) Experimental mineral/liquid partition coefficients of rare earth elements (REE), Sc and Sr for perovskite, spinel and melilite. Earth Planet Sci Lett 46:431–437
Nicholls IA (1974) A direct fusion method of preparing silicate rock glasses for energy dispersive electron microprobe analysis. Chem Geol 14:151–157
Nicholls IA, Harris KL (1980) Experimental rare earth element partition coefficients for garnet, clinopyroxene and amphibole coexisting with andesitic and basaltic liquids. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 44:287–308
Nixon PH (1987) Mantle xenoliths. Wiley, New York, pp 844
Norman MD (1998) Melting and metasomatism in the continental lithosphere: laser ablation ICPMS analysis of minerals in spinel lherzolites from eastern Australia. Contrib Mineral Petrol 130:240–255
O’Reilly SY, Griffin WL (1988) Mantle metasomatism beneath western Victoria, Autralia: I. Metasomatic processes in Cr-diopside lherzolites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:433–448
Perry FV, Baldridge WS, DePaolo DJ (1987) Role of asthenosphere and lithosphere in the genesis of late Cenozoic basaltic rocks from the Rio Grande rift and adjacent regions of the southwestern United States. J Geophys Res 92:9131–9213
Pollack HN, Chapman DS (1977) On the regional variation of heat flow, geotherms and lithospheric thickness. Tectonophysics 38:279–296
Ridley WI, Lichte FE (1998) Major, trace, and ultratrace element analysis by laser ablation ICP-MS. Rev Econ Geol 7:199–215
Roden MF, Murthy VR (1985) Mantle metasomatism. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 13:269–296
Roden MF, Shimizu N (1993) Ion microprobe analyses bearing on the composition of the upper mantle beneath the Basin and Range and Colorado Plateau provinces. J Geophys Res 98:14091–14108
Roden MF, Irving AJ, Murthy VR (1988) Isotopic and trace element composition of the upper mantle beneath a young continental rift: results from Kilbourne Hole, New Mexico. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 52:461–473
Sato K, Katsura T, Ito E (1996) Phase relation of phlogopite with and without enstatite up to 8 Gpa: implication to potassic magmatism and mantle metasomatism. Tech Rep of ISEI, Ser A 65:8
Sengor AHC, Burke K (1978) Relative timing of rifting and volcanism in earth and its tectonic implications. Geophs Res Lett 5:419–421
Solomon M (1963) Counting and sampling errors in modal analysis by point counter. J Petrol 4:367–382
Stosch HG (1982) Rare earth element partitioning between minerals from anhydrous spinel peridotite xenoliths. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 46:793–811
Stix J, Gauthier G, Ludden JN (1995) A critical look at quantitative laser-ablation ICP-MS analysis of natural and synthetic glasses. Can Mineral 33:435–444
Sun SS, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalt: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in ocean basins. Geol Soc London Spec Pub 42:313–345
Vaniman D, Laughlin AW, Gladney ES (1985) Navajo minettes in the Cerros de las Mujeres, New Mexico. Earth Planet Sci Lett 74:69–80
Warren RG (1978) Characterization of the lower crust-upper mantle of the Engle basin, Rio Grande rift, from a petrochemical and field geologic study of basalts and their inclusions. MS thesis. University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, pp156
Warren RG, Kudo AM, Keil K (1979) Geochemistry of lithic and single-crystal inclusions in basalt and a characterization of the upper mantle-lower crust in the Engle basin, Rio Grande rift, New Mexico. In: Riecker RE (ed) Rio Grande rift: tectonics and magmatism. American Geophysical Union Special Publication, Washington, pp 393–415
Wendlandt RF, Harrision WJ (1979) Rare earth partitioning between immiscible carbonate and silicate liquids and CO2 vapor: results and implications for the formation of light rare earth-enriched rocks. Contrib Mineral Petrol 69:409–419
Wendlandt RF, Eggler DH (1980) The origins of potassic magmas: 2. stability of phlogopite in natural spinel lherzolite and in the system KAlSiO4–MgO–SiO2–H2O at high pressures and high temperatures. Am J Sci 280:421–458
Wendlandt RF, Altherr R, Neumann E-R, Baldridge WS (1995) Petrology, geochemistry, isotopes. In: Olsen KH (ed) Continental rifts: evolution, structure, tectonics. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 47–60
Witt-Eickschen G, Seck HA (1987) Temperature of sheared mantle xenoliths from the West Eifel, West Germany: evidence for mantle diapirism beneath the Rhenish massif. J Petrol 28:475–493
Wyllie PJ (1977) Mantle fluid composition buffered in peridotite–CO2–H2O by carbonates, amphibole and phlogopite. J Geol 86:687–713
Xu X, O’Reilly SY, Griffin WL, Zhou X (2000) Genesis of young lithospheric mantle in southern China: an LAM-ICPMS trace element study. J Petrol 41:111–148
Yaxley GM, Crawford AJ, Green DH (1991) Evidence for carbonatite metasomatism in spinel peridotites from western Victoria Australia. Earth Planet Sci Lett 197:305–317
Zipfel J, Wörner G (1992) Four-and five-phase peridotites from a continental rift system: evidence for upper mantle uplift and cooling at the Ross Sea margin (Antarctica). Contrib Mineral Petrol 111:24–36
Acknowledgments
We thank Ian Ridley (US Geological Survey in Denver) for providing access to the LA-ICPMS facility and Charlie Blount for assistance with the Colorado School of Mines microprobe. Critical reviews by Michael Roden, Doug Smith, Craig Simmons, and Greg Holden are appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T.L. Groove.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kil, Y., Wendlandt, R.F. Depleted and enriched mantle processes under the Rio Grande rift: spinel peridotite xenoliths . Contrib Mineral Petrol 154, 135–151 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0183-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-007-0183-y