Abstract
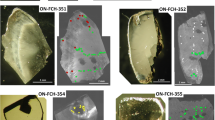
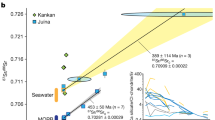
An extensive study of peridotitic sulfide inclusion bearing diamonds and their prospective harzburgitic host rocks from the 53 Ma Panda kimberlite pipe, Ekati Mine, NWT Canada, has been undertaken with the Re–Os system to establish their age and petrogenesis. Diamonds with peridotitic sulfide inclusions have poorly aggregated nitrogen (<30% N as B centers) at N contents of 200–800 ppm which differs from that of chromite and silicate bearing diamonds and indicates residence in the cooler portion of the Slave craton lithospheric mantle. For most of the sulfide inclusions, relatively low Re contents (average 0.457 ppm) and high Os contents (average 339 ppm) lead to extremely low 187Re/188Os, typically << 0.05. An age of 3.52 ± 0.17 Ga (MSWD = 0.46) and a precise initial 187Os/188Os of 0.1093 ± 0.0001 are given by a single regression of 11 inclusions from five diamonds that individually provide coincident internal isochrons. This initial Os isotopic composition is 6% enriched in 187Os over 3.5 Ga chondritic or primitive mantle. Sulfide inclusions with less radiogenic initial Os isotopic compositions reflect isotopic heterogeneity in diamond forming fluids. The harzburgites have even lower initial 187Os/188Os than the sulfide inclusions, some approaching the isotopic composition of 3.5 Ga chondritic mantle. In several cases isotopically distinct sulfides occur in different growth zones of the same diamond. This supports a model where C–O–H–S fluids carrying a radiogenic Os signature were introduced into depleted harzburgite and produced diamonds containing sulfides conforming to the 3.5 Ga isochron. Reaction of this fluid with harzburgite led to diamonds with less radiogenic inclusions while elevating the Os isotope ratios of some harzburgites. Subduction is a viable way of introducing such fluids. This implies a role for subduction in creating early continental nuclei at 3.5 Ga and generating peridotitic diamonds.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed AH, Arai S (2003) Platinum-group minerals in podiform chromitites of the Oman ophiolite. Can Mineral 41:597–616
Aulbach S, Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, O’Reilly SY, Kivi K, Doyle BJ (2004) Mantle formation and evolution, Slave craton: constraints from HSE abundances and Re-Os isotope systematics of sulfide inclusions in mantle xenocrysts. Chem Geol 208:61–88
Becker H, Shirey SB, Carlson RW (2001) Effects of melt percolation on the Re-Os systematics of peridotites from a Paleozoic convergent plate margin. Earth Planet Sci Lett 188:107–121
Bell DR, Gregoire M, Grove TL, Chatterjee N, Bowring SA (2003) Silica and carbon deposition in Kimberley peridotites. In: 8th International Kimberlite Conference, extended abstracts. Victoria, BC, Canada, p FLA_0289
Bleeker W (2001) The ca. 2680 Ma Raquette Lake formation and correlative units across the Slave Province, Northwest Territories: evidence for a craton-scale overlap sequence. Geological Survey of Canada, Current Research 2001-C7:11
Bleeker W (2003) The late Archean record; a puzzle in ca. 35 pieces. Lithos 71:99–134
Borg LE, Brandon AD, Clynne MA, Walker RJ (2000) Re-Os isotopic systematics of primitive lavas from the Lassen region of the Cascade arc, California. Earth Planet Sci Lett 177:301–317
Bowring SA, Williams IS, Compston W (1989) 3.96 Ga gneisses from the Slave Province, Northwest Territories, Canada; with supplementary data 89–17. Geology 17:971–975
Boyd FR (1989) Compositional distinction between oceanic and cratonic lithosphere. Earth Planet Sci Lett 96:15–26
Brandon AD, Creaser RA, Shirey SB, Carlson RW (1996) Osmium recycling in subduction zones. Science 272:861–864
Brandon AD, Becker H, Carlson RW, Shirey SB (1999) Isotopic constraints on time scales and mechanisms of slab material transport in the mantle wedge: evidence from the Simcoe mantle xenoliths, Washington, USA. Chem Geol 160:387–407
Brandon AD, Walker RJ, Puchtel IS, Becker H, Humayun M, Revillon S (2003) 186Os/188Os systematics of Gorgona Island komatiites; implications for early growth of the inner core. Earth Planet Sci Lett 206:411–426
Brenan JM (2002) Re-Os fractionation in magmatic sulfide melt by monosulfide solid solution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 199:257–268
Brey GP, Kohler T (1990) Geothermobarometry in four-phase lherzolites ii. New thermometers and practical assessment of existing thermometers. J Petrol 31:1353–1378
Buffett BA (2003) The thermal state of Earth’s core. Science 299:1675–1677
Buffett BA, Huppert HE, Lister JR, Woods AW (1992) Analytical model for solidification of the Earth’s core. Nature 356:329–331
Bulanova GP, Griffin WL, Ryan CG, Shestakova OY, Barnes SJ (1996) Trace elements in sulfide inclusions from Yakutia diamonds. Contrib Mineral Petrol 124:111–125
Bulatov V, Brey GP, Foley SF (1991) Origin of low-Ca, high-Cr garnets by recrystallization of low-pressure harzburgites. In: 5th International Kimberlite Conference, 2/91. CRPM Special Publication, Araxa, Brazil, pp 29–31
Burton KW, Bourdon B, Birck J-L, Allegre CJ, Hein JR (1999a) Osmium isotope variations in the oceans recorded by Fe-Mn crusts. Earth Planet Sci Lett 171:185–197
Burton KW, Schiano P, Birck J-L, Allegre CJ (1999b) Osmium isotope disequilibrium between mantle minerals in a spinel-lherzolite. Earth Planet Sci Lett 172:311–322
Canil D, Wei K (1992) Constraints on the origin of mantle-derived low-Ca garnets. Contrib Mineral Petrol 109:421–430
Carlson RW, Irving AJ (1994) Depletion and enrichment history of subcontinental lithospheric mantle: an Os, Sr, Nd and Pb isotopic study of ultramafic xenoliths from the northwestern Wyoming Craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 126:457–472
Carlson JA, Kirkley MB, Thomas EM, Hillier WD (1999a) Recent Canadian kimberlite discoveries. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The J. B. Dawson volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 81–89
Carlson RW, Pearson DG, Boyd FR, Shirey SB, Irvine G, Menzies AH, Gurney JJ (1999b) Re-Os systematics of lithospheric peridotites: implications for lithosphere formation and preservation. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The J. B. Dawson volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 99–108
Carlson RW, Pearson DG, James DE (2005) Physical, chemical and chronological characteristics of continental mantle. Rev Geophys 43:RG1001. DOI 10.1029/2004RG000156
Creaser RA, Grutter HS, Carlson JA, Crawford BB (2004) Macrocrystal phlogopite Rb/Sr dates for the Ekati property kimberlites, Slave Province, Canada; evidence for multiple intrusive episodes in the Paleocene and Eocene. Lithos 76:399–414
Davis WJ, Hegner E (1992) Neodymium isotopic evidence for the accretionary development of the late Archean Slave Province. Contrib Mineral Petrol 111:493–503
Davis WJ, Canil D, MacKenzie JM, Carbno GB (2003a) Petrology and U-Pb geochronology of lower crustal xenoliths and the development of a craton, Slave Province, Canada. Lithos 71:541–573
Davis WJ, Jones AG, Bleeker W, Grutter H (2003b) Lithosphere development in the Slave craton: a linked crustal and mantle perspective. Lithos 71:575–589
Deines P, Harris JW (1995) Sulfide inclusion chemistry and carbon isotopes of African diamonds. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:3173–3188
Dyck DR, Oshust PA, Carlson JA, Nowicki TE, Mullins MP (2004) Effective resource estimates for primary diamond deposits from the Ekati diamond mine, Canada. Lithos 76:317–335
Ebel DS, Naldrett AJ (1997) Crystallization of sulfide liquids and the interpretation of ore composition. Can J Earth Sci 34:352–365
Finnerty AA, Boyd FR (1984) Evaluation of thermobarometers for garnet peridotites. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:15–27
Fleet ME, Crocket JH, Liu M, Stone WE (1999) Laboratory partitioning of platinum-group elements (PGE) and gold with application to magmatic sulfide-PGE deposits. Lithos 47:127–142
Foster JG, Lambert DD, Frick LR, Maas R (1996) Re-Os isotopic evidence for genesis of Archean nickel ores from uncontaminated komatiites. Nature 382:703–706
Griffin WL, Gurney JJ, Ryan CG (1992) Variations in trapping temperatures and trace elements in peridotite-suite inclusions from African diamonds: evidence for two inclusion suites and implications for lithosphere stratigraphy. Contrib Mineral Petrol 110:1–15
Griffin WL, Doyle BJ, Ryan CG, Pearson NJ, O’Reilly SY, Davies R, Kivi K, van Achterbergh E, Natapov LM (1999) Layered mantle lithosphere in the Lac de Gras area, Slave craton; composition, structure and origin. J Petrol 40:705–727
Griffin WL, Spetsius ZV, Pearson NJ, O’Reilly SY (2002) In situ Re-Os analysis of sulfide inclusions in kimberlitic olivine; new constraints on depletion events in the Siberian lithospheric mantle. Geochem Geophys Geosyst–G3 3:25
Griffin WL, O’Reilly SY, Abe N, Aulbach S, Davies RM, Pearson NJ, Doyle BJ, Kivi K (2003) The origin and evolution of Archean lithospheric mantle. Precambrian Res 127:19–41
Gurney JJ (1989) Diamonds. In: Ross J, Jaques AL, Ferguson J, Green DH, O’Reilly SY, Danchin RV, Janse AJA (eds) Kimberlites and related rocks, Special Publication Number 14, vol. 2. Geological Society of Australia, Sydney, N.S.W., Australia, pp 935–965
Gurney JJ, Switzer GS (1973) The discovery of garnets closely related to diamonds in the Finsch pipe, South Africa. Contrib Mineral Petrol 39:103–116
Gurney JJ, Westerlund K, Carlson RW, Shirey SB (2003) Mineral compositions and Re-Os isotope systematics of harzburgite nodules from the Panda kimberlite, Slave craton. In: 8th International Kimberlite Conference, extended abstracts. Victoria, BC Canada, p FLA_0138
Harley SL (1984) An experimental study of the partitioning of Fe and Mg between garnet and orthopyroxene. Contrib Mineral Petrol 86:359–373
Hauri EH (2002) Osmium isotopes and mantle convection. Phil Trans Roy Soc A: Math Phys Eng Sci 360:2371–2382
Hauri EH, Wang J, Pearson DG, Bulanova GP (2002) Microanalysis of δ13C, δ15N, and N abundances in diamonds by secondary ion mass spectrometry. Chem Geol 185:149–163
Hoal KEO, Hoal BG, Erlank AJ, Shimizu N (1994) Metasomatism of the mantle lithosphere recorded by rare earth elements in garnets. Earth Planet Sci Lett 126:303–313
Irvine G (2002) Time constraints on the formation of lithospheric mantle beneath cratons: a Re-Os isotope and platinum group element study of peridotite xenoliths from northern Canada and Lesotho. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Durham, Durham, UK, 384 pp
Irvine G, Pearson DG, Kjarsgaard BA, Carlson RW, Kopylova MG, Dreibus G (2003) A Re-Os isotope and PGE study of kimbelite-derived peridotite xenoliths from Somerset Island and a comparison to the Slave and Kaapvaal cratons. Lithos 71:461–488
Jones AG, Lezaeta P, Ferguson IJ, Chave AD, Evans RL, Garcia X, Spratt J (2004) The electrical structure of the Slave craton. Lithos 71:505–527
Jordan TH (1979) Mineralogies, densities and seismic velocities of garnet lherzolites and their geophysical implications. In: Boyd FR, Meyer HOA (eds) The mantle sample; inclusions in kimberlites and other volcanics. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC, pp 1–14
Jordan TH (1981) Continents as a chemical boundary layer. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A 301:359–373
Jordan TH (1988) Structure and formation of the continental tectosphere. J Petrol Spec Lithosphere Issue: 11–37
Karup-Moller S, Mackovicky E (1998) The phase system Fe-Ni-S at 900°C. Neues Jahrb Min Monatschifte 1998:373–384
Keays RR (1995) The role of komatiitic and picritic magmatism and S-saturation in the formation of ore deposits. Lithos 34:1–18
Kelemen PB, Hart SR, Bernstein S (1998) Silica enrichment in the continental upper mantle via melt/rock reaction. Earth Planet Sci Lett 164:387–406
Kennedy CS, Kennedy GC (1976) The equilibrium boundary between graphite and diamond. J Geophys Res 81:2467–2470
Kesson S, Ringwood AE (1989) Slab-mantle interactions 2. The formation of diamonds. Chem Geol 78:97–118
Kopylova MG, Russell JK (2000) Chemical stratification of cratonic lithosphere; constraints from the northern Slave craton, Canada. Earth Planet Sci Lett 181:71–87
Labrosse S, Poirier J-P, Le Mouel J-L (1997) On cooling of the Earth’s core. Phys Earth Planet Inter 99:1–17
Lee C-TA, Wasserburg GJ, Kyte FT (2003) Platinum-group elements (PGE) and rhenium in marine sediments across the Cretaceous-Tertiary boundary; constraints on Re-PGE transport in the marine environment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 67:655–670
Lister JR, Buffett BA (1998) Stratification of the outer core at the core-mantle boundary. Phys Earth Planet Inter 105:5–19
Ludwig KR (2003) Isoplot 3.0: a geochronological toolkit for Microsoft Excel, Special Publication Number 4. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Berkeley, CA, 70 pp
MacGregor ID (1974) The system MgO-Al2O3-SiO2; solubility of Al2O3 in enstatite for spinel and garnet peridotite compositions. Am Mineral 59:110–119
McDaniel DK, Walker RJ, Hemming SR, Horan MF, Becker H, Grauch RI (2004) Sources of osmium to the modern oceans: new evidence from the 190 Pt-186 Os system. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 68:1243–1252
McDonough WF, Sun SS (1995) The composition of the Earth. Chem Geol 120:223–253
Meisel T, Walker RJ, Irving AJ, Lorand J-P (2001) Osmium isotopic compositions of mantle xenoliths; a global perspective. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:1311–1323
Menzies AH, Westerlund K, Grutter H, Gurney JJ, Carlson JA, Fung A, Nowicki T (2004) Peridotitic mantle xenoliths from kimberlites on the Ekati diamond mine property, NWT, Canada: major element compositions and implications for the lithosphere beneath the central Slave craton. Lithos 77:395–412
Morgan JW (1986) Ultramafic xenoliths: clues to Earth’s late accretionary history. J Geophys Res 91:12375–312387
Naldrett AJ (1989) Magmatic sulfide deposits, 14. Oxford University Press, New York, 186 pp
Navon O (1999) Diamond formation in the Earth’s mantle. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The P. H. Nixon volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 584–604
Nickel KG, Green DH (1985) Empirical geothermobarometry for garnet peridotites and implications for the nature of the lithosphere, kimberlites and diamonds. Earth Planet Sci Lett 73:158–170
Nowicki T, Crawford BB, Dyck DR, Carlson JA, McElroy R, Oshust P, Helmstaedt H (2004) The geology of kimberlite pipes of the Ekati property, Northwest Territories, Canada. Lithos 76:1–27
O’Neill HSC, Wood BJ (1979) An experimental study of Fe-Mg partitioning between garnet and olivine and its calibration as a geothermometer. Contrib Mineral Petrol 70:59–70
Pearson DG, Shirey SB (1999) Isotopic dating of diamonds. In: Lambert David D, Ruiz J (eds) Application of radiogenic isotopes to ore deposit research and exploration, 12. Society of Economic Geologists, Boulder, CO, United States, pp 143–171
Pearson DG, Carlson RW, Shirey SB, Boyd FR, Nixon PH (1995a) Stabilisation of Archean lithospheric mantle; a Re-Os isotope study of peridotite xenoliths from the Kaapvaal craton. Earth Planet Sci Lett 134:341–357
Pearson DG, Shirey SB, Carlson RW, Boyd FR, Pokhilenko NP, Shimizu N (1995b) Re-Os, Sm-Nd, and Rb-Sr isotope evidence for thick Archean lithospheric mantle beneath the siberian craton modified by multistage metasomatism. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 59:959–977
Pearson DG, Shirey SB, Harris JW, Carlson RW (1998) Sulfide inclusions in diamonds from the Koffiefontein kimberlite, S. Africa: constraints on diamond ages and mantle Re-Os systematics. Earth Planet Sci Lett 160:311–326
Pearson DG, Shirey SB, Bulanova GP, Carlson RW, Milledge HJ (1999a) Dating and paragenetic distinction of diamonds using the Re-Os isotope system; application to some Siberian diamonds. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The P. H. Nixon volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 637–643
Pearson DG, Shirey SB, Bulanova GP, Carlson RW, Milledge HJ (1999b) Re-Os isotope measurements of single sulfide inclusions in a Siberian diamond and its nitrogen aggregation systematics. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63:703–711
Pearson NJ, Griffin WL, Doyle BJ, O’Reilly SY, van Achterbergh E, Kivi K (1999c) Xenoliths from kimberlite pipes of the Lac de Gras area, Slave craton, Canada. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The P. H. Nixon volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 644–658
Pearson DG, Canil D, Shirey SB (2003) Chapter 7–Mantle samples included in volcanic rocks: xenoliths and diamonds. In: Carlson RW (ed) Treatise on geochemistry: vol. 2, the Mantle. Elsevier, New York, pp 171–277
Pegram WJ, Turekian KK (1999) The osmium isotopic composition change of Cenozoic sea water as inferred from a deep-sea core corrected for meteoritic contributions. Geochim et Cosmochim Acta 63:4053–4058
Peucker-Ehrenbrink B, Ravizza G, Hofmann AW (1995) The marine 187Os/188Os record of the past 80 million years. Earth Planet Sci Lett 130:155–167
Puchtel I, Brugmann G, Hofmann A (2001) 187Os-enriched domain in an Archean mantle plume: evidence from 2.8 Ga komatiites of the Kostomuksha greenstone belt, NW Baltic Shield. Earth Planet Sci Lett 186:513–526
Richardson SH, Gurney JJ, Erlank AJ, Harris JW (1984) Origin of diamonds in old enriched mantle. Nature 310:198–202
Richardson SH, Shirey SB, Harris JW, Carlson RW (2001) Archean subduction recorded by Re-Os isotopes in eclogitic sulfide inclusions in Kimberley diamonds. Earth Planet Sci Lett 191:257–266
Richardson SH, Shirey SB, Harris JW (2004) Episodic diamond genesis at Jwaneng, Botswana, and implications for Kaapvaal craton evolution. Lithos 77:143–154
Robb LJ, Knoll AH, Plumb KA, Shields GA, Strauss H, Veizer J (2004) Chapter 9. The Precambrian: the Archean and Proterozoic eons. In: A geological time scale 2004. Cambridge University Press, New York, p 589
Rudnick RL, Nyblade AA (1999) The thickness and heat production of Archean lithosphere; constraints from xenolith thermobarometry and surface heat flow. In: Fei Y, Bertka CM, Mysen BO (eds) Mantle petrology: field observations and high pressure experimentation, special publication number 6. Geochemical Society, pp 3–12
Ruiz J, McCandless TE, Helmstaedt HH (1999) Re-Os model ages for eclogite xenoliths from the Colorado Plateau. In: Gurney JJ, Gurney JL, Pascoe MD, Richardson SH (eds) The P. H. Nixon volume–proceedings of the 7th International Kimberlite Conference, Cape Town. Red Roof Design, Cape Town, pp 736–740
Ryan CG, Griffin WL, Pearson NJ (1996) Garnet geotherms; pressure-temperature data from Cr-Pyrope garnet xenocrysts in volcanic rocks. J Geophys Res B, Solid Earth Planet 101:5611–5625
Schiano P, Clocchiatti R, Shimizu N, Maury RC, Jochum KP, Hofmann AW (1995) Hydrous, silica-rich melts in the sub-arc mantle and their relationship with erupted arc lavas. Nature 377:595–600
Schulze DJ (1995) Low-Ca garnet harzburgites from Kimberley, South Africa; abundance and bearing on the structure and evolution of the lithosphere. J Geophys Res B, Solid Earth Planet 100:12513–512526
Shimizu N, Richardson SH (1987) Trace element abundance patterns of garnet inclusions in peridotite-suite diamonds. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 51:755–758
Shirey SB, Walker RJ (1995) Carius tube digestion for low-blank rhenium-osmium analysis. Anal Chem 34:2136–2141
Shirey SB, Walker RJ (1998) The Re-Os isotope system in cosmochemistry and high-temperature geochemistry. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci. 26:423–500
Shirey SB, Pearson DG, Richardson SH, Harris JW, Carlson RW (2000) Application of Re-Os microchemistry to sulfide inclusions in diamond and implications for Archean craton evolution. Eos Trans Am Geophys Union 81:S428
Shirey SB, Harris JW, Richardson SH, Fouch MJ, James DE, Cartigny P, Deines P, Viljoen F (2002) Diamond genesis, seismic structure, and evolution of the Kaapvaal-Zimbabwe craton. Science 297:1683–1686
Shirey SB, Richardson Stephen H, Harris JW (2004) Integrated models of diamond formation and craton evolution. Lithos 77:923–944
Sobolev NV, Laurent’ev Yu G, Pokhilenko NP (1973) Chrome-rich garnets from the kimberlites of Yakutia and their paragenesis. Contrib Mineral Petrol 40:39–52
Spetsius ZV, Belousova EA, Griffin WL, O’Reilly SY, Pearson NJ (2002) Archean sulfide inclusions in Paleozoic zircon megacrysts from the Mir kimberlite, Yakutia; implications for the dating of diamonds. Earth Planet Sci Lett 199:111–126
Stachel T, Harris JW (1997) Diamond precipitation and mantle metasomatism; evidence from the trace element chemistry of silicate inclusions in diamonds from Akwatia, Ghana. Contrib Mineral Petrol 129:143–154
Stachel T, Viljoen KS, Brey G, Harris JW (1998) Metasomatic processes in lherzolitic and harzburgitic domains of diamondiferous lithospheric mantle; REE in garnets from xenoliths and inclusions in diamonds. Earth Planet Sci Lett 159:1–12
Stachel T, Harris JW, Tappert R, Brey GP (2003) Peridotitic diamonds from the Slave and Kaapvaal cratons–similarities and differences based on a preliminary data set. Lithos 71:489–5003
Stevenson D, Spohn T, Schubert G (1983) Magmatism and thermal evolution of the terrestrial planets. Icarus 54:466–489
Takahashi E (1986) Melting of a dry peridotite KLB-1 up to 14 GPa: implications for the origin of peridotite upper mantle. J Geophys Res 91:9367–9382
Taylor LA, Anand M (2004) Diamonds: time capsules from the Siberian mantle. Chem Erde 64:1–74
Tronnes RG, Canil D, Wei KJ (1992) Element partitioning between silicate minerals and coexisting melts at pressures of 1–27 GPa and implications for mantle evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 111:241–255
Walker RJ, Shirey SB, Stecher O (1988) Comparative Re-Os, Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr isotope and trace element systematics for Archean komatiite flows from Munro Township, Abitibi Belt, Ontario. Earth Planet Sci Lett 87:1–12
Walker RJ, Carlson RW, Shirey SB, Boyd FR (1989) Os, Sr, Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of southern African peridotite xenoliths; implications for the chemical evolution of subcontinental mantle. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53:1583–1595
Walker RJ, Echeverria LM, Shirey SB, Horan MF (1991) Re-Os isotopic constraints on the origin of volcanic rocks, Gorgona Island, Colombia; Os isotopic evidence for ancient heterogeneities in the mantle. Contrib Mineral Petrol 107:150–162
Walker RJ, Morgan JW, Horan MF (1995) 187Os enrichment in some plumes: evidence for core-mantle interaction. Science 269:819–822
Westerlund K (2005) A geochemical study of diamonds, mineral inclusions in diamonds and mantle xenoliths from the Panda kimberlite, Slave craton. Unpublished Ph.D. thesis, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 170 pp
Westerlund K, Hauri EH, Gurney JJ (2003) FTIR absorption and stable nitrogen and carbon isotope microanalysis of mid-Archean diamonds from the Panda kimberlite. In: 8th International Kimberlite Conference, extended abstracts. Victoria, BC Canada, p FLA_0137
Widom E, Kepezhinkas P, Defant M (2003) The nature of metasomatism in the sub-arc mantle wedge: evidence from Re-Os isotopes in Kamchatka peridotite xenoliths. Chem Geol 196:283–306
Woodland SJ, Pearson DG, Thirlwall MF (2002) A platinum group element and Re-Os isotope investigation of siderophile element recycling in subduction zones: comparison of Grenada, Lesser Antilles arc, and the Izu-Bonin arc. J Petrol 43:171–198
Acknowledgments
Discussions with Graham Pearson and Mark Schmitz are greatly appreciated. The authors are grateful to BHP Diamonds and to the Diamond Trading Company (a De Beers Group Company) for making diamonds available for study. Mary Horan and Tim Mock are thanked for their help in the DTM chemistry and mass spectrometry labs (respectively). Judith Milledge at the University College London is thanked for her continuous support over the years with ideas and software for the reduction of FTIR absorption data. Frank Spear assisted in calculating garnet compositions. Bill Davis and Wouter Bleeker generously shared their perspectives on Slave craton evolution. The manuscript benefited from the careful reviews of Mark Schmitz and Maya Kopylova. This work was supported in the USA chiefly by the Carnegie Institution of Washington and NSF EAR Continental Dynamics Grant 9526840 and in South Africa by the Department of Geological Sciences of the University of Cape Town and the National Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. L. Grove
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westerlund, K.J., Shirey, S.B., Richardson, S.H. et al. A subduction wedge origin for Paleoarchean peridotitic diamonds and harzburgites from the Panda kimberlite, Slave craton: evidence from Re–Os isotope systematics. Contrib Mineral Petrol 152, 275–294 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0101-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-006-0101-8