Abstract
Rationale
The Saint George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) is a frequently used tool to assess health status in pulmonary disease patients. However, its performance characteristics in sarcoidosis patients are not well characterized.
Methods
Data from a clinical trial of 138 symptomatic adults with sarcoidosis were used to examine the performance characteristics of SGRQ. Data were available at both baseline and week 24. Other assessments included FVC, FEV1, ATS dyspnea score, Borg’s CR 10 dyspnea score, 6-min walk distance (6MWD), and Short Form-36 Physical Component Summary (SF-36 PCS) score.
Results
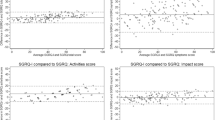
Baseline SGRQ was 46.8, indicating impaired health status. At baseline, SGRQ total score correlated significantly with % predicted FVC, FEV1, ATS dyspnea score, Borg’s CR 10 dyspnea score, 6MWD, and SF-36 PCS (r = − 0.37, − 0.32, 0.57, 0.40, − 0.55, and − 0.80, respectively, p < 0.001). Change from baseline in SGRQ score also statistically significantly correlated with change from baseline in these parameters at week 24: r = − 0.25, − 0.20, 0.30, 0.22, − 0.20, − 0.45, respectively (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
The SGRQ correlated with other outcome measures in sarcoidosis initially and with treatment. Improvement in FVC % predicted correlated with improvement in SGRQ. These data suggest the SGRQ may function as a reliable endpoint in clinical sarcoidosis trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data sharing policy of Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson is available at https://www.janssen.com/clinical-trials/transparency. As noted on this site, requests for access to the study data can be submitted through Yale Open Data Access (YODA) Project site at http://yoda.yale.edu.
References
Baughman RP, Lower EE, Gibson K (2012) Pulmonary manifestations of sarcoidosis. Presse Med 41:e289–e302
Highland KB, Retalis P, Coppage L, Schabel SI, Judson MA (1997) Is there an anatomic explanation for chest pain in patients with pulmonary sarcoidosis? South Med J 90(9):911–914
Patel AS, Siegert RJ, Creamer D, Larkin G, Maher TM, Renzoni EA et al (2013) The development and validation of the King's Sarcoidosis Questionnaire for the assessment of health status. Thorax 68(1):57–65
Cox CE, Donohue JF, Brown CD, Kataria YP, Judson MA (2004) Health-related quality of life of persons with sarcoidosis. Chest 125(3):997–1004
Gvozdenovic BS, Mihailovic-Vucinic V, Ilic-Dudvarski A, Zugic V, Judson MA (2008) Differences in symptom severity and health status impairment between patients with pulmonary and pulmonary plus extrapulmonary sarcoidosis. Respir Med 102(11):1636–1642
Victorson DE, Cella D, Judson MA (2008) Quality of life evaluation in sarcoidosis: current status and future directions. Curr Opin Pulm Med 14(5):470–477
Baughman RP, Costabel U, du Bois RM (2008) Treatment of sarcoidosis. Clin Chest Med 29(3):533–548
Keir G, Wells AU (2010) Assessing pulmonary disease and response to therapy: which test? Semin Respir Crit Care Med 31(4):409–418
Jones PW, Quirk FH, Baveystock CM, Littlejohns P (1992) A self-complete measure of health status for chronic airflow limitation. The St. George's respiratory questionnaire. Am Rev Respir Dis 145(6):1321–1327
Wilson CB, Jones PW, O'Leary CJ, Cole PJ, Wilson R (1997) Validation of the St. George's respiratory questionnaire in bronchiectasis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(2 Pt 1):536–541
Chang JA, Curtis JR, Patrick DL, Raghu G (1999) Assessment of health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial lung disease. Chest 116(5):1175–1182
Beretta L, Santaniello A, Lemos A, Masciocchi M, Scorza R (2007) Validity of the Saint George's respiratory questionnaire in the evaluation of the health-related quality of life in patients with interstitial lung disease secondary to systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(2):296–301
Swigris JJ, Brown KK, Behr J, du Bois RM, King TE, Raghu G et al (2010) The SF-36 and SGRQ: validity and first look at minimum important differences in IPF. Respir Med 104(2):296–304
Stavem K, Bjortuft O, Lund MB, Kongshaug K, Geiran O, Boe J (2000) Health-related quality of life in lung transplant candidates and recipients. Respiration 67(2):159–165
Antoniou KM, Tzanakis N, Tzouvelekis A, Samiou M, Symvoulakis EK, Siafakas NM et al (2006) Quality of life in patients with active sarcoidosis in Greece. Eur J Intern Med 17(6):421–426
Gvozdenovic BS, Mihailovic-Vucinic V, Vukovic M, Lower EE, Baughman RP, Dudvarski-Ilic A et al (2013) Effect of obesity on patient-reported outcomes in sarcoidosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 17(4):559–564
Baughman RP, Sparkman BK, Lower EE (2007) Six-minute walk test and health status assessment in sarcoidosis. Chest 132(1):207–213
Cox CE, Donohue JF, Brown CD, Kataria YP, Judson MA (2003) The sarcoidosis health questionnaire. A new measure of health-related quality of life. Am J Resp Crit Care Med 168:323–329
Baughman RP, Judson MA, Lower EE, Highland K, Kwor S, Craft N et al (2009) Inhaled iloprost for sarcoidosis associated pulmonary hypertension. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 26:110–120
Judson MA, Highland KB, Kwon S, Donohue JF, Aris R, Craft N et al (2011) Ambrisentan for sarcoidosis associated pulmonary hypertension. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 28(2):139–145
Baughman RP, Drent M, Kavuru M, Judson MA, Costabel U, Du BR et al (2006) Infliximab therapy in patients with chronic sarcoidosis and pulmonary involvement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174(7):795–802
Borg G (1982) Psychophysical bases of perceived exertion. Med Sci Sports Exerc 14:377–381
Judson MA, Baughman RP, Costabel U, Flavin S, Lo KH, Kavuru MS et al (2008) Efficacy of infliximab in extrapulmonary sarcoidosis: results from a randomised trial. Eur Respir J 31(6):1189–1196
Hankinson JL, Odencrantz JR, Fedan KB (1999) Spirometric reference values from a sample of the general U.S. population. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159(1):179–187
Baughman RP, Drent M, Culver DA, Grutters JC, Handa T, Humbert M et al (2012) Endpoints for clinical trials of sarcoidosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 29:90–98
Papiris SA, Daniil ZD, Malagari K, Kapotsis GE, Sotiropoulou C, Milic-Emili J et al (2005) The Medical Research Council dyspnea scale in the estimation of disease severity in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Med 99(6):755–761
ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories (2002) ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 166(1):111–117
Ware JE Jr, Sherbourne CD (1992) The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care 30(6):473–483
McHorney CA, Ware JE Jr, Raczek AE (1993) The MOS 36-Item Short-Form Health Survey (SF-36): II. Psychometric and clinical tests of validity in measuring physical and mental health constructs. Med Care 31(3):247–263
Calverley P, Pauwels R, Vestbo J, Jones P, Pride N, Gulsvik A et al (2003) Combined salmeterol and fluticasone in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 361(9356):449–456
Swigris JJ, Wamboldt FS, Behr J, du Bois RM, King TE, Raghu G et al (2010) The 6 minute walk in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: longitudinal changes and minimum important difference. Thorax 65(2):173–177
Chen H, Taichman DB, Doyle RL (2008) Health-related quality of life and patient-reported outcomes in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Proc Am Thorac Soc 5(5):623–630
Stahl E, Lindberg A, Jansson SA, Ronmark E, Svensson K, Andersson F et al (2005) Health-related quality of life is related to COPD disease severity. Health Qual Life Outcomes 3:56
Baughman RP, Barriuso R, Beyer K, Boyd J, Hochreiter J, Knoet C et al (2018) Sarcoidosis: patient treatment priorities. ERJ Open Res 4(4):00141–02018
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Janssen provided financial support for the conduct of the research and/or preparation of the article and to briefly describe the role of the sponsor(s). Co-authors KL, YW, and EB are employees of Janssen and were part of team involved in study design; in the collection, analysis and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the article for publication. JD and RB received grant funding from Janssen as participants in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, K.H., Donohue, J., Judson, M.A. et al. The St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire in Pulmonary Sarcoidosis. Lung 198, 917–924 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00394-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-020-00394-7