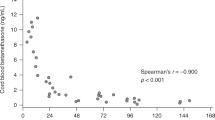
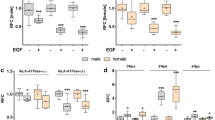
Abstract
Purpose
Glucocorticoids and progesterone exert stimulatory effects on epithelial Na+ transport, including increased mRNA expression of the participating ion transporters (epithelial Na+ channels [ENaC] and Na,K-ATPases) and their electrophysiological activity. Fetuses threatened by preterm labor may receive high doses of glucocorticoids to stimulate lung maturation and are naturally exposed to high levels of female sex steroids. However, it is still unknown how the combination of both hormones influences the epithelial Na+ transport, which is crucial for alveolar fluid clearance.
Methods
Fetal distal lung epithelial cells were incubated in media supplemented with dexamethasone and progesterone. Real-time qPCR and Ussing chamber analysis were used to determine the effects on ENaC mRNA expression and channel activity. In addition, the specific progesterone receptor antagonist (PF-02367982) and the glucocorticoid receptor antagonist mifepristone were used to identify the involved hormone receptors.
Results
Both dexamethasone and progesterone increased ENaC subunit expression and channel activity. However, the combination of dexamethasone and progesterone reduced the α- and γ-ENaC subunit expression compared to the effect of dexamethasone alone. Furthermore, higher dexamethasone concentrations in combination with progesterone also significantly reduced Na+ transport in Ussing chamber measurements. Hormone receptor antagonists showed that inhibition of the progesterone receptor increased the mRNA expression of α- and γ-ENaC, whereas mifepristone decreased mRNA expression of all ENaC subunits.
Conclusion
Glucocorticoids and progesterone individually increase ENaC mRNA expression; however, the combination of both hormones decreases the stimulatory effects of dexamethasone on Na+ transport and ENaC mRNA expression.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCray PB Jr, Bettencourt JD, Bastacky J (1992) Developing bronchopulmonary epithelium of the human fetus secretes fluid. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 262:L270–L279
Matalon S, O’Brodovich H (1999) Sodium channels in alveolar epithelial cells: molecular characterization, biophysical properties, and physiological significance. Annu Rev Physiol 61:627–661
O’Brodovich HM (1996) Immature epithelial Na + channel expression is one of the pathogenetic mechanisms leading to human neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Proc Assoc Am Physicians 108(5):345–355
Helve O, Pitkänen OM, Andersson S, O’Brodovich H, Kirjavainen T, Otulakowski G (2004) Low expression of human epithelial sodium channel in airway epithelium of preterm infants with respiratory distress. Pediatrics 113(5):1267–1272
Summa V, Mordasini D, Roger F, Bens M, Martin PY, Vandewalle A, Verrey F, Féraille E (2001) Short term effect of aldosterone on Na, K-ATPase cell surface expression in kidney collecting duct cells. J Biol Chem 276(50):47087–47093
Hummler E, Barker P, Gatzy J, Beermann F, Verdumo C, Schmidt A, Boucher R, Rossier BC (1996) Early death due to defective neonatal lung liquid clearance in alpha-ENaC-deficient mice. Nat Genet 12(3):325–328
Canessa CM, Schild L, Buell G, Thorens B, Gautschi I, Horisberger JD, Rossier BC (1994) Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na + channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 367(6462):463–467
O’Brodovich H (1991) Epithelial ion transport in the fetal and perinatal lung. Am J Physiol 261(4 Pt 1):C555–C564
Siew ML, Wallace MJ, Allison BJ, Kitchen MJ, Te Pas AB, Islam MS et al (2013) The role of lung inflation and sodium transport in airway liquid clearance during lung aeration in newborn rabbits. Pediatr Res 73(4):443–449
Folkesson HG, Norlin A, Wang Y, Abedinpour P, Matthay MA (2000) Dexamethasone and thyroid hormone pretreatment upregulate alveolar epithelial fluid clearance in adult rats. J Appl Physiol 88(2):416–424
Mustafa SB, DiGeronimo RJ, Petershack JA, Alcorn JL, Seidner SR (2003) Postnatal glucocorticoids induce α-ENaC formation and regulate glucocorticoid receptors in the preterm rabbit lung. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 286:L73–L80
Bland RD (2001) Loss of liquid from the lung lumen in labor: more than a simple “squeeze”. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 280(4):L602–L605
Finley N, Norlin A, Baines DL, Folkesson HG (1998) Alveolar epithelial fluid clearance is mediated by endogenous catecholamines at birth in guinea pigs. J Clin Invest 101(5):972–981
Trotter A, Ebsen M, Kiossis E, Meggle S, Küppers E, Beyer C, Pohlandt F, Maier L, Thome UH (2006) Prenatal estrogen and progesterone deprivation impairs alveolar formation and fluid clearance in newborn piglets. Pediatr Res 60(1):60–64
Stevenson DK, Verter J, Fanaroff AA, Oh W, Ehrenkranz RA, Shankaran S et al (2000) Sex differences in outcomes of very low birthweight infants: the newborn male disadvantage. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 83:F182–F185
Hallman M, Haataja R (2003) Genetic influences and neonatal lung disease. Semin Neonatol 8(1):19–27
Rubaltelli FF, Bonafe L, Tangucci M, Spagnolo A, Dani C (1998) Epidemiology of neonatal acute respiratory disorders. A multicenter study on incidence and fatality rates of neonatal acute respiratory disorders according to gestational age, maternal age, pregnancy complications and type of delivery. Biol Neonate 74(1):7–15
Laube M, Küppers E, Thome UH (2011) Modulation of sodium transport in alveolar epithelial cells by estradiol and progesterone. Pediatr Res 69(3):200–205
Nakamura K, Stokes JB, Mc Cray PB Jr (2002) Endogenous and exogenous glucocorticoid regulation of ENaC mRNA expression in developing kidney and lung. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:762–772
Thome UH, Davis IC, Nguyen SV, Shelton BJ, Matalon S (2003) Modulation of sodium transport in fetal alveolar epithelial cells by oxygen and corticosterone. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 284(2):L376–L385
Von Langen J, Fritzemeier KH, Diekmann S, Hillisch A (2005) Molecular basis of the interaction specificity between the human glucocorticoid receptor and its endogenous steroid ligand cortisol. ChemBioChem 6(6):1110–1118
Shao R, Egecioglu E, Weijdegård B, Ljungström K, Ling C, Fernandez-Rodriguez J, Billig H (2006) Developmental and hormonal regulation of progesterone receptor A-form expression in female mouse lung in vivo: interaction with glucocorticoid receptors. J Endocrinol 190(3):857–870
Pearce D, Yamamoto KR (1993) Mineralocorticoid and glucocorticoid receptor activities distinguished by nonreceptor factors at a composite response element. Science 259(5098):1161–1165
Liu W, Wang J, Sauter NK, Pearce D (1995) Steroid receptor heterodimerization demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(26):12480–12484
Oakley RH, Jewell CM, Yudt MR, Bofetiado DM, Cidlowski JA (1999) The dominant negative activity of the human glucocorticoid receptor beta isoform. Specificity and mechanisms of action. J Biol Chem 274(39):27857–27866
Vegeto E, Shahbaz MM, Wen DX, Goldman ME, O’Malley BW, McDonnell DP (1993) Human progesterone receptor A form is a cell- and promoter-specific repressor of human progesterone receptor B function. Mol Endocrinol 7(10):1244–1255
Pujols L, Mullol J, Pérez M, Roca-Ferrer J, Juan M, Xaubet A, Cidlowski JA, Picado C (2001) Expression of the human glucocorticoid receptor a and b isoforms in human respiratory epithelial cells and their regulation by dexamethasone. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24(1):49–57
Jassal D, Han RN, Caniggia I, Post M, Tanswell AK (1991) Growth of distal fetal rat lung epithelial cells in a defined serum-free medium. Vitro Cell Dev Biol 27A(8):625–632
Sweezey N, Tchepichev S, Gagnon S, Fertuck K, O’Brodovich H (1998) Female gender hormones regulate mRNA levels and function of the rat lung epithelial Na channel. Am J Physiol 274:C379–C386
Cadepond F, Ulmann A, Baulieu EE (1997) RU486 (mifepristone): mechanisms of action and clinical uses. Annu Rev Med 48:129–156
de Giorgio-Miller A, Bungay P, Tutt M, Owen J, Goodwin D, Pullen N (2008) The translational pharmacology of a novel, potent, and selective nonsteroidal progesterone receptor antagonist, 2-[4-(4-cyano-phenoxy)-3,5-dicyclopropyl-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-N-methylacetamide (PF-02367982). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 327(1):78–87
Lazrak A, Samanta A, Venetsanou K, Barbry P, Matalon S (2000) Modification of biophysical properties of lung epithelial Na(+) channels by dexamethasone. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C762–C770
Tchepichev S, Ueda J, Canessa C, Rossier BC, O´Brodovich H (1995) Lung epithelial Na channel subunits are differentially regulated during development and by steroids. Am J Physiol 269(3 Pt 1):C805–C812
Venkatesh VC, Katzberg HD (1997) Glucocorticoid regulation of epithelial sodium channel genes in human fetal lung. Am J Physiol 273(1 Pt 1):L227–L233
Snyder PM, Olson DR, Thomas BC (2002) Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase modulates Nedd4-2-mediated inhibition of the epithelial Na + channel. J Biol Chem 277(1):5–8
Itani OA, Auerbach SD, Husted RF, Volk KA, Ageloff S, Knepper MA, Stokes JB, Thomas CP (2002) Glucocorticoid-stimulated lung epithelial Na+ transport is associated with regulated ENaC and sgk1 expression. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L631–L641
Wright AP, McEwan IJ, Dahlman-Wright K, Gustafsson JA (1991) High level expression of the major transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor in yeast cells inhibits endogenous gene expression and cell growth. Mol Endocrinol 5(10):1366–1372
Beato M, Klug J (2000) Steroid hormone receptors: an update. Hum Reprod Update 6(3):225–236
Shimkets RA, Warnock DG, Bositis CM, Nelson-Williams C, Hansson JH, Schambelan M, Gill JR Jr, Ulick S, Milora RV, Findling JW et al (1994) Liddle’s syndrome: heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the beta subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 79(3):407–414
Kalinyak JE, Dorin RI, Hoffman AR, Perlman AJ (1987) Tissue-specific regulation of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem 262(22):10441–10444
Pujols L, Mullol J, Torrego A, Picado C (2004) Glucocorticoid receptors in human airways. Allergy 59(10):1042–1052
Whorwood CB, Donovan SJ, Wood PJ, Phillips DI (2001) Regulation of glucocorticoids receptor alpha and beta isoforms and type I 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase expression in human skeletal muscle cells: a key role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85(5):2296–2308
Matthay MA, Clerici C, Saumon G (2002) Invited Review: active fluid clearance from the distal air spaces of the lung. J Appl Physiol 93:1533–1541
Jesse NM, McCartney J, Feng X, Richards EM, Wood CE, Keller-Wood M (2009) Expression of ENaC subunits, chloride channels, and aquaporins in ovine fetal lung: ontogeny of expression and effects of altered fetal cortisol concentrations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R453–R461
Smith DF, Faber LE, Toft DO (1990) Purification of unactivated progesterone receptor and identification of novel receptor-associated proteins. J Biol Chem 265(7):3996–4003
Mall M, Grubb BR, Harkema JR, O’Neal WK, Boucher RC (2004) Increased airway epithelial Na + absorption produces cystic fibrosis-like lung disease in mice. Nat Med 10(5):487–493
Sayegh R, Auerbach SD, Li X, Loftus RW, Husted RF, Stokes JB, Thomas CP (1999) Glucocorticoid induction of epithelial sodium channel expression in lung and renal epithelia occurs via trans-activation of a hormone response element in the 5´-flanking region of the human epithelial sodium channel a subunit gene. J Biol Chem 274:12431–12437
McNicholas CM, Canessa CM (1997) Diversity of channels generated by different combinations of epithelial sodium channel subunits. J Gen Physiol 109(6):681–692
Schmidt M, Renner C, Löffler G (1998) Progesterone inhibits glucocorticoid-dependent aromatase induction in human adipose fibroblasts. J Endocrinol 158(3):401–407
Attardi BJ, Zeleznik A, Simhan H, Chiao JP, Mattison DR, Caritis SN (2007) Comparison of progesterone and glucocorticoid receptor binding and stimulation of gene expression by progesterone, 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate, and related progestins. Am J Obstet Gynecol 197(6):599.e1–599.e7
McDonnell DP, Shahbaz MM, Vegeto E, Goldman ME (1994) The human progesterone receptor A-form functions as a transcriptional modulator of mineralocorticoid receptor transcriptional activity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 48(5–6):425–432
McDonnell DP (1995) Unraveling the human progesterone receptor signal transduction pathway: insights into antiprogestin action. Trends Endocrinol Metab 6(4):133–138
Wen DX, Xu YF, Mais DE, Goldman ME, Mc Donnell DF (1994) The A and B isoforms of the human progesterone receptor operate through distinct signaling pathways within target cells. Mol Cell Biol 14(12):8356–8364
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Sylvia Taube, Maike Ziegler, and Jessica Schneider for excellent technical assistance. The specific PR antagonist PF-02367982 was kindly provided by Pfizer. All animal care and experimental procedures were approved by the responsible authority (Landesdirektion Leipzig).
Conflict of interest
No Grants or conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, C., Klammt, J., Thome, U.H. et al. The Interaction of Glucocorticoids and Progesterone Distinctively Affects Epithelial Sodium Transport. Lung 192, 935–946 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-014-9640-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-014-9640-3