Abstract
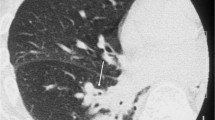
The reversed halo sign (RHS) is a chest computed tomography (CT) pattern defined as a focal round area of ground-glass attenuation surrounded by a crescent or ring of consolidation. The RHS was first described as being relatively specific for cryptogenic organizing pneumonia but was later observed in several other infectious and noninfectious diseases. Although the presence of the RHS on CT may help narrow the range of diseases considered in differential diagnoses, final diagnoses should be based on correlation with the clinical scenario and the presence of additional disease-specific CT findings. However, frequently a biopsy may be needed to establish the diagnosis. Organizing pneumonia is the most frequent cause of the RHS. This is a distinct clinical and pathologic entity that can be cryptogenic or secondary to other known causes. Morphologic aspects of the halo, particularly the presence of small nodules in the wall or inside the lesion, usually indicate an active granulomatous disease (tuberculosis or sarcoidosis) rather than organizing pneumonia. Immunocompromised patients presenting with the RHS on CT examination should be considered to have an infection until further analyses prove otherwise. Pulmonary zygomycosis and invasive pulmonary aspergillosis are typically seen in patients with severe immunosuppression, most commonly secondary to hematological malignancies. Other causes of the RHS include noninvasive fungal infections such as paracoccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Furthermore, Wegener’s granulomatosis, radiofrequency ablation, and lymphomatoid granulomatosis may also lead to this finding. Based on a search of the PubMed and Scopus databases, we review the different diseases that can manifest with the RHS on CT.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Voloudaki AE, Bouros DE, Froudarakis ME, Datseris GE, Apostolaki EG, Gourtsoyiannis NC (1996) Crescentic and ring-shaped opacities. CT features in two cases of bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP). Acta Radiol 37:889–892
Zompatori M, Poletti V, Battista G, Diegoli M (1999) Bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (BOOP), presenting as a ring-shaped opacity at HRCT (the atoll sign). A case report. Radiol Med 97(4):308e10
Kim SJ, Lee KS, Ryu YH, Yoon YC, Choe KO, Kim TS, Sung KJ (2003) Reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia: diagnostic implications. AJR Am J Roentgenol 180(5):1251–1254
Hansell DM, Bankier AA, MacMahon H, McLoud TC, Müller NL, Remy J (2008) Fleischner Society: glossary of terms for thoracic imaging. Radiology 246(3):697–722
Walsh SL, Roberton BJ (2010) The atoll sign. Thorax 65(11):1029–1030
Polverosi R, Maffessanti M, Dalpiaz G (2006) Organizing pneumonia: typical and atypical HRCT patterns. Radiol Med 111:202–212
Marchiori E, Irion KL, Zanetti G, Hochhegger B (2011) Atoll sign or reversed halo sign? Which term should be used? Thorax 66(11):1009–1010
Gasparetto EL, Escuissato DL, Davaus T, de Cerqueira EM, Souza AS Jr, Marchiori E, Müller NL (2005) Reversed halo sign in pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 184(6):1932–1934
Georgiadou SP, Sipsas NV, Marom EM, Kontoyiannis DP (2011) The diagnostic value of halo and reversed halo signs for invasive mold infections in compromised hosts. Clin Infect Dis 52(9):1144–1155
Marchiori E, Melo SM, Vianna FG, Melo BS, Melo SS, Zanetti G (2011) Pulmonary histoplasmosis presenting with the reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT scan. Chest 140(3):789–791
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Meirelles GS, Escuissato DL, Souza AS Jr, Hochhegger B (2011) The reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT in infectious and noninfectious pulmonary diseases. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(1):W69–W75
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Escuissato DL, Souza AS Jr, Meirelles GD, Fagundes J, Souza CA, Hochhegger B, Marom EM, Godoy MC (2012) Reversed halo sign: high-resolution CT findings in 79 patients. Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.11-1050
Walker CM, Mohammed TL, Chung JH (2011) Reversed halo sign. J Thorac Imaging 26(3):W80
Maimon N (2010) A 47-year-old female with shortness of breath and “reversed halo sign”. Eur Respir Rev 19(115):83–85
Bravo Soberón A, Torres Sánchez MI, García Río F, Sánchez Almaraz C, Parrón Pajares M, Pardo Rodríguez M (2006) High resolution computed tomography patterns of organizing pneumonia. Arch Bronconeumol 42(8):413–416
Drakopanagiotakis F, Paschalaki K, Abu-Hijleh M, Aswad B, Karagianidis N, Kastanakis E, Braman SS, Polychronopoulos V (2011) Cryptogenic and secondary organizing pneumonia: clinical presentation, radiographic findings, treatment response and prognosis. Chest 139(4):893–900
Gudavalli R, Diaz-Guzman E, Arrossi AV, Chapman JT, Mehta AC (2011) Fleeting alveolar infiltrates and reversed halo sign in patients with breast cancer treated with tangential beam irradiation. Chest 139(2):454–459
Tokuyasu H, Isowa N, Shimizu E, Yamadori I (2010) Reversed halo sign associated with dermatomyositis. Intern Med 49(15):1677–1678
Kanaji N, Bandoh S, Nagamura N et al (2007) Lipoid pneumonia showing multiple pulmonary nodules and reversed halo sign. Respir Med Extra 3(3):98–101
Hong SH, Kang EY, Shin BK, Shim JJ (2011) Reversed halo sign on thin-section CT in a patient with non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Br J Radiol 84(1001):e103–e105
Tzilas V, Bastas A, Provata A, Koti A, Tzouda V, Tsoukalas G (2010) The “reversed halo” sign in pneumonococcal pneumonia: a review with a case report. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 14(5):481–486
Marlow TJ, Krapiva PI, Schabel, Judson MA (1999) The “fairy ring”: a new radiographic finding in sarcoidosis. Chest 115(1):275–276
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Barreto MM, Azeredo F, Rodrigues RS (2011) Atypical distribution of small nodules on high resolution CT studies: patterns and differentials. Respir Med 105:1263–1267
Kumazoe H, Matsunaga K, Nagata N, Komori M, Wakamatsu K, Kajiki A, Nakazono T, Kudo S (2009) “Reversed halo sign” of high-resolution computed tomography in pulmonary sarcoidosis. J Thorac Imaging 24(1):66–68
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Barreto MM, Rodrigues RS (2011) Pulmonary sarcoidosis: still more aspects of the “great pretender”. Clin Radiol 66:484–487
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Hochhegger B, Carvalho J (2011) Sarcoid cluster sign and the reversed halo sign: extending the spectrum of radiographic manifestations in sarcoidosis. Eur J Radiol 80(2):567–568
Marchiori E, Irion KL, Zanetti G, Hochhegger B (2011) Sarcoidosis and the reversed halo sign. Radiographics 31(3):892–893 author reply 893
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Hochhegger B, Irion KL (2010) The reversed halo sign: another atypical manifestation of sarcoidosis. Korean J Radiol 11(2):251–252
Ahuja A, Gothi D, Joshi JM (2007) A 15-year-old boy with “reversed halo”. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 49(3):99–101
Marchiori E, Grando RD, Simões Dos Santos CE, Maffazzioli Santos Balzan L, Zanetti G, Mano CM, Gutierrez RS (2010) Pulmonary tuberculosis associated with the reversed halo sign on high-resolution CT. Br J Radiol 83(987):e58–e60
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Irion KL, Nobre LF, Hochhegger B, Mançano AD, Escuissato DL (2011) Reversed halo sign in active pulmonary tuberculosis: criteria for differential diagnosis from cryptogenic organizing pneumonia. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:1324–1327
Marchiori E, Zanetti G, Hochhegger B, Irion KL (2010) Reversed halo sign: nodular wall as criteria for differentiation between cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and active granulomatous diseases. Clin Radiol 65(9):770–771
Wahba H, Truong MT, Lei X, Kontoyiannis PD, Marom EM (2008) Reversed halo sign in invasive pulmonary fungal infections. Clin Infect Dis 46(11):1733–1737
Chung JH, Godwin JD, Chien JW, Pipavath MSSJ (2010) Pulmonary mucormycosis. Radiology 256(2):667–670
Godoy MC, Marom EM (2011) Reversed halo sign in pulmonary zygomycosis. Thorax 66(6):544
Marom EM, Kontoyiannis DP (2011) Imaging studies for diagnosing invasive fungal pneumonia in immunocompromised patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis 24(4):309–314
Busca A, Limerutti G, Locatelli F, Barbui A, De Rosa FG, Falda M (2011) The reversed halo sign as the initial radiographic sign of pulmonary zygomycosis. Infection 40(1):77–80
Souza AS Jr, Gasparetto EL, Davaus T, Escuissato DL, Marchiori E (2006) High-resolution CT findings of 77 patients with untreated pulmonary paracoccidioidomycosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187(5):1248–1252
Otera H, Tada K, Sakurai T, Hashimoto K, Ikeda A (2010) Reversed halo sign in pneumocystis pneumonia: a case report. BMC Med Imaging 10:26
Choi YH, Im JG, Park CK (2002) Notes from the 2001 Annual Meeting of the Korean Society of Thoracic Radiology. J Thorac Imaging 17(2):170–175
Agarwal R, Agarwal AN, Gupta D (2007) Another cause of reverse halo sign: Wegener’s granulomatosis. Br J Radiol 80(958):849–850
Mango VL, Naidich DP, Godoy MC (2011) Reversed halo sign after radiofrequency ablation of a lung nodule. J Thorac Imaging 26(4):W150–W152
Benamore RE, Weisbrod GL, Hwang DM, Bailey DJ, Pierre AF, Lazar NM, Maimon N (2007) Reversed halo sign in lymphomatoid granulomatosis. Br J Radiol 80(956):E162–E166
Conflict of interest
Edson Marchiori, Gláucia Zanetti, Bruno Hochhegger, Klaus L Irion, Antonio Carlos Pires Carvalho, and Myrna C. B. Godoy have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchiori, E., Zanetti, G., Hochhegger, B. et al. Reversed Halo Sign on Computed Tomography: State-of-the-Art Review. Lung 190, 389–394 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-012-9392-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-012-9392-x