Abstract
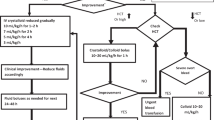
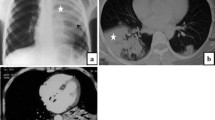
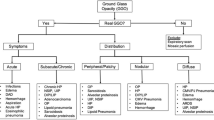
Leptospirosis, a spirochetal zoonosis, is frequently unrecognized due to its manifestation as an undifferentiated fever. It is an emerging infectious disease that has changed from an occupational disease of veterinarians, farmers, butchers, and other animal handlers to a cause of epidemics in poor and decayed urban communities in developing countries. Humans are infected when mucous membranes or abraded skin come into direct contact with the urine of infected animals, especially rats and dogs. Mortality from severe leptospirosis is high, even when optimal treatment is provided. The diagnosis of leptospirosis is based on clinical findings, history of direct or indirect exposure to infected animals in endemic areas, and positive serological tests. It should be considered in the differential diagnosis of patients with febrile illnesses associated with pneumonitis and respiratory failure, especially when hemoptysis is present. Severe pulmonary involvement in leptospirosis consists primarily of hemorrhagic pneumonitis. In advanced cases, adult respiratory distress syndrome and massive pulmonary hemorrhage may occur. Chest radiographs show bilateral alveolar infiltrates and/or resemble viral pneumonia, bronchopneumonia, tuberculosis, adult respiratory distress syndrome, and other causes of pulmonary hemorrhage such as Goodpasture syndrome. High-resolution computed tomography scans may show nodular infiltrates, areas of consolidation, ground-glass attenuation, and crazy-paving patterns. Bronchoalveolar lavage and autopsy studies have suggested that ground-glass opacities and air-space consolidations are secondary to pulmonary hemorrhage. Although not specific, the presence of these computed tomography findings in a febrile patient with an appropriate history should suggest a diagnosis of leptospirosis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma KK, Kalawat U (2008) Early diagnosis of leptospirosis by conventional methods: one-year prospective study. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 51:209–211
Charon NW, Goldstein SF (2002) Genetics of motility and chemotaxis of a fascinating group of bacteria: the spirochetes. Annu Rev Genet 36:47–73
Wang Z, Jin L, Wegrzyn A (2007) Leptospirosis vaccines. Microb Cell Fact 6:39
Herrmann-Storck C, Saint-Louis M, Foucand T, Lamaury I, Deloumeaux J, Baranton G, Simonetti M, Sertour N, Nicolas M, Salin J, Cornet M (2010) Severe leptospirosis in hospitalized patients, Guadeloupe. Emerg Infect Dis 16:331–334
Dupont H, Dupont-Perdrizet D, Perie JL, Zehner-Hansen S, Jarrige B, Daijardin JB (1997) Leptospirosis: prognostic factors associated with mortality. Clin Infect Dis 25:720–724
Brown K, Prescott J (2008) Leptospirosis in the family dog: a public health perspective. CMAJ 178:399–401
Luchini D, Meacci F, Oggioni MR, Morabito G, D’Amato V, Gabbrielli M, Pozzi G (2008) Molecular detection of Leptospira interrogans in human tissues and environmental samples in a lethal case of leptospirosis. Int J Legal Med 122:229–233
Im JG, Yeon KM, Han MC, Kim CW, Webb WR, Lee JS, Han YC, Chang WH, Chi JG (1989) Leptospirosis of the lung: radiographic findings in 58 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 152:955–959
Dolhnikoff M, Mauad T, Bethlem EP, Carvalho CRR (2007) Pathology and pathophysiology of pulmonary manifestations in leptospirosis. Braz J Infect Dis 11:142–148
McBride AJA, Athanazio DA, Reis MG, Ko AI (2005) Leptospirosis. Curr Opin Infect Dis 18:376–386
Trevejo RT, Rigau-Perez JG, Ashford DA, McClure EM, Jarquin-Gonzalez C, Amador JJ, Reyes JO, Gonzalez A, Zaki SR, Shieh WJ, McLean RG, Nasci RS, Weyant RS, Bolin CA, Bragg SL, Perkings BA, Spiegel RA (1998) Epidemic leptospirosis associated with pulmonary hemorrhage—Nicaragua, 1995. J Infect Dis 178:1457–1463
Paganin F, Bourdin A, Dalban C, Courtin JP, Poubeau P, Borgherini G, Michault A, Sally JC, Tixier F, Genin R, Arvin-Berod C (2007) Leptospirosis in Reunion Island (Indian Ocean): analysis of factors associated with severity in 147 confirmed cases. Intensive Care Med 33:1959–1966
Vieira SRR, Brauner JS (2002) Leptospirosis as a cause of acute respiratory failure: clinical features and outcome in 35 critical care patients. Braz J Infect Dis 6:135–139
Abgueguen P, Delbos V, Blanvillain J, Chennebault JM, Cottin J, Fanello S, Pichard E (2008) Clinical aspects and prognostic factors of leptospirosis in adults. Retrospective study in France. J Infect 57:171–178
Sethi S, Sharma N, Kakkar N, Taneja J, Chatterjee SS, Banga SS, Sharma M (2010) Increasing trends of leptospirosis in northern India: a clinicoepidemiological study. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4:e579
Lacerda HG, Monteiro GR, Oliveira CCC, Suassuna FB, Queiroz JW, Barbosa JDA, Martins DR, Reis MG, Ko AI, Jerônimo SMB (2008) Leptospirosis in a subsistence farming community in Brazil. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 102:1233–1238
Zavala-Velazquez J, Cárdenas-Marrufo M, Vado-Solís I, Cetina-Cámara M, Cano-Tur J, Laviada-Molina H (2008) Hemorrhagic pulmonary leptospirosis: three cases from the Yucatan peninsula, Mexico. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 41:404–408
Plank R, Dean D (2000) Overview of the epidemiology, microbiology, and pathogenesis of Leptospira spp. in humans. Microbes Infect 2:1265–1276
Houpikian P, Perolat P, Baranton G, Brouqui P (2002) Leptospiroses. Encycl Méd Chir, Maladies Infectieuses, 8-039-Q-10
Dassanayake DL, Wimalaratna H, Agampodi SB, Liyanapathirana VC, Piyarathna TA, Goonapienuwala BL (2009) Evaluation of surveillance case definition in the diagnosis of leptospirosis, using the microscopic agglutination test: a validation study. BMC Infect Dis 9:48
Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz MM, Lovett MA, Levett PN, Gilman RH, Willig MR, Gotuzzo E, Vinetz JM (2003) Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis 3:757–771
Levett PN, Haake DA (2010) Leptospira species (Leptospirosis). In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R (eds) Mandell, Douglas and Bennett’s principles and practice of infectious diseases, 7th edn. Churchill-Livingstone, Philadelphia
Simpson FG, Green KA, Haug GJ, Brookes DL (1998) Leptospirosis associated with severe pulmonary haemorrhage in Far North Queensland. Med J Aust 169:151–153
Croda J, Neto AN, Brasil RA, Pagliari C, Nicodemo AC, Duarte MI (2010) Leptospirosis pulmonary haemorrhage syndrome is associated with linear deposition of immunoglobulin and complement on the alveolar surface. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:593–599
Lomar AV, Diament D, Torres JR (2000) Leptospirosis in Latin America. Infect Dis Clin North Am 14:23–39
Chakurkar G, Vaideeswar P, Pandit SP, Divate SA (2008) Cardiovascular lesions in leptospirosis: an autopsy study. J Infect 56:197–203
Kurtoglu MG, Tuncer O, Bozkurt H, Caksen H, Berktas M, Ceylan E, Kirimi E (2003) Report of three children with leptospirosis in rural area of the east of Turkey. Tohoku J Exp Med 201:55–60
Silva AA, Ducroquet M, Pedrozo JC Jr (2009) Bilateral facial palsy associated with leptospirosis. Braz J Infect Dis 13:319–321
Daher EdeF, Brunetta DM, de Silva Junior GB, Puster RA, Patrocinio RM (2003) Pancreatic involvement in fatal human leptospirosis: clinical and histopathological features. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 45:307–313
Marotto PC, Marotto MS, Santos DL, Souza TN, Seguro AC (1997) Outcome of leptospirosis in children. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56:307–310
Trivedi SV, Vasava AH, Patel TC, Bhatia LC (2009) Cyclophosphamide in pulmonary alveolar hemorrhage due to leptospirosis. Indian J Crit Care Med 13:79–84
Marotto PC, Ko AI, Murta-Nascimento C, Seguro AC, Prado RR, Barbosa MC, Cleto SA, Eluf-Neto J (2010) Early identification of leptospirosis-associated pulmonary hemorrhage syndrome by use of a validated prediction model. J Infect 60:218–223
Silva JJ, Dalston MO, Carvalho JE, Setubal S, Oliveira JM, Pereira MM (2002) Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features of the severe pulmonary form of leptospirosis. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 35:395–399
Suputtamongkol Y, Pongtavornpinyo W, Lubell Y, Suttinont C, Hoontrakul S, Phimda K, Losuwanaluk K, Suwancharoen D, Silpasakorn S, Chierakul W, Day N (2010) Strategies for diagnosis and treatment of suspected leptospirosis: a cost-benefit analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4:e610
Srinivas R, Agarwal R, Gupta D (2007) Severe sepsis due to severe falciparum malaria and leptospirosis co-infection treated with activated protein C. Malar J 6:42
Spichler A, Moock M, Chapola EG, Vinetz J (2005) Weil’s disease: an unusually fulminant presentation characterized by pulmonary hemorrhage and shock. Braz J Infect Dis 9:336–340
Park SK, Lee SH, Rhee YK, Kang SK, Kim KJ, Kim MC, Kim KW, Chang WH (1989) Leptospirosis in Chonbuk Province of Korea in 1987: a study of 93 patients. Am J Trop Med Hyg 41:345–351
Cerqueira TB, Athanazio DA, Spichler AS, Seguro AC (2008) Renal involvement in leptospirosis—new insights into pathophysiology and treatment. Braz J Infect Dis 12:248–252
Costa E, Lopes AA, Sacramento E, Costa YA, Matos ED, Lopes MB, Bina JC (2003) Penicillin at the late stage of leptospirosis: a randomized controlled trial. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo 45:141–145
Niwattayakul K, Kaewtasi S, Chueasuwanchai S, Hoontrakul S, Chareonwat S, Suttinont C, Phimda K, Chierakul W, Silpasakorn S, Suputtamongkol Y (2009) An open randomized controlled trial of desmopressin and pulse dexamethasone as adjunct therapy in patients with pulmonary involvement associated with severe leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Infect 16:1207–1212
Tatopoulos A, Herbain D, Kazmierczak C, Bollaert PE, Gibot S (2010) Parenteral use of recombinant activated factor VII during diffuse alveolar hemorrhage secondary to leptospirosis. Intensive Care Med 36:555–556
Teglia OF, Battagliotti C, Villavicencio RL, Cunha BA (1995) Leptospiral pneumonia. Chest 108:874–875
Daher E, Zanetta DM, Cavalcante MB, Abdulkader RC (1999) Risk factors for death and changing patterns in leptospirosis acute renal failure. Am J Trop Med Hyg 61:630–644
Medeiros FdaR, Spichler A, Athanazio DA (2010) Leptospirosis-associated disturbances of blood vessels, lungs and hemostasis. Acta Trop 115:155–162
Nicodemo AC, Duarte MI, Alves VA, Takakura CF, Santos RT, Nicodemo EL (1997) Lung lesions in human leptospirosis: microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural features related to thrombocytopenia. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56:181–187
Yang HL, Jiang XC, Zhang XY, Li WJ, Hu BY, Zhao GP, Guo XK (2006) Thrombocytopenia in the experimental leptospirosis of guinea pig is not related to disseminated intravascular coagulation. BMC Infect Dis 6:19
Nally JE, Chantranuwat C, Wu XY, Fishbein MC, Pereira MM, Silva JJ, Blanco DR, Lovett MA (2004) Alveolar septal deposition of immunoglobulin and complement parallels pulmonary hemorrhage in a guinea pig model of severe pulmonary leptospirosis. Am J Pathol 164:1115–1127
Arean VM (1962) The pathologic anatomy and pathogenesis of fatal human leptospirosis (Weil’s disease). Am J Pathol 40:393–423
Matos ED, Costa E, Sacramento E, Caymmi AL, Neto CA, Barreto Lopes M, Lopes AA (2001) Chest radiograph abnormalities in patients hospitalized with leptospirosis in the city of Salvador, Bahia, Brazil. Braz J Infect Dis 5:73–77
Marchiori E, Muller NL (2002) Leptospirosis of the lung: high-resolution computed tomography findings in five patients. J Thorac Imaging 17:151–153
Marchiori E, Gasparetto TD, Escuissato DL, Zanetti G (2008) Leptospirosis of the lung presenting with crazy-paving pattern: high-resolution ct and pathological findings. Rev Port Pneumol 14:887–891
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marchiori, E., Lourenço, S., Setúbal, S. et al. Clinical and Imaging Manifestations of Hemorrhagic Pulmonary Leptospirosis: A State-of-the-Art Review. Lung 189, 1–9 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-010-9273-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-010-9273-0