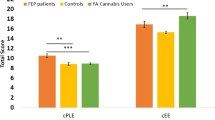
Abstract
The objective of this study is to determine whether cannabis influences BDNF levels in patients with psychosis (FEP) and healthy volunteers (HV) to help understand the role of BDNF in psychosis. We assessed the association between BDNF and cannabis in a cohort of FEP antipsychotic-naïve patients and HV, whilst controlling for other potential confounding factors. 70 FEP drug-naive patients and 57 HV were recruited. A sociodemographic variable collection, structured clinical interview, weight and height measurement, substance use determination, and blood collection to determine BDNF levels by ELISA analysis were done. In FEP patients, cannabis use was associated with BDNF levels (high cannabis use was associated with lower BDNF levels). Moreover, cannabis use was statistically significantly associated with age (high use of cannabis was associated with younger age). In HV, no relationship between cannabis use and BDNF levels was observed. Otherwise, cannabis use was significantly associated with tobacco use, so that high cannabis users were also high tobacco users. This study showed a different association between cannabis use and BDNF levels in FEP patients compared with HV, particularly, with high doses of cannabis. These findings may help understand the deleterious effects of cannabis in some vulnerable individuals, as well as discrepancies in the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO. 2019 (https://www.who.int/mental_health/management/schizophrenia/en/)
Lakhan SE, Vieira K, Hamlat E (2010) Biomarkers in psychiatry: drawbacks and potential for misuse. Int Arch Med 12(3):1
Lupien SJ, Sasseville M, François N, Giguère CE, Boissonneault J, Plusquellec P, Godbout R, Xiong L, Potvin S, Kouassi E, Lesage A (2017) Signature consortium. The DSM5/RDoC debate on the future of mental health research: implication for studies on human stress and presentation of the signature bank. Stress 20(1):95–111
Libman-Sokołowska M, Drozdowicz E, Nasierowski T (2015) BDNF as a biomarker in the course and treatment of schizophrenia. Psychiatr Pol 49(6):1149–1158
Nurjono M, Lee J, Chong SA (2012) A review of brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a candidate biomarker in schizophrenia. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 10(2):61–70
Dieni S, Matsumoto T, Dekkers M, Rauskolb S, Ionescu MS, Deogracias R, Gundelfinger ED, Kojima M, Nestel S, Frotscher M, Barde YA (2012) BDNF and its pro-peptide are stored in presynaptic dense core vesicles in brain neurons. J Cell Biol 196(6):775–788
Numakawa T, Odaka H, Adachi N (2018) Derived neurotrophin factor in the neurogenesis and neuronal function, and its involvement in the pathophysiology of brain diseases. Int J Mol Sci 19(11):3650
Pillai A, Kale A, Joshi S, Naphade N, Raju MS, Nasrallah H, Mahadik SP (2010) Decreased BDNF levels in CSF of drug-naive first episode psychotic subjects: correlation with plasma BDNF and psychopathology. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 13(4):535–539
Green MJ, Matheson SL, Shepherd A, Weickert CS, Carr VJ (2011) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in schizophrenia: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Mol Psychiatry 16(9):960–972
Zhang XY, Chen DC, Tan YL, Tan SP, Wang ZR, Yang FD, Xiu MH, Hui L, Lv MH, Zunta-Soares GB, Soares JC (2014) Gender difference in association of cognition with BDNF in chronic schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 48:136–146
González-Pinto A, Mosquera F, Palomino A, Alberich S, Gutiérrez A, Haidar K, Vega P, Barbeito S, Ortiz A, Matute C (2010) Increase in brain-derived neurotrophic factor in first episode psychotic patients after treatmentwith atypical antipsychotics. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 25(4):241–245
Fernandes BS, Steiner J, Berk M, Molendijk ML, Gonzalez-Pinto A, Turck CW, Nardin P, Gonçalves CA (2015) Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenia and the role of antipsychotics: meta-analysis and implications. Mol Psychiatry 20(9):1108–1119
Toll A, Mané A (2015) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in first episode of psychosis: a systematic review. World J Psychiatry 5(1):154–159
Barbeito S, Vega P, Ruiz de Azúa S, Saenz M, Martinez-Cengotitabengoa M, González-Ortega I, Bermudez C, Hernanz M, Corres BF, González-Pinto A (2013) Cannabis use and involuntary admission may mediate long-term adherence in first-episode psychosis patients: a prospective longitudinal study. BMC Psychiatry 13:326
Colizzi M, Carra E, Fraietta S, Lally J, Quattrone D, Bonaccorso S, Mondelli V, Ajnakina O, Dazzan P, Trotta A, Sideli L, Kolliakou A, Gaughran F, Khondoker M, David AS, Murray RM, MacCabe JH, Di Forti M (2016) Substance use, medication adherence and outcome one year following a first episode of psychosis. Schizophr Res 170(2–3):311–317
Murray RM, Englund A, Abi-Dargham A, Lewis DA, Di Forti M, Davies C, Sherif M, McGuire P, D'Souza DC (2017) Cannabis-associated psychosis: neural substrate and clinical impact. Neuropharmacology 15(124):89–104
D'Souza DC, Pittman B, Perry E, Simen A (2009) Preliminary evidence of cannabinoid effects on brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels in humans. Psychopharmacology 202(4):569–578
Jockers-Scherübl MC, Danker-Hopfe H, Mahlberg R, Selig F, Rentzsch J, Schürer F, Lang UE, Hellweg R (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor serum concentrations are increased in drug-naive schizophrenic patients with chronic cannabis abuse and multiple substance abuse. Neurosci Lett 371(1):79–83
Arranz S, Monferrer N, Jose Algora M, Cabezas A, Sole M, Vilella E, Labad J, Sanchez-Gistau V (2018) The relationship between the level of exposure to stress factors and cannabis in recent onset psychosis. Schizophr Res 201:352–359
Barbeito S, Vega P, Ruiz de Azúa S, Saenz M, Martinez-Cengotitabengoa M, González-Ortega I, Bermudez C, Hernanz M, Corres BF, González-Pinto A (2013) Cannabis use and involuntary admission may mediate long-term adherence in first-episode psychosis patients: a prospective longitudinal study. BMC Psychiatry. 13:326
Zhang XY, Xiu MH, Chen DC, Yang FD, Wu GY, Lu L, Kosten TA, Kosten TR (2010) Nicotine dependence and serum BDNF levels in male patients with schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 212(3):301–307
Yang F, Wang K, Du X, Deng H, Wu HE, Yin G, Ning Y, Huang X, Teixeira AL, de Quevedo J, Soares JC, Li X, Lang X, Zhang XY (2018) Sex difference in the association of body mass index and BDNF levels in Chinese patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 236(2):753–762
Di Forti M, Sallis H, Allegri F, Trotta A, Ferraro L, Stilo SA, Marconi A, La Cascia C, Reis Marques T, Pariante C, Dazzan P, Mondelli V, Paparelli A, Kolliakou A, Prata D, Gaughran F, David AS, Morgan C, Stahl D, Khondoker M, MacCabe JH, Murray RM (2014) Daily use, especially of high-potency cannabis, drives the earlier onset of psychosis in cannabis users. Schizophr Bull 40(6):1509–1517
Di Forti M, Morgan C, Dazzan P, Pariante C, Mondelli V, Reis Marques T, Handley R, Luzi S, Russo M, Paparelli A, Butt A, Stilo S, Wiffen B, Powell J, Murray RM (2009) High-potency cannabis and the risk of psychosis. BJP 195:488–491
Barkus EJ, Stirling J, Hopkins RS, Lewis S (2006) Cannabis-induced psychosis-like experiences are associated with high schizotypy. Psychopathology 39(4):175–178
Kay SR (1990) Positive-negative symptom assessment in schizophrenia: psychometric issues and scale comparison. Psychiatr Q 61(3):163–178
Aas IH (2011) Guidelines for rating Global Assessment of Functioning (GAF). Ann Gen Psychiatry 10:2
Piccinni A, Marazziti D, Del Debbio A, Bianchi C, Roncaglia I, Mannari C, Origlia N, Catena Dell'Osso M, Massimetti G, Domenici L, Dell'Osso L (2008) Diurnal variation of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in humans: an analysis of sex differences. Chronobiol Int 25(5):819–826
Blázquez C, Chiarlone A, Bellocchio L, Resel E, Pruunsild P, García-Rincón D, Sendtner M, Timmusk T, Lutz B, Galve-Roperh I, Guzmán M (2015) The CB1 cannabinoid receptor signals striatal neuroprotection via a PI3K/Akt/mTORC1/BDNF pathway. Cell Death Differ 22(10):1618–1629
Derkinderen P, Valjent E, Toutant M, Corvol JC, Enslen H, Ledent C, Trzaskos J, Caboche J, Girault JA (2003) Regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase by cannabinoids in hippocampus. J Neurosci 23(6):2371–2382
Segal-Gavish H, Gazit N, Barhum Y, Ben-Zur T, Taler M, Hornfeld SH, Gil-Ad I, Weizman A, Slutsky I, Niwa M, Kamiya A, Sawa A, Offen D, Barzilay R (2017) BDNF overexpression prevents cognitive deficit elicited by adolescent cannabis exposure and host susceptibility interaction. Hum Mol Genet 26(13):2462–2471
Egan MF, Weinberger DR, Lu B (2003) Schizophrenia, III: brain-derived neurotropic factor and genetic risk. Am J Psychiatry 160(7):1242
Begliuomini S, Lenzi E, Ninni F, Casarosa E, Merlini S, Pluchino N, Valentino V, Luisi S, Luisi M, Genazzani AR (2008) Plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor daily variations in men: correlation with cortisolcircadian rhythm. J Endocrinol 197(2):429–435
Xiaoyu W (2015) The exposure to nicotine affects expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and nerve growth factor (NGF) in neonate rats. Neurol Sci 36(2):289–295
Kenny PJ, File SE, Rattray M (2000) Acute nicotine decreases, and chronic nicotine increases the expression of brain-derivedneurotrophic factor mRNA in rat hippocampus. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 85(1–2):234–238
Neves CDC, Lacerda ACR, Lima LP, Lage VKS, Balthazar CH, Leite HR, Mendonça VA (2017) Different levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cortisol in healthy heavy smokers. Braz J Med Biol Res 50(12):e6424
Jamal M, van der Does W, Elzinga BM, Molendijk ML, Penninx BW (2015) Association Between Smoking, Nicotine Dependence, and BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism with BDNF Concentrations in Serum. Nicotine Tob Res 17(3):323–329
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Wellman CL (1995) Characteristics of BDNF-induced weight loss. Exp Neurol 131(2):229–238
Lommatzsch M, Zingler D, Schuhbaeck K, Schloetcke K, Zingler C, Schuff-Werner P, Virchow JC (2005) The impact of age, weight and gender on BDNF levels in human platelets and plasma. Neurobiol Aging 26(1):115–123
Zhang XY, Tan YL, Zhou DF, Cao LY, Wu GY, Xu Q, Shen Y, Haile CN, Kosten TA, Kosten TR (2007) Serum BDNF levels and weight gain in schizophrenic patients on long-term treatment with antipsychotics. J Psychiatr Res 41(12):997–1004
Nurjono M, Tay YH, Lee J (2014) The relationship between serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and cardiometabolic indices in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 157(1–3):244–248
Bonaccorso S, Sodhi M, Li J, Bobo WV, Chen Y, Tumuklu M, Theleritis C, Jayathilake K, Meltzer HY (2015) The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism is associated with increased body mass index and insulin resistance measures in bipolar disorder and schizophrenia. Bipolar Disord 17(5):528–535
Fang H, Zhen YF, Liu XY, Xu G, Soares JC, Zhao J, Zhang XY (2016) Association of the BDNF Val66Met polymorphism with BMI in chronic schizophrenic patients and healthy controls. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 31(6):353–357
Hahn B (2018) The potential of cannabidiol treatment for cannabis users with recent-onset psychosis. Schizophr Bull 44(1):46–53
Kim HJ, Song BK, So B, Lee O, Song W, Kim Y (2014) Increase of circulating BDNF levels and its relation to improvement of physical fitness following 12 weeks of combined exercise in chronic patients with schizophrenia: a pilot study. Psychiatry Res 220(3):792–796
Sanada K, Zorrilla I, Iwata Y, BermúdezAmpudia C, GraffGuerrero A, MartínezCengotitabengoa M, GonzálezPinto A (2016) The efficacy of nonpharmacological interventions on brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Mol Sci. 17(10):1766
Campos C, Rocha NBF, Lattari E, Nardi AE (2017) Exercise induced neuroplasticity to enhance therapeutic outcomes of cognitive remediation in schizophrenia: analyzing the role of brain derived neurotrophic factor. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16(6):638–651
Lisano JK, Kisiolek JN, Smoak P, Phillips KT, Stewart LK (2019) Chronic cannabis use and circulating biomarkers of neural health, stress, and inflammation in physically active individuals. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2019-0300
Yoshida T, Ishikawa M, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2012) Serum levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its precursor proBDNF in healthy subjects. Open Clin Chem J 5:7–12
Yoshida T, Ishikawa M, Niitsu T et al (2012) Decreased serum levels of mature brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), but not its precursor proBDNF, in patients with major depressive. PLoS One 7(8):e42676
Hashimoto K (2016) Ethnic differences in the serum levels of proBDNF, a precursor of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), in mood disorders. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 266(3):285–287
Yang B, Ren Q, Zhang JC, Chen QX, Hashimoto K (2017) Altered expression of BDNF, BDNF pro-peptide and their precursor proBDNF in brain and liver tissues from psychiatric disorders: rethinking the brain-liver axis. Transl Psychiatry 7(5):e1128
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all healthy volunteers and patients that have participated in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Mané and Dr. Bergé have received financial support to attend meetings, travel support, and served as a speaker from Otsuka and Janssen Cilag. Dr. Fernandez-Egea has received consultant fees from Recordati and Angelini. The other authors of this manuscript do not have any conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Kenji Hashimoto.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toll, A., Bergé, D., Burling, K. et al. Cannabis use influence on peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in antipsychotic-naïve first-episode psychosis. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270, 851–858 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-020-01117-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-020-01117-y