Abstract
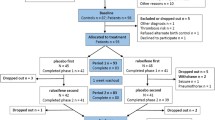
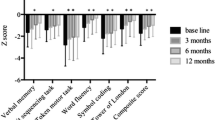
We assessed the utility of raloxifene (60 mg/day) as an adjuvant treatment for cognitive symptoms in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia in a 24-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Patients were recruited from the inpatient and outpatient services of Parc Sanitari Sant Joan de Déu, Hospital Universitari Institut Pere Mata, and Corporació Sanitària Parc Taulí. Seventy eight postmenopausal women with schizophrenia were randomized to either adjunctive raloxifene or placebo. Sixty-eight began the clinical trial (37 women on raloxifene adjunct) and 31 on placebo adjunct. The outcome measures were: memory, attention and executive function. Assessment was conducted at baseline and at week 24. Between groups homogeneity was tested with the Student's t test for continuous variables and/or the Mann–Whitney U test for ordinal variables and the χ2 test or Fisher's exact test for categorical variables. The differences between the two groups in neuropsychological test scores were compared using the Student's t test. The sample was homogenous with respect to age, formal education, illness duration and previous pharmacological treatment. The addition of raloxifene to antipsychotic treatment as usual showed no differences in cognitive function. The daily use of 60 mg raloxifene as an adjuvant treatment in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia has no appreciable effect.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT01573637.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fioravanti M, Bianchi V, Cinti ME (2012) Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: an updated metanalysis of the scientific evidence. BMC Psychiatry 12:64. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-244X-12-64
Tandon R, Nasrallah HA, Keshavan MS (2010) Schizophrenia, “just the facts” 5. Treatment and prevention. Past, present, and future. Schizophr Res 122:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2010.05.025
Üçok A, Çakır S, Duman ZÇ et al (2006) Cognitive predictors of skill acquisition on social problem solving in patients with schizophrenia. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 256:388–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-006-0651-9
Soria V, González-Rodríguez A, Huerta-Ramos E et al (2018) Targeting hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hormones and sex steroids for improving cognition in major mood disorders and schizophrenia: a systematic review and narrative synthesis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.04.012
Audesirk T, Cabell L, Kern M, Audesirk G (2003) Beta-estradiol influences differentiation of hippocampal neurons in vitro through an estrogen receptor-mediated process. Neuroscience 121:927–934
Ciriza I, Carrero P, Azcoitia I et al (2004) Selective estrogen receptor modulators protect hippocampal neurons from kainic acid excitotoxicity: differences with the effect of estradiol. J Neurobiol 61:209–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/neu.20043
Steinberg KK, Thacker SB, Smith SJ et al (1991) A meta-analysis of the effect of estrogen replacement therapy on the risk of breast cancer. JAMA 265:1985–1990
Velázquez-Zamora DA, Garcia-Segura LM, González-Burgos I (2012) Effects of selective estrogen receptor modulators on allocentric working memory performance and on dendritic spines in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons of ovariectomized rats. Horm Behav 61:512–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.01.010
Goekoop R, Barkhof F, Duschek EJJ et al (2006) Raloxifene treatment enhances brain activation during recognition of familiar items: a pharmacological fMRI study in healthy elderly males. Neuropsychopharmacology. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.npp.1300956
Wong J, Seeman MV, Shapiro H (2003) Case report: raloxifene in postmenopausal women with psychosis: preliminary findings. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry Off J Am Assoc Geriatr Psychiatry 11(697):698
Kulkarni J, Gurvich C, Gilbert H et al (2008) Hormone modulation: a novel therapeutic approach for women with severe mental illness. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 42:83–88. https://doi.org/10.1080/00048670701732715
Huerta-Ramos E, Iniesta R, Ochoa S et al (2014) Effects of raloxifene on cognition in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:223–231
Huerta-Ramos E, Ochoa S, Roca M et al (2015) The effect of raloxifene on symptoms and cognitive functioning in a postmenopausal schizophrenia patient: a case report. Arch Womens Ment Health 18:259–261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-015-0500-9
Weickert TW, Weinberg D, Lenroot R et al (2015) Adjunctive raloxifene treatment improves attention and memory in men and women with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 20:685–694. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2015.11
Ji E, Weickert CS, Lenroot R et al (2016) Adjunctive selective estrogen receptor modulator increases neural activity in the hippocampus and inferior frontal gyrus during emotional face recognition in schizophrenia. Transl Psychiatry 6:e795. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2016.59
Kulkarni J, Gavrilidis E, Gwini SM et al (2016) Effect of adjunctive raloxifene therapy on severity of refractory schizophrenia in women: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 73:947–954. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.1383
Kindler J, Weickert CS, Schofield PR et al (2016) Raloxifene increases prefrontal activity during emotional inhibition in schizophrenia based on estrogen receptor genotype. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol J Eur Coll Neuropsychopharmacol 26:1930–1940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.10.009
Weiser M, Levi L, Burshtein S et al (2017) Raloxifene plus antipsychotics versus placebo plus antipsychotics in severely ill decompensated postmenopausal women with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.15m10498
de Boer J, Prikken M, Lei WU et al (2018) The effect of raloxifene augmentation in men and women with a schizophrenia spectrum disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Schizophrenia 4:1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-017-0043-3
Usall J, Huerta-Ramos E, Labad J et al (2016) Raloxifene as an adjunctive treatment for postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a 24-week double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Bull 42:309–317. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv149
Labad J, Martorell L, Huerta-Ramos E et al (2016) Pharmacogenetic study of the effects of raloxifene on negative symptoms of postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 26:1683–1689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2016.08.006
Bieber E, Sanfilippo JS, Horowitz IR, MIS (2006) Clinical gynecology. Cambridge University Press, Philadelphia
JAVA (2013) Declaration of Helsinki World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Bull World Health Organ 79:373–374
Usall J, Huerta-Ramos E, Labad J et al (2016) Raloxifene as an adjunctive treatment for postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a 24-week double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled trial. Schizophr Bull. https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbv149
Gardner DM, Murphy AL, O’Donnell H et al (2010) International consensus study of antipsychotic dosing. Am J Psychiatry 167:686–693. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.09060802
Kay SR, Fiszbein A, Opler LA (1987) The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 13:261–276
Benedet MJ, Alexandre MA (1998) Test de Aprendizaje Verbal España-Complutense (TAVEC). TEA Ediciones, Madrid
Moscovitch M, Umiltà C (1990) Modularity and neuropsychology: implications for the organization of attention and memory in normal and brain-damaged people. In: Schwartz MF (ed) Modular deficits in Alzheimer type dementia. MIT Press, Cambridge
Conners CK (2002) Conners’ Continuous Performance Test CPT-II. Technical Guide and Software Manual. Multi Health Systems, North Tonawanda, NY
Reitan R, Wolfson D (1995) Category test and Trail Making Test as measures of frontal lobe functions. Clin Neuropsychol 9:50–56
Stroop JR (1935) Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. J Exp Psychol 18:643–662
Reeve WV, Schandler SL (2001) Frontal lobe functioning in adolescents with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. Adolescence 36:749–765
Fisher LM, Freed DM, Corkin S (1990) Stroop Color-Word Test performance in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 12:745–758. https://doi.org/10.1080/01688639008401016
Seisdedos N, Corral S, Cordero A, de la Cruz MVH, Pereña JMV (1999) WAIS III. Manual Técnico. TEA Ediciones, Madrid
Strauss E, Sherman EMS, Spreen O (2006) A compendium of neuropsychological tests: administration, norms, and commentary, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Bender R, Lange S (2001) Adjusting for multiple testing–when and how? J Clin Epidemiol 54:343–349
Lingjaerde O, Ahlfors UG, Bech P et al (1987) The UKU side effect rating scale. A new comprehensive rating scale for psychotropic drugs and a cross-sectional study of side effects in neuroleptic-treated patients. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl 334:1–100
Iikuni N, Hamaya E, Nihojima S et al (2012) Safety and effectiveness profile of raloxifene in long-term, prospective, postmarketing surveillance. J Bone Miner Metab 30:674–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-012-0365-1
Yang ZD, Yu J, Zhang Q (2013) Effects of raloxifene on cognition, mental health, sleep and sexual function in menopausal women: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Maturitas 75:341–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2013.05.010
Gurvich C, Hudaib A, Gavrilidis E et al (2019) Raloxifene as a treatment for cognition in women with schizophrenia: the influence of menopause status. Psychoneuroendocrinology 100:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.10.001
Yin W, Maguire SM, Pham B et al (2015) Testing the critical window hypothesis of timing and duration of estradiol treatment on hypothalamic gene networks in reproductively mature and aging female rats. Endocrinology. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2015-1032
Vila È, Huerta-Ramos E, Núñez C et al (2018) Specificity proteins 1 and 4 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a 24-week double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-018-0938-7
Acknowledgements
The Stanley Medical Research Institute (#10T-1392). The members of RALOPSYCAT Group are Carolina Rodríguez (nurse), Isabel Beneitez (psychiatrist), Joan Costa (clinician), Lourdes Castro (nurse), Silvia Teba (nurse), Laura Milian (nurse), Alexandrina Foix (nurse), Sonia Rivero (psychiatrist), Marian Cavero (psychiatrist), María Argemí (psychiatrist), Fernando Teba (psychiatrist), Belén Arranz (psychiatrist), Elena Rubio (psychiatrist), Marta Coromina (psychiatrist), Ángeles Santos (nurse), Jose Luis Bogas (nurse), Ana Barber (nurse), Carlota Romans (psychiatrist), Manel Márquez (psychiatrist), Anna Sabata (nurse), Lourdes Nieto (psychologist), Eva Willikens (psychologist), Enrich Blanch (nurse), Siddharta Acebillo (psychiatrist), Ramón Coronas (psychiatrist), Laura Ortega (nurse), Ignasi Coll (psychiatrist), Joaquín Valero (psychiatrist), Jesús Rodríguez (psychiatrist), Modesto Pérez (psychiatrist), Inés Niubó (psychiatrist), Montse Tost (psychologist), Mari Pau Monfort (pharmacist), Lourdes Martorell (biologist), Elisabet Vilella (biologist), Judith Usall (psychiatrist), Elena Huerta-Ramos (psychologist), Javier Labad (psychiatrist), Jesús Cobo (psychiatrist), Christian Núñez (psychologist), Marta Creus (psychologist), Gemma García-Parés (psychiatrist), Daniel Cuadras (statistical), José Franco (psychiatrist), Eva Miquel (pharmacist), Julio-César Reyes (psychiatrist), Mercedes Roca (psychiatrist).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
The members of RALOPSYCAT Group are listed in acknowledgements.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huerta-Ramos, E., Labad, J., Cobo, J. et al. Effects of raloxifene on cognition in postmenopausal women with schizophrenia: a 24-week double-blind, randomized, parallel, placebo-controlled trial. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 270, 729–737 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01079-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-019-01079-w